Routine Load is a routine import method. StarRocks allows you to use this method to continuously import data from Apache Kafka and control the pause, resumption, and stop of import jobs by using SQL statements. This topic describes the basic principles, import example, and FAQ of Routine Load.
Terms
- RoutineLoadJob: a routine import job that is submitted
- JobScheduler: the routine import job scheduler that is used to schedule and split a RoutineLoadJob into multiple tasks
- Task: the task that is split from a RoutineLoadJob by JobScheduler based on rules
- TaskScheduler: the task scheduler that is used to schedule the execution of a task
Basic principles
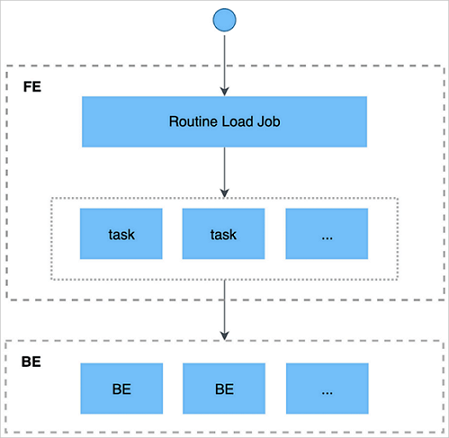
- You submit a Kafka import job to the frontend by using a client that supports the MySQL protocol.
- The frontend splits the import job into multiple tasks. Each task imports a specified part of data.
- Each task is assigned to the specified backend for execution. On the backend, a task is regarded as a regular import job and imports data based on the import mechanism of Stream Load.
- After the import process is completed on the backend, the backend reports the import result to the frontend.
- The frontend continues to generate new tasks or retry failed tasks based on the import result.
- The frontend continuously generates new tasks to achieve the uninterrupted import of data.
Import process
Environment requirements
You can access Kafka clusters that do not require authentication and Kafka clusters that require Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) authentication.
A message can be in one of the following formats:
CSV format. In this format, each message occupies one row, and the end of the row does not contain a line feed.
JSON format.
The Array type is not supported.
Only Kafka 0.10.0.0 and later are supported.
Create an import job
Syntax
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD <database>.<job_name> ON <table_name> [COLUMNS TERMINATED BY "column_separator" ,] [COLUMNS (col1, col2, ...) ,] [WHERE where_condition ,] [PARTITION (part1, part2, ...)] [PROPERTIES ("key" = "value", ...)] FROM [DATA_SOURCE] [(data_source_properties1 = 'value1', data_source_properties2 = 'value2', ...)]The following table describes the parameters in the preceding command.
Parameter Required Description job_name Yes The name of the import job. The name of the import database can be placed in the front. The name is usually in the format of timestamp plus table name. The name of the job must be unique in a database. table_name Yes The name of the destination table. COLUMNS TERMINATED clause No The column delimiter in the source data file. Default value: \t. COLUMNS clause No The mapping between columns in the source data file and columns in the destination table. - Mapped columns: For example, the destination table has three columns, col1, col2, and col3, whereas the source data file has four columns, and the first, second, and fourth columns in the destination table correspond to col2, col1, and col3 in the source data file. In this case, the clause can be written as
COLUMNS (col2, col1, temp, col3). The temp column does not exist and is used to skip the third column in the source data file. - Derived columns: StarRocks can not only read the data in a column of the source data file but also provide processing operations on data columns. For example, a column col4 is added to the destination table, and the value of col4 is equal to the value of col1 plus the value of col2. In this case, the clause can be written as
COLUMNS (col2, col1, temp, col3, col4 = col1 + col2).
