This topic describes how to configure token-based identity authentication for the Kyuubi Gateway in EMR Serverless Spark. This method uses tokens bound to Resource Access Management (RAM) users to enable fine-grained access control for Paimon Catalog data in Data Lake Formation (DLF). Different clients can use their unique identity credentials to access the same Kyuubi gateway, but can only query data for which they have permissions.
Use cases
In an enterprise data analytics platform, multiple users or applications access data through a unified SQL gateway, such as a Kyuubi Gateway. To ensure data security, access for different identities must be isolated. This ensures that each user can access only data within their authorized scope. For example, Analyst A can query only business reports, while Data Engineer B can access the underlying raw datasets. This solution provides data permission isolation in a multitenancy environment and delivers end-to-end identity authentication and access control.

Procedure
Step 1: Prepare the environment and RAM user permissions
Prepare basic resources.
Create a workspace. For more information, see Manage workspaces.
Create and start a Kyuubi Gateway in the workspace. For more information, see Manage Kyuubi Gateways.
Create a data catalog in DLF and prepare the required database and tables.
Configure a RAM user and permissions. Prepare a RAM user and grant the necessary permissions to it.
EMR Serverless Spark permissions: Grant the RAM user the basic operation permissions required to access EMR Serverless Spark. For more information, see Grant permissions to a RAM user.
Workspace permissions: Add the RAM user to the workspace and assign a role to the user based on their function. For more information, see Manage users and roles.
Step 2: Grant table permissions to the RAM user in DLF
Grant the RAM user access permissions for specific tables in DLF. To ensure the Kyuubi Gateway can initialize a Spark session, you must also grant the RAM user the Describe permission for the default database in DLF.
Log on to the .
Navigate to the database and table in the target catalog.
Select the table for which you want to grant permissions and click the Permissions tab.
Click Grant Permissions.
Principal: select DLF User/DLF Role.
Select DLF User: select the target RAM user.
Permissions: select the required permissions.
Click OK. The authorization is complete.
NoteEMR Serverless Spark enables caching for DLF metadata and data by default. If you re-grant permissions for a table, the changes take about 10 minutes to take effect.
If you want the permission changes to take effect immediately, add the
spark.sql.catalog.lakehouse.cache-enabled falseconfiguration to the Spark configuration in the Kyuubi Gateway.
Step 3: Generate a Kyuubi token for the RAM user
On the Kyuubi Gateway page, find the target gateway, and in the Actions column, click Tokens.
Click Create Token. In the dialog box that appears, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the new token.
Expired At
Set the expiration time for the token. The value must be 1 or greater. By default, this feature is enabled and the token expires after 365 days.
Assigned To
From the drop-down list, select the target RAM user.
Copy the token information.
ImportantAfter the token is created, you must copy the token information immediately. You cannot retrieve it later. If your token expires or is lost, you must create a new one or reset the existing one.
Step 4: Connect using Beeline and verify permissions
Construct the JDBC connection command.
beeline -u "jdbc:hive2://<endpoint>:<port>/;transportMode=http;user=<UserName or RoleName>;httpPath=cliservice/token/<Token>"Parameter description:
Parameter
Description
<endpoint>The Endpoint of the Kyuubi Gateway.
<port>The access port. The port for a public Endpoint is
443. The port for an internal network Endpoint is80.<UserName or RoleName>The RAM user or RAM role. You can use the short name or the full name. Examples:
RAM user:
agentoragent@xxxx05398154xxxx.onaliyun.comRAM role:
AliyunServiceRoleForDataworksEngine
<Token>The token generated for the RAM user in Step 3.
