StarRocks provides an Apache Flink connector (Flink Connector), which allows you to import data into StarRocks tables through Flink. Compared to Flink's built-in flink-connector-jdbc, StarRocks' Flink Connector offers superior performance and stability, making it particularly suitable for large-scale data import scenarios.
Background
StarRocks Flink Connector significantly improves data import efficiency by caching small batches of data in memory and utilizing StarRocks' Stream Load feature for batch imports. It supports DataStream API, Table API & SQL, and Python API.
Prerequisites
You have created a cluster that includes Flink services.
This topic uses a DataFlow cluster with Flink services (hereinafter referred to as a Flink cluster) created in EMR on ECS as an example. For more information, see Create a cluster.
You have created an EMR Serverless StarRocks instance. For more information, see Create an instance.
Limitations
Ensure that the machine where Flink is running can access the http_port port (default
8030) and query_port port (default9030) of the FE node in the StarRocks instance, along with the be_http_port port (default8040) of the BE node.Using the Flink Connector to import data into StarRocks requires SELECT and INSERT permissions on the target table.
The compatibility requirements for Flink Connector versions with Java, Scala environments, and Flink versions are as follows.
Connector
Flink
StarRocks
Java
Scala
1.2.9
1.15~1.18
2.1 and above
8
2.11, 2.12
1.2.8
1.13~1.17
2.1 and above
8
2.11, 2.12
1.2.7
1.11~1.15
2.1 and above
8
2.11, 2.12
Configuration
This section introduces StarRocks parameter settings and corresponding data type mappings. For more detailed information, please refer to Continuously load data from Apache Flink® | StarRocks.
Parameters
Parameter | Required | Default value | Description |
| Yes | NONE | Specifies the connector as StarRocks, fixed to |
| Yes | NONE | The JDBC URL that is used to connect to StarRocks and perform queries in StarRocks. Example: jdbc:mysql://fe-c-9b354c83e891****-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com:9030. Here, Note For information about how to obtain the internal address of the FE node of an EMR Serverless StarRocks instance, see View instance list and details. |
| Yes | NONE | Specifies the internal address and HTTP port of the FE node, in the format of Example: fe-c-9b354c83e891****-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com:8030. |
| Yes | NONE | The name of the StarRocks database. |
| Yes | NONE | The name of the StarRocks table. |
| Yes | NONE | The username of the StarRocks instance. For example, the default admin. Using the Flink Connector to import data into StarRocks requires SELECT and INSERT permissions on the target table. If your user account does not have these permissions, you need to grant them. For more information, see Manage users and data authorization. |
| Yes | NONE | The password of the StarRocks instance user. |
| No | at-least-once | Defines the level of semantic guarantee for the sink, ensuring reliability and consistency when data is written to the target system. Valid values:
|
| No | AUTO | The interface for importing data. This parameter is supported starting from Flink Connector 1.2.4.
|
| No | NONE | Specifies the prefix for the label used by Stream Load. If the Flink Connector version is 1.2.8 or later, and the sink guarantees exactly-once semantics, it is recommended to configure a label prefix. |
| No | 94371840(90M) | The maximum size of data accumulated in memory, after which the data is imported into StarRocks at once through Stream Load. Setting a larger value can improve import performance but may lead to higher import latency. Valid values: [64MB, 10GB]. Note
|
sink.buffer-flush.max-rows | No | 500000 | The maximum number of data rows accumulated in memory, after which the data is imported into StarRocks at once through Stream Load. Valid values: [64000, 5000000]. Note This parameter is effective only when |
sink.buffer-flush.interval-ms | No | 300000 | Sets the time interval for data sending, controlling the latency of data written to StarRocks. Valid values: [1000, 3600000]. Note This parameter is effective only when |
sink.max-retries | No | 3 | The number of retries after a Stream Load failure. If this number is exceeded, the data import task reports an error. Valid values: [0, 10]. Note This parameter is effective only when |