WHERE clause No The filter conditions that you want to use to filter out the rows that you do not need. The filter conditions can be specified on mapped columns or derived columns. For example, if only rows with k1 greater than 100 and k2 equal to 1000 are imported, the clause can be written as
WHERE k1 > 100 and k2 = 1000.PARTITION clause No The partition of the destination table. If you do not specify the partition, the source data file is automatically imported to the corresponding partition. PROPERTIES clause No The common parameters for the import job. desired_concurrent_number No The maximum number of tasks into which the import job can be split. The value must be greater than 0. Default value: 3. max_batch_interval No The maximum execution time of each task. Valid values: 5 to 60. Unit: seconds. Default value: 10. In V1.15 and later, this parameter specifies the scheduling time of the task. You can specify how often the task is executed. routine_load_task_consume_second in fe.conf specifies the amount of time required by the task to consume data. Default value: 3s. routine_load_task_timeout_second in fe.conf specifies the execution timeout period of the task. Default value: 15s.
max_batch_rows No The maximum number of rows that each task can read. The value must be greater than or equal to 200000. Default value: 200000. In V1.15 and later, this parameter is used only to define the range of the error detection window. The range of the window is 10 × max-batch-rows.
max_batch_size No The maximum number of bytes that each task can read. Unit: bytes. Valid value: 100 MB to 1 GB. Default value: 100 MB. In V1.15 and later, this parameter is discarded. routine_load_task_consume_second in fe.conf specifies the amount of time required by the task to consume data. Default value: 3s.
max_error_number No The maximum number of error rows allowed in the sampling window. The value must be greater than or equal to 0. Default value: 0. No error row is allowed. Important Rows filtered out by the WHERE condition are not error rows.strict_mode No Specifies whether to enable the strict mode. By default, this mode is enabled. If the column type of non-empty raw data is changed to NULL after you enable the strict mode, the data is filtered out. To disable the strict mode, set this parameter to false.
timezone No The time zone that is used for the import job. By default, the value of the timezone parameter of the session is used. This parameter affects the results of all time zone-related functions involved in the import.
DATA_SOURCE Yes The type of the data source. Set the value to KAFKA. data_source_properties No The information about the data source. The value includes the following fields: - kafka_broker_list: the connection information about the Kafka broker. Format:
ip:host. Separate multiple brokers with commas (,). - kafka_topic: the Kafka topic to which you want to subscribe. Note The kafka_broker_list and kafka_topic fields are required.
- kafka_partitions and kafka_offsets: the Kafka partitions to which you want to subscribe and the start offset of each partition.
- property: Kafka-related properties. This field is equivalent to the
--propertyparameter in Kafka Shell. You can run theHELP ROUTINE LOAD;command to view the more detailed syntax for creating an import job.
- Mapped columns: For example, the destination table has three columns, col1, col2, and col3, whereas the source data file has four columns, and the first, second, and fourth columns in the destination table correspond to col2, col1, and col3 in the source data file. In this case, the clause can be written as
Example: Submit an unauthenticated Routine Load import job named example_tbl2_ordertest to StarRocks to continuously consume messages from the ordertest2 topic of the Kafka cluster and import the messages to the example_tbl2 table. The import job consumes messages from the earliest offset of a specific partition of the topic.
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD load_test.example_tbl2_ordertest ON example_tbl COLUMNS(commodity_id, customer_name, country, pay_time, price, pay_dt=from_unixtime(pay_time, '%Y%m%d')) PROPERTIES ( "desired_concurrent_number"="5", "format" ="json", "jsonpaths" ="[\"$.commodity_id\",\"$.customer_name\",\"$.country\",\"$.pay_time\",\"$.price\"]" ) FROM KAFKA ( "kafka_broker_list" ="<kafka_broker1_ip>:<kafka_broker1_port>,<kafka_broker2_ip>:<kafka_broker2_port>", "kafka_topic" = "ordertest2", "kafka_partitions" ="0,1,2,3,4", "property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING" );Example: Use the SSL protocol to access Kafka. Sample code:
-- Specify SSL as the security protocol. "property.security.protocol" = "ssl", -- Specify the location for storing the CA certificate. "property.ssl.ca.location" = "FILE:ca-cert", -- If client authentication is enabled for the Kafka server, you must configure the following parameters: -- Specify the location of the public key for the Kafka client. "property.ssl.certificate.location" = "FILE:client.pem", -- Specify the location of the private key for the Kafka client. "property.ssl.key.location" = "FILE:client.key", -- Specify the password of the private key for the Kafka client. "property.ssl.key.password" = "******"For information about the CREATE FILE statement, see CREATE FILE.