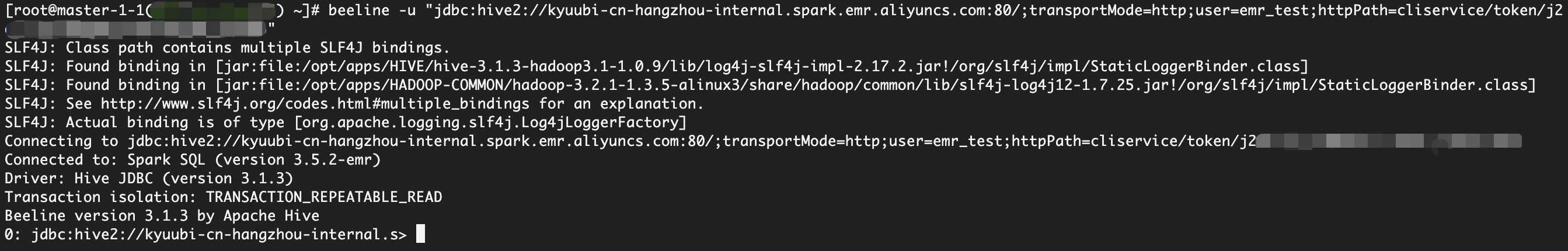
Verify the access control effect.
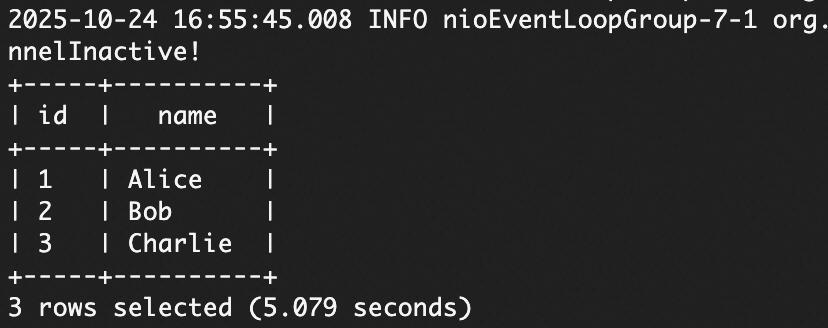
Query an authorized table:
SELECT * FROM <database_name>.<authorized_table_name> LIMIT 10;The query data is returned successfully.
Query an unauthorized table:
SELECT * FROM <database_name>.<unauthorized_table_name> LIMIT 10;The query fails and a permission-related error is returned, such as
emr_test doesn't have privilege SELECT on TABLE.
FAQ
Q1: After I grant permissions, I can still query an unauthorized table and retrieve results. Have the permissions not taken effect?
This issue can occur for the following reasons:
DLF metadata cache: The Spark engine caches table schema information, which can cause the authorization check to be bypassed.
Solution: Addspark.sql.catalog.lakehouse.cache-enabled falseto the Spark configuration to disable metadata caching.Permission latency: In rare cases, DLF permission synchronization may have a short delay, usually no more than 10 seconds.
Suggestion: Wait a moment and retry, or confirm that the permissions are correctly granted in the DLF console.
Q2: I cannot view the token after it is created. What should I do if it is lost?
The plaintext token is displayed only once in the dialog box after it is created. The system does not store the original value. If the token is lost or leaked, you must take the following actions immediately:
On the Token Management page, find the corresponding entry and click Reset Token.
The old token is automatically invalidated and a new credential is generated.
Update all client configurations with the new token.
Q3: Why do RAM users need the Describe permission for the default database to connect to a Kyuubi Gateway?
By default, when a Spark session is established, the Kyuubi Gateway attempts to load the default database as the initial context. If the current identity does not have permission to access this database, the session initialization fails and the connection is terminated. This check is mandatory, even if your business tables are located in other databases. Therefore, all RAM users who connect to the gateway must have the DescribeDatabase permission for the default database.
Appendix: Identity proxy and permission execution flow
The core of this solution is to use a Kyuubi Gateway token as an identity credential. The gateway proxies access requests on behalf of the token owner, which is a RAM user. This process integrates the Data Lake Formation (DLF) permission system into the EMR Serverless Spark query workflow.
The workflow is as follows:
Token generation: A temporary token is generated for a specified RAM user in the Kyuubi Gateway. This token is uniquely bound to the identity of that RAM user.
Client authentication: When a client, such as Beeline, establishes a Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) connection, it includes this token and the corresponding RAM username in the connection request to the Kyuubi Gateway.
Identity proxy: The Kyuubi Gateway validates the token. During a Spark SQL query, the EMR Serverless Spark engine impersonates the RAM user's identity.
DLF authorization: When the Spark engine accesses metadata or data in DLF, it sends a request to DLF using the impersonated RAM user's identity.
Permission enforcement: DLF authorizes the request based on the access policy that is configured for the RAM user and returns a result.