sink.connect.timeout-ms | No | 30000 | The timeout period for establishing an HTTP connection with the FE. Valid values: [100, 60000]. Before Flink Connector v1.2.9, the default value was |
sink.socket.timeout-ms | No | -1 | This parameter is supported starting from Flink connector 1.2.10. The timeout period for the HTTP client to wait for data. Unit: milliseconds. The default value |
sink.wait-for-continue.timeout-ms | No | 10000 | This parameter is supported starting from Flink Connector 1.2.7. The timeout period for waiting for the FE HTTP 100-continue response. Valid values: [3000, 60000]. |
sink.ignore.update-before | No | TRUE | This parameter is supported starting from Flink Connector 1.2.8. When importing data into a primary key table, specifies whether to ignore UPDATE_BEFORE records from Flink. If this parameter is set to false, the record is treated as a DELETE operation in the primary key table. |
sink.parallelism | No | NONE | The parallelism of writing, applicable only to Flink SQL. If not set, the Flink planner will determine the parallelism. In multi-parallelism scenarios, users need to ensure that data is written in the correct order. |
sink.properties.* | No | NONE | Parameters for Stream Load, controlling Stream Load import behavior. |
sink.properties.format | No | csv | The data format for Stream Load import. The Flink Connector converts the data in memory to the corresponding format and then imports it into StarRocks through Stream Load. Valid values: CSV or JSON. |
sink.properties.column_separator | No | \t | The column separator for CSV data. |
sink.properties.row_delimiter | No | \n | The row delimiter for CSV data. |
sink.properties.max_filter_ratio | No | 0 | The maximum tolerance rate for import jobs, which is the maximum proportion of data rows that can be filtered out due to data quality issues. Valid values: 0~1. |
sink.properties.partial_update | No | false | Specifies whether to use partial update. Valid values include |
sink.properties.partial_update_mode | No | row | Specifies the mode for partial update. Valid values:
|
sink.properties.strict_mode | No | false | Specifies whether to enable strict mode for Stream Load. Strict mode affects import behavior when unqualified rows (such as inconsistent column values) appear in the imported data. Valid values: |
sink.properties.compression | No | NONE | This parameter is supported starting from Flink Connector 1.2.10. Specifies the compression algorithm for Stream Load. Currently, only JSON format compression is supported. Valid value: Note Only StarRocks v3.2.7 and higher versions support JSON format compression. |
Data type mapping
Data type of Flink | Data type of StarRocks |
BOOLEAN | BOOLEAN |
TINYINT | TINYINT |
SMALLINT | SMALLINT |
INTEGER | INTEGER |
BIGINT | BIGINT |
FLOAT | FLOAT |
DOUBLE | DOUBLE |
DECIMAL | DECIMAL |
BINARY | INT |
CHAR | STRING |
VARCHAR | STRING |
STRING | STRING |
DATE | DATE |
TIMESTAMP_WITHOUT_TIME_ZONE(N) | DATETIME |
TIMESTAMP_WITH_LOCAL_TIME_ZONE(N) | DATETIME |
ARRAY<T> | ARRAY<T> |
MAP<KT,VT> | JSON STRING |
ROW<arg T...> | JSON STRING |
Preparations
Get the Flink Connector JAR and upload it to the Flink cluster
You can obtain the Flink Connector JAR package through the following methods.
Method 1: Direct download
Get different versions of Flink Connector JAR files from the Maven Central Repository.
Method 2: Maven dependency
In the
pom.xmlfile of your Maven project, add the Flink Connector as a dependency using the following format.For Flink Connector applicable to Flink version 1.15 and later.
<dependency> <groupId>com.starrocks</groupId> <artifactId>flink-connector-starrocks</artifactId> <version>${connector_version}_flink-${flink_version}</version> </dependency>For Flink Connector applicable to Flink versions before 1.15.
<dependency> <groupId>com.starrocks</groupId> <artifactId>flink-connector-starrocks</artifactId> <version>${connector_version}_flink-${flink_version}_${scala_version}</version> </dependency>
Method 3: Manual compilation
Download the Flink Connector code.
Run the following command to compile the source code of the Flink Connector into a JAR file.
sh build.sh <flink_version>For example, if the Flink version in your environment is 1.17, you need to run the following command.
sh build.sh 1.17After compilation is complete, find the generated JAR file in the
target/directory.For example, the file name is typically in the format of
flink-connector-starrocks-1.2.7_flink-1.17-SNAPSHOT.jar.NoteUnofficial releases of Flink Connector versions will have a
SNAPSHOTsuffix.
