Instances with separated storage and compute resources are ideal for business scenarios that are sensitive to storage costs and have low query efficiency requirements, such as online analytical processing (OLAP) multidimensional analysis and data warehouse applications. These instances are also ideal for querying data in data lakes, such as Apache Hive, Apache Iceberg, Apache Hudi, and Apache Paimon. Supported platforms include Object Storage Service (OSS), OSS-HDFS, and Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). With these instances, you can quickly query and analyze data in data lakes without migrating the data. The performance is three to five times higher than Presto. This instance type uses a storage-compute separation architecture and stores data in Alibaba Cloud OSS.
Prerequisites
You have registered an Alibaba Cloud account and completed identity verification.
If you are a Resource Access Management (RAM) user, you have been granted the AliyunEMRStarRocksFullAccess system policy. For more information, see Grant permissions to a RAM user.
NoteThe AliyunEMRStarRocksFullAccess system policy is required for creating and managing StarRocks instances.
Precautions
The runtime environment of the code is managed and configured by the owner of the environment.
Procedure
Step 1: Create a StarRocks instance with separated storage and compute resources
Go to the EMR Serverless StarRocks instance list page.
Log on to the E-MapReduce console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
In the top menu bar, select the required region.
On the Instance List page, click Create Instance.
On the E-MapReduce Serverless StarRocks page, configure the instance parameters.
Configuration Item
Example
Description
Product Type
Pay-as-you-go
Select Pay-as-you-go. For more information about billing, see Pay-as-you-go.
Region
China (Beijing)
The physical location of the instance.
ImportantYou cannot change the region after the instance is created. Select a region with caution.
Network And Zone
vpc_Hangzhou/vpc-bp1f4epmkvncimpgs****
Zone I
vsw_i/vsw-bp1e2f5fhaplp0g6p****
Select a virtual private cloud (VPC), a zone, and the corresponding vSwitch.
Virtual private cloud: A VPC is an isolated network environment that you define on Alibaba Cloud. You have full control over your VPC.
Select an existing VPC, or click Create a VPC to go to the VPC console and create one. For more information, see Create and manage a VPC.
NoteWhen you create a VPC, the IPv4 CIDR block must be from one of the following private network segments defined in RFC 1918:
10.0.0.0/8(10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255)172.16.0.0/12(172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255)192.168.0.0/16(192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255)
If your Serverless StarRocks instance needs to access the Internet, for example, to import data or query foreign tables, make sure that its VPC has Internet access. You can deploy an Internet NAT gateway in the VPC and enable the SNAT feature. This allows the Serverless StarRocks instance to access Internet resources through the gateway. For more information, see Use the SNAT feature of an Internet NAT gateway to access the Internet.
Zone: The zone where the instance is located.
vSwitch: A vSwitch is a basic network module of a VPC that connects different cloud resources.
Select an existing vSwitch, or click Create vSwitch to go to the VPC console and create one. For more information, see Create and manage a vSwitch.
Instance Type
Shared-data
Suitable for scenarios with relatively low query efficiency requirements, such as OLAP multidimensional analysis, data lake analytics, federated queries on foreign tables, real-time data analytics, and data warehouses.
IInstance Edition
Standard Edition
Supports Basic Edition and Standard Edition. For more information, see Instance series.
NoteStarter Edition is available only in the China (Beijing), China (Shanghai), China (Shenzhen), and China (Hangzhou) regions.
Kernel Version
3.3
The community version number of StarRocks.
FE Specifications
Specification Type: Standard Specificatio
Compute CU: 8 CU
Data Disk: PL1 ESSD,
High Availability: Enabled by default.
Number of Nodes: 3
Load Balancing: Built-in PrivateZone
Specification Type: Different StarRocks instance families have different specification types for FE nodes.
Basic Edition: Supports Standard Specifications.
Standard Edition: Supports Standard Specifications and Memory-optimized Specification.
Compute CUs: Select a compute unit (CU).
Select CU specifications as needed. For more information about CU fees, see Billable items.
Data Disk: Supports only PL1 ESSDs. The size of the data disk ranges from 100 GB to 65,000 GB in increments of 100 GB.
For more information about cloud disks, see ESSDs.
HA: Enabled by default. For the Standard Edition, if you enable high availability, the number of StarRocks frontend (FE) nodes increases from 1 to 3 to reduce the risk of failures.
ImportantHigh availability is strongly recommended for production environments.
Number of Nodes: The number of FE nodes. The value must be an odd number from 1 to 11.
Load balancing: The following methods are supported.
Built-in PrivateZone: Automatically distributes traffic using PrivateZone domain name resolution. This option incurs no additional costs and is suitable for lightweight scenarios or cost-sensitive environments.