NoteWhen you use the CREATE FILE statement, specify the HTTP address of Object Storage Service (OSS) as the
URL. For more information, see Use an endpoint that supports IPv6 to access OSS.
View the status of an import job
Query all routine import jobs in the load_test database, including the jobs that are stopped or canceled. The jobs are displayed in one or more rows.
USE load_test; SHOW ALL ROUTINE LOAD;Query the running routine import job named example_tbl2_ordertest in load_test.
SHOW ROUTINE LOAD FOR load_test.example_tbl2_ordertest;Perform the following operations to view the status of an import job on the Kafka Import tab: Go to the EMR StarRocks Manager page. In the left-side navigation pane, click Metadata Management. Click the name of the desired database. On the page that appears, click the Tasks tab.
StarRocks allows you to view only the running jobs. You cannot view completed jobs and jobs that have not been run.
You can run the SHOW ALL ROUTINE LOAD command to view all running Routine Load jobs. The following output is returned:
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Id: 14093
Name: routine_load_wikipedia
CreateTime: 2020-05-16 16:00:48
PauseTime: N/A
EndTime: N/A
DbName: default_cluster:load_test
TableName: routine_wiki_edit
State: RUNNING
DataSourceType: KAFKA
CurrentTaskNum: 1
JobProperties: {"partitions":"*","columnToColumnExpr":"event_time,channel,user,is_anonymous,is_minor,is_new,is_robot,is_unpatrolled,delta,added,deleted","maxBatchIntervalS":"10","whereExpr":"*","maxBatchSizeBytes":"104857600","columnSeparator":"','","maxErrorNum":"1000","currentTaskConcurrentNum":"1","maxBatchRows":"200000"}
DataSourceProperties: {"topic":"starrocks-load","currentKafkaPartitions":"0","brokerList":"localhost:9092"}
CustomProperties: {}
Statistic: {"receivedBytes":150821770,"errorRows":122,"committedTaskNum":12,"loadedRows":2399878,"loadRowsRate":199000,"abortedTaskNum":1,"totalRows":2400000,"unselectedRows":0,"receivedBytesRate":12523000,"taskExecuteTimeMs":12043}
Progress: {"0":"13634667"}
ReasonOfStateChanged:
ErrorLogUrls: http://172.26.**.**:9122/api/_load_error_log?file=__shard_53/error_log_insert_stmt_47e8a1d107ed4932-8f1ddf7b01ad2fee_47e8a1d107ed4932_8f1ddf7b01ad2fee, http://172.26.**.**:9122/api/_load_error_log?file=__shard_54/error_log_insert_stmt_e0c0c6b040c044fd-a162b16f6bad53e6_e0c0c6b040c044fd_a162b16f6bad53e6, http://172.26.**.**:9122/api/_load_error_log?file=__shard_55/error_log_insert_stmt_ce4c95f0c72440ef-a442bb300bd743c8_ce4c95f0c72440ef_a442bb300bd743c8
OtherMsg:
1 row in set (0.00 sec)In this example, an import job named routine_load_wikipedia is created. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter | Description |
State | The status of the import job. The value RUNNING indicates that the import job is continuously running. |
Statistic | The progress information, which includes the import information since the job is created. |
receivedBytes | The size of the received data. Unit: bytes. |
errorRows | The number of imported error rows. |
committedTaskNum | The number of tasks submitted by the frontend node. |
loadedRows | The number of imported rows. |
loadRowsRate | The rate at which data is imported. Unit: rows/s. |
abortedTaskNum | The number of failed tasks on the backend node. |
totalRows | The total number of received rows. |
unselectedRows | The number of rows that are filtered out by the WHERE condition. |
receivedBytesRate | The rate at which data is received. Unit: bytes/s. |
taskExecuteTimeMs | The import duration. Unit: milliseconds. |
ErrorLogUrls | The error message log. You can use the URL to view the error message during the import process. |
Pause the import job
Execute the PAUSE statement to pause an import job. After you execute the statement, the import job enters the PAUSED state. Data import is paused, but the job is not terminated. You can execute the RESUME statement to resume the job.