The naming format of Flink Connector JAR files is as follows:
For Flink Connector applicable to Flink version 1.15 and later, the naming format is
flink-connector-starrocks-${connector_version}_flink-${flink_version}.jar. For example, if you have installed Flink 1.17 and want to use Flink Connector version 1.2.8, you can useflink-connector-starrocks-1.2.8_flink-1.17.jar.For Flink Connector applicable to Flink versions before 1.15, the naming format is
flink-connector-starrocks-${connector_version}_flink-${flink_version}_${scala_version}.jar. For example, if you have installed Flink 1.14 and Scala 2.12, and you want to use Flink Connector version 1.2.7, you can useflink-connector-starrocks-1.2.7_flink-1.14_2.12.jar.NotePlease replace the following information according to your actual situation:
flink_version: The version number of Flink.scala_version: The version number of Scala.connector_version: The version number of the Flink Connector.
Upload the obtained Flink Connector JAR file to the
flink-{flink_version}/libdirectory of the Flink cluster.For example, if you are using an EMR cluster with version EMR-5.19.0, the JAR file should be placed in the
/opt/apps/FLINK/flink-current/libdirectory.
Start the Flink cluster
Log on to the master node of the Flink cluster. For more information, see Log on to a cluster.
Run the following command to start the Flink cluster.
/opt/apps/FLINK/flink-current/bin/start-cluster.sh
Examples
Write data using Flink SQL
Create a database named
testin StarRocks, and create a primary key table namedscore_boardin it.CREATE DATABASE test; CREATE TABLE test.score_board( id int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT "", name varchar(65533) NULL DEFAULT "" COMMENT "", score int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT "0" COMMENT "" ) ENGINE=OLAP PRIMARY KEY(id) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(id);Log on to the master node of the Flink cluster. For more information, see Log on to a cluster.
Run the following command to start Flink SQL:
/opt/apps/FLINK/flink-current/bin/sql-client.shRun the following command to create a table named
score_boardand insert data into it.CREATE TABLE `score_board` ( `id` INT, `name` STRING, `score` INT, PRIMARY KEY (id) NOT ENFORCED ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'starrocks', 'jdbc-url' = 'jdbc:mysql://<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:9030', 'load-url' = '<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:8030', 'database-name' = 'test', 'table-name' = 'score_board', 'username' = 'admin', 'password' = '<password>', ); INSERT INTO `score_board` VALUES (1, 'starrocks', 100), (2, 'flink', 100);If the target is to import data into a StarRocks primary key table, you must explicitly specify the primary key in the DDL of the Flink table. For other types of StarRocks tables (such as Duplicate Key tables), defining a primary key is optional.
Write data using Flink DataStream
Write corresponding Flink DataStream jobs based on different types of input records.
Write string data in CSV format
If the input records are strings in CSV format, the main code of the corresponding Flink DataStream job is shown below. For the complete code, see LoadCsvRecords.
/** * Generate CSV-format records. Each record has three values separated by "\t". * These values will be loaded to the columns `id`, `name`, and `score` in the StarRocks table. */ String[] records = new String[]{ "1\tstarrocks-csv\t100", "2\tflink-csv\t100" }; DataStream<String> source = env.fromElements(records); /** * Configure the Flink connector with the required properties. * You also need to add properties "sink.properties.format" and "sink.properties.column_separator" * to tell the Flink connector the input records are CSV-format, and the column separator is "\t". * You can also use other column separators in the CSV-format records, * but remember to modify the "sink.properties.column_separator" correspondingly. */ StarRocksSinkOptions options = StarRocksSinkOptions.builder() .withProperty("jdbc-url", jdbcUrl) .withProperty("load-url", loadUrl) .withProperty("database-name", "test") .withProperty("table-name", "score_board") .withProperty("username", "root") .withProperty("password", "") .withProperty("sink.properties.format", "csv") .withProperty("sink.properties.column_separator", "\t") .build(); // Create the sink with the options. SinkFunction<String> starRockSink = StarRocksSink.sink(options); source.addSink(starRockSink);Write string data in JSON format
If the input records are strings in JSON format, the main code of the corresponding Flink DataStream job is shown below. For the complete code, see LoadJsonRecords.