Suitable for non-production environments or services with low requirements for load balancing performance.
Load balancing SLB: Provides high-performance load balancing by activating the SLB service. Recommended for production environments, especially for workloads that require high system performance and reliability.
The feature that removes the FE leader from handling query traffic is available only after SLB is enabled.
You need to enable the SLB service, which incurs additional fees. For more information, see CLB Billing overview.
CN Specifications
Specification Type: Standard Specification
Compute CU: 8 CU
Data Disk: PL1 ESSD, 200 GB, 1
Number of Nodes: 3
Specification Type: The specification types for CN nodes vary depending on the StarRocks instance family.
Basic Edition: Supports Standard Specifications.
Standard Edition: Supports the following specifications.
Standard Specifications: The default specifications. One CU is equal to 1 CPU core and 4 GiB of memory. Enterprise SSDs (ESSDs) are used for data storage.
Memory-optimized Specifications: One CU is equal to 1 CPU core and 8 GiB of memory. This option is suitable for scenarios in which a large amount of memory resources are required, such as scenarios where complex queries are made or scenarios where high concurrency is required. ESSDs are used for data storage.
Network-enhanced Specifications: One CU is equal to 1 CPU core and 4 GiB of memory. The network bandwidth is two or more times that of the standard specifications. This option is suitable for analysis of external tables that contain a large amount of data. ESSDs are used for data storage.
High-performance storage: If you select this option, you must select the desired specifications based on your business requirements. This option is suitable for scenarios in which high storage I/O performance is required. Local SSDs are used for data storage.
High-specification Storage: If you select this option, you must select the desired specifications based on your business requirements. Local HDDs are used for data storage. This option is suitable for scenarios in which a large volume of data needs to be stored and cost-effective storage is required, but high storage I/O performance is not required.
Compute CUs: Select compute units (CUs).
Select the appropriate CU specifications based on your actual requirements. For more information about CU fees, see Billing items.
Data Disk: Supports ESSD PL0, PL1 ESSD (Recommended), PL2 ESSD, PL3 ESSD, Elastic Ephemeral Disk (Standard Edition), and Elastic Ephemeral Disk (Premium Edition). For more information about disk and elastic ephemeral disk fees, see Billing.
For more information, see enterprise SSD (ESSD) and elastic ephemeral disk.
NoteYou can enter the required storage capacity, and the system automatically provides a default recommended configuration. If the disk capacity you select exceeds the recommended threshold, the system displays a prompt to help you make appropriate adjustments for optimal performance.
Only the Standard, Memory-enhanced, and Compute-optimized instance families support elastic ephemeral disks, which are subject to region and zone limitations.
Number Of Nodes: The number of CN nodes. Value range: 1 to 100.
Instance Name
Custom instance name.
The name of the instance. The name must be 1 to 64 characters in length and can contain Chinese characters, letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
Administrator
admin
The administrator used to manage StarRocks. The default value is admin and cannot be changed.
Password and Confirm Password
Custom password.
The password for the built-in administrator `admin` of the StarRocks instance. Record this password. You need it to manage and use the StarRocks instance. If you forget the password, you can reset it. For more information, see How do I reset the password of an instance?
For more information about the instance parameters, see Create an instance.
Read and accept the Terms of Service, click Create Instance, and then complete the payment as prompted.
After you complete the payment, return to the instance management page to view the new instance. The instance is created when its Status changes to Running.
Step 2: Connect to the StarRocks instance
On the Instance List page, in the Actions column, click Connect To Instance.
You can also connect to the StarRocks instance in other ways.
Connect to the StarRocks instance.
Configure the following parameters on the New Connection tab.
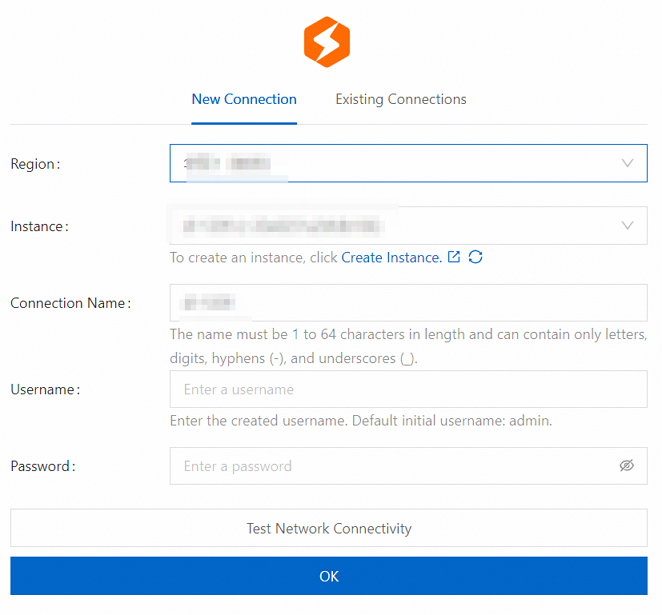
Parameter
Example
Description
Region
China (Hangzhou)
Select the physical location of the created StarRocks instance.