PAUSE ROUTINE LOAD FOR <job_name>;After the import job is paused, the import information in Statistic and Progress stops updating. You can execute the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement to view the paused import job.
Resume the import job
Execute the RESUME statement to resume the import job. After you execute the statement, the job temporarily enters the NEED_SCHEDULE state, which indicates that the job is being rescheduled. After a specific period of time, the job enters the RUNNING state and data import continues.
RESUME ROUTINE LOAD FOR <job_name>;Stop the import job
Execute the STOP statement to stop the import job. After you execute the statement, the import job enters the STOPPED state. Data import is stopped, and the job is terminated. In this case, data import cannot be resumed.
STOP ROUTINE LOAD FOR <job_name>;After the import job is stopped, the import information in Statistic and Progress is no longer updated. In this case, you cannot execute the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement to view the stopped import job.
Best practices
In this example, a Routine Load import job is created to continuously consume data in the CSV format from a Kafka cluster and then import the CSV data to StarRocks.
Perform the following operations in a Kafka cluster:
Create a test topic.
kafka-topics.sh --create --topic order_sr_topic --replication-factor 3 --partitions 10 --bootstrap-server "core-1-1:9092,core-1-2:9092,core-1-3:9092"Run the following command to produce data.
kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list core-1-1:9092 --topic order_sr_topicInsert the following data:
2020050802,2020-05-08,Johann Georg Faust,Deutschland,male,895 2020050802,2020-05-08,Julien Sorel,France,male,893 2020050803,2020-05-08,Dorian Grey,UK,male,1262 2020051001,2020-05-10,Tess Durbeyfield,US,female,986 2020051101,2020-05-11,Edogawa Conan,japan,male,8924
Perform the following operations in a StarRocks cluster:
Run the following command to create a destination database and a table.
Create a table named routine_load_tbl_csv in the load_test database of the StarRocks cluster based on the columns that you want to import. In this example, all columns, except for the fifth column, are imported. The fifth column displays the gender information.
CREATE TABLE load_test.routine_load_tbl_csv ( `order_id` bigint NOT NULL COMMENT "Order ID", 'pay_dt' date NOT NULL COMMENT "Purchase date", 'customer_name' varchar(26) NULL COMMENT "Customer name", 'nationality' varchar(26) NULL COMMENT "Country", 'price' double NULL COMMENT "Payment amount" ) ENGINE=OLAP PRIMARY KEY (order_id,pay_dt) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`order_id`) BUCKETS 5;Execute the following statement to create an import job:
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD load_test.routine_load_tbl_ordertest_csv ON routine_load_tbl_csv COLUMNS TERMINATED BY ",", COLUMNS (order_id, pay_dt, customer_name, nationality, temp_gender, price) PROPERTIES ( "desired_concurrent_number" = "5" ) FROM KAFKA ( "kafka_broker_list" ="192.168.**.**:9092,192.168.**.**:9092,192.168.**.**:9092", "kafka_topic" = "order_sr_topic", "kafka_partitions" ="0,1,2,3,4", "property.kafka_default_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING" )Execute the following statement to view information about the routine_load_tbl_ordertest_csv import job:
SHOW ROUTINE LOAD FOR routine_load_tbl_ordertest_csv;If the status is RUNNING, the job runs as expected.
Run the following command to query the destination table. The result shows that data synchronization is complete.
You can also perform the following operations on a job:
Pause the import job
PAUSE ROUTINE LOAD FOR routine_load_tbl_ordertest_csv;Resume the import job
RESUME ROUTINE LOAD FOR routine_load_tbl_ordertest_csv;Modify the import job
NoteOnly jobs in the PAUSED state can be modified.
For example, you can change the value of desired_concurrent_number to 6.
ALTER ROUTINE LOAD FOR routine_load_tbl_ordertest_csv PROPERTIES ( "desired_concurrent_number" = "6" )Stop the import job
STOP ROUTINE LOAD FOR routine_load_tbl_ordertest_csv;