/** * Generate JSON-format records. * Each record has three key-value pairs corresponding to the columns id, name, and score in the StarRocks table. */ String[] records = new String[]{ "{\"id\":1, \"name\":\"starrocks-json\", \"score\":100}", "{\"id\":2, \"name\":\"flink-json\", \"score\":100}", }; DataStream<String> source = env.fromElements(records); /** * Configure the Flink connector with the required properties. * You also need to add properties "sink.properties.format" and "sink.properties.strip_outer_array" * to tell the Flink connector the input records are JSON-format and to strip the outermost array structure. */ StarRocksSinkOptions options = StarRocksSinkOptions.builder() .withProperty("jdbc-url", jdbcUrl) .withProperty("load-url", loadUrl) .withProperty("database-name", "test") .withProperty("table-name", "score_board") .withProperty("username", "root") .withProperty("password", "") .withProperty("sink.properties.format", "json") .withProperty("sink.properties.strip_outer_array", "true") .build(); // Create the sink with the options. SinkFunction<String> starRockSink = StarRocksSink.sink(options); source.addSink(starRockSink);Write custom Java object data
If the input records are custom Java objects, the main code of the corresponding Flink DataStream job is shown below. For the complete code, see LoadCustomJavaRecords.
In this example, a simple POJO class
RowDatais defined to represent each record.public static class RowData { public int id; public String name; public int score; public RowData() {} public RowData(int id, String name, int score) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.score = score; } }The main code is shown below.
// Generate records which use RowData as the container. RowData[] records = new RowData[]{ new RowData(1, "starrocks-rowdata", 100), new RowData(2, "flink-rowdata", 100), }; DataStream<RowData> source = env.fromElements(records); // Configure the Flink connector with the required properties. StarRocksSinkOptions options = StarRocksSinkOptions.builder() .withProperty("jdbc-url", jdbcUrl) .withProperty("load-url", loadUrl) .withProperty("database-name", "test") .withProperty("table-name", "score_board") .withProperty("username", "root") .withProperty("password", "") .build(); /** * The Flink connector will use a Java object array (Object[]) to represent a row to be loaded into the StarRocks table, * and each element is the value for a column. * You need to define the schema of the Object[] which matches that of the StarRocks table. */ TableSchema schema = TableSchema.builder() .field("id", DataTypes.INT().notNull()) .field("name", DataTypes.STRING()) .field("score", DataTypes.INT()) // When the StarRocks table is a Primary Key table, you must specify notNull(), for example, DataTypes.INT().notNull(), for the primary key `id`. .primaryKey("id") .build(); // Transform the RowData to the Object[] according to the schema. RowDataTransformer transformer = new RowDataTransformer(); // Create the sink with the schema, options, and transformer. SinkFunction<RowData> starRockSink = StarRocksSink.sink(schema, options, transformer); source.addSink(starRockSink);The
RowDataTransformeris defined as follows.private static class RowDataTransformer implements StarRocksSinkRowBuilder<RowData> { /** * Set each element of the object array according to the input RowData. * The schema of the array matches that of the StarRocks table. */ @Override public void accept(Object[] internalRow, RowData rowData) { internalRow[0] = rowData.id; internalRow[1] = rowData.name; internalRow[2] = rowData.score; // When the StarRocks table is a Primary Key table, you need to set the last element to indicate whether the data loading is an UPSERT or DELETE operation. internalRow[internalRow.length - 1] = StarRocksSinkOP.UPSERT.ordinal(); } }
Synchronize data using Flink CDC 3.0
The Flink CDC 3.0 framework allows you to easily build streaming ELT pipelines from CDC data sources (such as MySQL, Kafka) to StarRocks. Through this pipeline, you can achieve the following functions:
Automatic creation of databases and tables
Synchronization of full and incremental data
Synchronization of Schema Changes
Starting from StarRocks Flink Connector v1.2.9, the connector has been integrated into the Flink CDC 3.0 framework and is named StarRocks Pipeline Connector. This connector has all the above features and is recommended to be used with StarRocks v3.2.1 and above to fully utilize the fast_schema_evolution feature, which further improves the speed of adding and removing columns and reduces resource consumption.
Best practices
Import to primary key tables
Create a database named
testin StarRocks, and create a primary key tablescore_boardin it.CREATE DATABASE `test`; CREATE TABLE `test`.`score_board` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT "", `name` varchar(65533) NULL DEFAULT "" COMMENT "", `score` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT "0" COMMENT "" ) ENGINE=OLAP PRIMARY KEY(`id`) COMMENT "OLAP" DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`id`);Insert data into the StarRocks table.
INSERT INTO `test`.`score_board` VALUES (1, 'starrocks', 100), (2, 'flink', 100);Run the following command to start the Flink SQL client.
/opt/apps/FLINK/flink-current/bin/sql-client.shUpdate data.