Instance
StarRocks_Serverless
Select the name of the created StarRocks instance.
Connection Name
Connection_Serverless
Enter a custom connection name.
The name must be 1 to 64 characters in length and can contain only Chinese characters, letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
Username
Enter a username as needed.
The default initial username is admin. You can use this username to connect, or create other users as needed. For more information about how to create a user, see Manage users and grant permissions.
Password
Enter a password as needed.
The password that corresponds to the username created in the StarRocks instance.
Click Test Connection.
After the connection is authenticated, click OK.
You are redirected to the SQL Editor page, where you can run SQL statements. For more information, see Connect to a StarRocks instance using EMR StarRocks Manager.
Step 3: Run an SQL query
On the Query List page in SQL Editor, click the
 icon.
icon.In the New File dialog box, click OK.
Enter the following commands in the new file, select all of them, and click Run.
/**Create a database**/ CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS load_test; /**Use the database**/ USE load_test; /**Create a table**/ CREATE TABLE insert_wiki_edit ( event_time DATETIME, channel VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT '', user VARCHAR(128) DEFAULT '', is_anonymous TINYINT DEFAULT '0', is_minor TINYINT DEFAULT '0', is_new TINYINT DEFAULT '0', is_robot TINYINT DEFAULT '0', is_unpatrolled TINYINT DEFAULT '0', delta INT SUM DEFAULT '0', added INT SUM DEFAULT '0', deleted INT SUM DEFAULT '0' ) AGGREGATE KEY(event_time, channel, user, is_anonymous, is_minor, is_new, is_robot, is_unpatrolled) PARTITION BY RANGE(event_time) ( PARTITION p06 VALUES LESS THAN ('2015-09-12 06:00:00'), PARTITION p12 VALUES LESS THAN ('2015-09-12 12:00:00'), PARTITION p18 VALUES LESS THAN ('2015-09-12 18:00:00'), PARTITION p24 VALUES LESS THAN ('2015-09-13 00:00:00') ) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(user) BUCKETS 10 PROPERTIES("replication_num" = "1"); /**Insert data**/ INSERT INTO insert_wiki_edit VALUES("2015-09-12 00:00:00","#en.wikipedia","GELongstreet",0,0,0,0,0,36,36,0),("2015-09-12 00:00:00","#ca.wikipedia","PereBot",0,1,0,1,0,17,17,0); /**Query data**/ select * from insert_wiki_edit;
The following result is returned.

You can run the SHOW CREATE TABLE load_test.insert_wiki_edit; command and check the result for the datacache.enable property to confirm that the storage-compute separated instance is working correctly. After the database and table for the storage-compute separation architecture are created, you can also find the new database and table directories in the OSS bucket.

Step 4: View table information
In the new file, enter the following command to view the databases.
SHOW PROC '/dbs';The following result is returned.
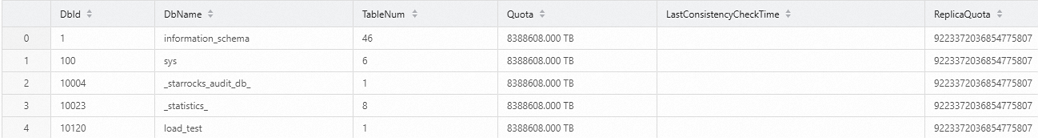
Enter the following command to view the details of the table.
SHOW PROC '/dbs/10120';The following result is returned.

In storage-compute separation mode,
CLOUD_NATIVEis the identifier for the table type field.StoragePathis the path of the table in OSS. You can use this path to find the data storage location of the table.
Step 5: Demonstrate the cache feature
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
Find the target query and click the query ID.
Click the Execution Details tab.
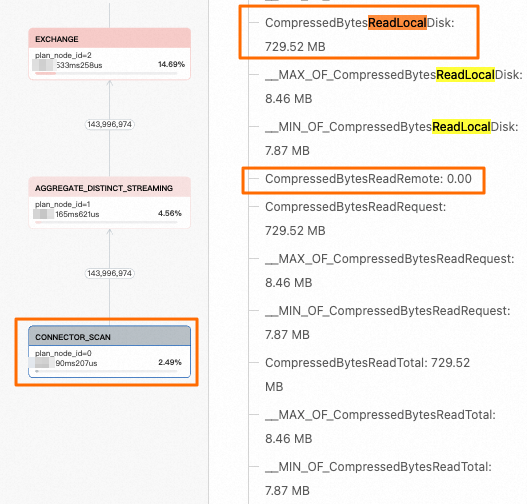
By viewing the Profile execution tree, you can find the relevant nodes and focus on two metrics on the right: CompressedBytesReadLocalDisk (data read from the local cache) and CompressedBytesReadRemote (data read from the remote OSS).