Partial update
Partial update allows you to update only specified columns (such as
name) without affecting other columns (such asscore).Create a table
score_boardin the Flink SQL client and enable the partial update feature.CREATE TABLE `score_board` ( `id` INT, `name` STRING, PRIMARY KEY (id) NOT ENFORCED ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'starrocks', 'jdbc-url' = 'jdbc:mysql://<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:9030', 'load-url' = '<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:8030', 'database-name' = 'test', 'table-name' = 'score_board', 'username' = 'admin', 'password' = '<password>', 'sink.properties.partial_update' = 'true', -- only for Flink connector version <= 1.2.7 'sink.properties.columns' = 'id,name,__op' );sink.properties.partial_update: Enables partial update.sink.properties.columns: Specifies the columns to be updated. If the Flink Connector version is less than or equal to 1.2.7, you also need to set the optionsink.properties.columnstoid,name,__opto tell the Flink connector which columns need to be updated. Note that you need to append the field__opat the end. The field__opindicates whether the import is an UPSERT or DELETE operation, and its value is automatically set by the Flink connector.
Insert update data.
Insert two rows of data with the same primary keys as the existing data, but with modified values in the
namecolumn.INSERT INTO score_board VALUES (1, 'starrocks-update'), (2, 'flink-update');Query the StarRocks table in SQL Editor.
SELECT * FROM `test`.`score_board`;You will see that only the values in the
namecolumn have changed, while thescorecolumn remains unchanged.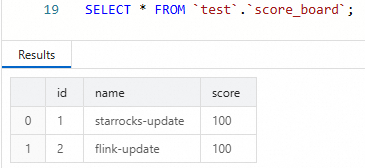
Conditional update
This example shows how to perform conditional updates based on the value of the
scorecolumn. A data row is updated only when thescorecolumn value in the imported data is greater than or equal to the current value in the StarRocks table.Create a table
score_boardin the Flink SQL client as follows.CREATE TABLE `score_board` ( `id` INT, `name` STRING, `score` INT, PRIMARY KEY (id) NOT ENFORCED ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'starrocks', 'jdbc-url' = 'jdbc:mysql://<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:9030', 'load-url' = '<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:8030', 'database-name' = 'test', 'table-name' = 'score_board', 'username' = 'admin', 'password' = '<password>', 'sink.properties.merge_condition' = 'score', 'sink.version' = 'V1' );sink.properties.merge_condition: Set toscore, indicating that when data is written, the Flink Connector will use thescorecolumn as the update condition.sink.version: Set toV1, indicating that the Flink Connector uses the Stream Load interface to import data.
Insert two rows of data into the table in the Flink SQL client.
The data rows have the same primary keys as the rows in the StarRocks table. The first data row has a smaller value in the
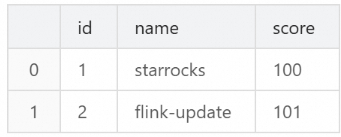
scorecolumn, while the second data row has a larger value in thescorecolumn.INSERT INTO `score_board` VALUES (1, 'starrocks-update', 99), (2, 'flink-update', 101);Query the StarRocks table in SQL Editor.
SELECT * FROM `test`.`score_board`;You will see that only the second row of data has changed, while the first row of data remains unchanged.
Import to Bitmap columns
The Bitmap type is commonly used to accelerate exact deduplication counting scenarios, such as calculating unique visitors (UV). Below is a complete example showing how to import data into a Bitmap column in a StarRocks table through Flink SQL and query the UV count in StarRocks.
Create a StarRocks aggregate table in SQL Editor.
Create an aggregate table named
page_uvin thetestdatabase, where:The
visit_userscolumn is defined as a BITMAP type and configured with the BITMAP_UNION aggregate function.page_idandvisit_dateserve as aggregate keys (AGGREGATE KEY) for grouping and deduplication.
CREATE TABLE `test`.`page_uv` ( `page_id` INT NOT NULL COMMENT 'page ID', `visit_date` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT 'access time', `visit_users` BITMAP BITMAP_UNION NOT NULL COMMENT 'user ID' ) ENGINE=OLAP AGGREGATE KEY(`page_id`, `visit_date`) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`page_id`);Create a table in the Flink SQL client.
Since Flink does not support the Bitmap type, column mapping and type conversion need to be implemented as follows:
In the Flink table, define the
visit_user_idcolumn as BIGINT type to represent thevisit_userscolumn in the StarRocks table.Use the
sink.properties.columnsconfiguration to convert the data in thevisit_user_idcolumn to Bitmap type through the to_bitmap function.
CREATE TABLE `page_uv` ( `page_id` INT, `visit_date` TIMESTAMP, `visit_user_id` BIGINT ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'starrocks', 'jdbc-url' = 'jdbc:mysql://<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:9030', 'load-url' = '<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:8030', 'database-name' = 'test', 'table-name' = 'page_uv', 'username' = 'admin', 'password' = '<password>', 'sink.properties.columns' = 'page_id,visit_date,visit_user_id,visit_users=to_bitmap(visit_user_id)' );Insert data in the Flink SQL client.
Insert multiple rows of data into the
page_uvtable, simulating different users accessing pages at different times.visit_user_idis of BIGINT type, and Flink will automatically convert it to Bitmap type.INSERT INTO `page_uv` VALUES (1, CAST('2020-06-23 01:30:30' AS TIMESTAMP), 13), (1, CAST('2020-06-23 01:30:30' AS TIMESTAMP), 23), (1, CAST('2020-06-23 01:30:30' AS TIMESTAMP), 33), (1, CAST('2020-06-23 02:30:30' AS TIMESTAMP), 13), (2, CAST('2020-06-23 01:30:30' AS TIMESTAMP), 23);Query the UV count in SQL Editor.
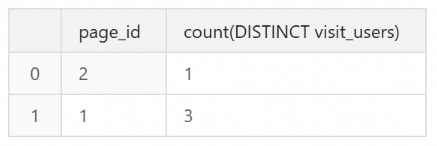
Use StarRocks' aggregation capability to calculate the unique visitor count (UV) for each page using
COUNT(DISTINCT visit_users).SELECT page_id, COUNT(DISTINCT visit_users) FROM page_uv GROUP BY page_id;The returned result is shown below.
Import to HLL columns
HLL (HyperLogLog) is a data type used for approximate deduplication counting, suitable for calculating unique visitors (UV) in large-scale data scenarios. Below is a complete example showing how to import data into an HLL column in a StarRocks table through Flink SQL and query the UV count in StarRocks.
Create a StarRocks aggregate table in SQL Editor.
Create an aggregate table named
hll_uvin thetestdatabase, where:The
visit_userscolumn is defined as an HLL type and configured with the HLL_UNION aggregate function.page_idandvisit_dateserve as aggregate keys (AGGREGATE KEY) for grouping and deduplication.
CREATE TABLE `test`.`hll_uv` ( `page_id` INT NOT NULL COMMENT 'page ID', `visit_date` DATETIME NOT NULL COMMENT 'access time', `visit_users` HLL HLL_UNION NOT NULL COMMENT 'user ID' ) ENGINE=OLAP AGGREGATE KEY(`page_id`, `visit_date`) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`page_id`);Create a table in the Flink SQL client.
Since Flink does not support the HLL type, column mapping and type conversion need to be implemented as follows:
In the Flink table, define the
visit_user_idcolumn as BIGINT type to represent thevisit_userscolumn in the StarRocks table.Use the
sink.properties.columnsconfiguration for column mapping, and convert the BIGINT typevisit_user_iddata to HLL type through the hll_hash function.
CREATE TABLE `hll_uv` ( `page_id` INT, `visit_date` TIMESTAMP, `visit_user_id` BIGINT ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'starrocks', 'jdbc-url' = 'jdbc:mysql://<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:9030', 'load-url' = '<fe-{srClusterId}-internal.starrocks.aliyuncs.com>:8030', 'database-name' = 'test', 'table-name' = 'hll_uv', 'username' = 'admin', 'password' = '<password>', 'sink.properties.columns' = 'page_id,visit_date,visit_user_id,visit_users=hll_hash(visit_user_id)' );Insert data in the Flink SQL client.
Insert multiple rows of data into the
hll_uvtable, simulating different users accessing pages at different times.visit_user_idis of BIGINT type, and Flink will automatically convert it to HLL type.INSERT INTO `hll_uv` VALUES (3, CAST('2023-07-24 12:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP), 78), (4, CAST('2023-07-24 13:20:10' AS TIMESTAMP), 2), (3, CAST('2023-07-24 12:30:00' AS TIMESTAMP), 674);Query the UV count in SQL Editor.
Use StarRocks' aggregation capability to calculate the unique visitor count (UV) for each page using
COUNT(DISTINCT visit_users).SELECT `page_id`, COUNT(DISTINCT `visit_users`) FROM `hll_uv` GROUP BY `page_id`;The returned result is shown below.