In this example, the local cache feature is enabled for the `insert_wiki_edit_cache` table. By observing the metric values, you can determine that the query fully hit the local cache.
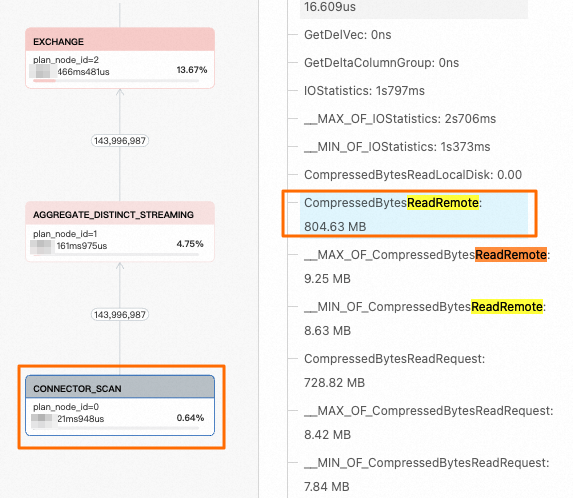
The local cache feature is not enabled for the `insert_wiki_edit_nocache` table. By analyzing its corresponding metric values, you can determine that the query on this table did not hit the local cache. All data was read from the remote OSS.
Step 6: Perform a performance test
This example compares the query performance of the storage-compute separation mode (with local cache) with the storage-compute integration mode. You can use the SSB test dataset for a more detailed performance comparison. For more information, see SSB performance test.
Prepare the data environment.
Cluster resource configuration: 1 FE (8 CUs) + 3 CNs (Computing power: 16 CUs | Storage: 1000 GB).
Cluster parameters: Use the default settings. Enable local cache for the storage-compute separation cluster.
Data volume: 500 GB (sf=500)
Test results.
Storage-compute integration total time: 21.586 s.
Storage-compute separation total time (with local cache enabled on the second execution): 27.364 s.
Storage-compute separation without local cache total time: 117.529 s.
After you run the sh ssb_query.sh ssb script to perform the SSB test, the results show that when local cache is enabled, the query performance of the storage-compute separation mode is almost the same as that of the storage-compute integration mode. Both are significantly better than the performance of a cluster without local cache.
SQL | Storage-compute integration | Storage-compute separation with data cache enabled | Storage-compute separation with data cache disabled |
Q1.1 | 0m0.373s | 0m0.380s | 0m2.080s |
Q1.2 | 0m0.303s | 0m0.292s | 0m2.141s |
Q1.3 | 0m0.101s | 0m0.097s | 0m0.144s |
Q2.1 | 0m2.461s | 0m2.821s | 0m14.401s |
Q2.2 | 0m2.272s | 0m2.735s | 0m13.048s |
Q2.3 | 0m2.168s | 0m2.588s | 0m13.957s |
Q3.1 | 0m4.536s | 0m4.864s | 0m14.810s |
Q3.2 | 0m2.371s | 0m2.682s | 0m11.292s |
Q3.3 | 0m2.082s | 0m2.648s | 0m13.651s |
Q3.4 | 0m0.195s | 0m0.212s | 0m0.572s |
Q4.1 | 0m5.122s | 0m5.847s | 0m29.576s |
Q4.2 | 0m1.141s | 0m1.369s | 0m1.465s |
Q4.3 | 0m0.661s | 0m0.829s | 0m0.792s |
Total | 21.586s | 27.364s | 117.529 s |
(Optional) Step 7: Release the instance
This operation deletes the instance and all its resources. This action is irreversible. Proceed with caution.
If you no longer need an instance, you can release it to avoid incurring further charges.
On the Instance List page, click Release in the Actions column of the instance you want to release.
In the dialog box that appears, click OK.
References
For more information about operations in the SQL Editor, see SQL Editor.
To view the SQL query information of the current instance, analyze the SQL execution plan, and promptly diagnose and troubleshoot SQL issues, see Diagnostics and analysis.
To view and analyze all operations that occurred in the database, see Audit log.
Contact us
If you have any questions, search for the DingTalk group ID 24010016636 and join the group to ask your questions.