Alibaba Cloud EMR Serverless Spark Notebooks integrate DuckDB, providing enhanced integration with cloud data sources. This allows for passwordless access to OSS and OSS-HDFS to efficiently operate on various data file formats. You can also directly query metadata tables in Data Lake Formation (DLF) using SQL, enabling a streamlined and lightweight process for data lake exploration and analysis.
Background information
DuckDB is a lightweight, high-performance, embedded analytical database engine optimized for Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) scenarios.
Features
Embedded architecture: Embeds directly into an application as a library, similar to SQLite, without requiring a separate server. It supports both in-memory and on-disk modes.
Columnar storage: Stores data by column to optimize the performance of aggregate queries and scans.
Vectorized execution: Uses SIMD instructions to process data batches in parallel, which reduces CPU overhead.
Standard compatibility: Supports SQL-92 and SQL:2011 standards, including Common Table Expressions (CTEs), window functions, JOINs (including ASOF JOIN), and subqueries.
Direct read for multiple formats: Query CSV, Parquet, and JSON files directly without importing them.
Zero-copy integration: Seamlessly integrates with in-memory data structures, such as Pandas and Arrow, to avoid data migration overhead.
Federated query: Uses the
httpfsextension to access remote files, such as files on S3, or connect to external databases, such as PostgreSQL, for federated queries.
Scenarios
Interactive analytics: Processes datasets that range from gigabytes to terabytes. It can be used as a replacement for Pandas or Excel when handling big data.
Edge computing: Can be deployed on edge devices for local data analytics.
Data science: Seamlessly integrates with the Python and R ecosystems to serve as a pre-processing engine for machine learning (ML).
Real-time OLAP: Supports analytical needs that require both frequent updates and complex queries.
Limits
Version requirements:
esr-4.x: esr-4.7.0 and later.
esr-3.x: esr-3.6.0 and later.
The following limits apply when you read Paimon tables using DuckDB:
Operations: You can only read Paimon append-only tables. Reading primary key tables or writing data is not supported.
Table format: Only Paimon tables with
file.format = 'parquet'are supported.
Procedure
On the EMR Serverless Spark page, click Data Development in the left navigation pane.
Create a Notebook.
On the Development tab, click the
 icon.
icon.In the dialog box that appears, enter a name, set Type to , and then click OK.
In the upper-right corner, select a Notebook session instance that has been created and started.
You can also select Create Notebook Session from the drop-down list to create a new Notebook session instance. For more information, see Manage Notebook sessions.
NoteDuckDB is a single-node SQL engine that uses only the resources of the Notebook Spark driver. Therefore, you may need to increase the resource configurations for the Spark driver's
spark.driver.coresandspark.driver.memoryparameters.To use DuckDB in the Python code of a Notebook, run
import duckdb. The following examples demonstrate common use cases.Read files
View the content of Parquet, CSV, and JSON files.
import duckdb # View the content of a Parquet file duckdb.sql("SELECT * FROM 'oss://bucket/path/to/test.parquet'") # View the content of a CSV file duckdb.sql("SELECT * FROM 'oss://bucket/path/to/test.csv'") # View the content of a JSON file duckdb.sql("SELECT * FROM 'oss://bucket/path/to/test.json'")
View the schema of a Parquet file.
import duckdb # View the schema of a Parquet file duckdb.sql("SELECT * FROM parquet_schema('oss://bucket/path/to/test.parquet')")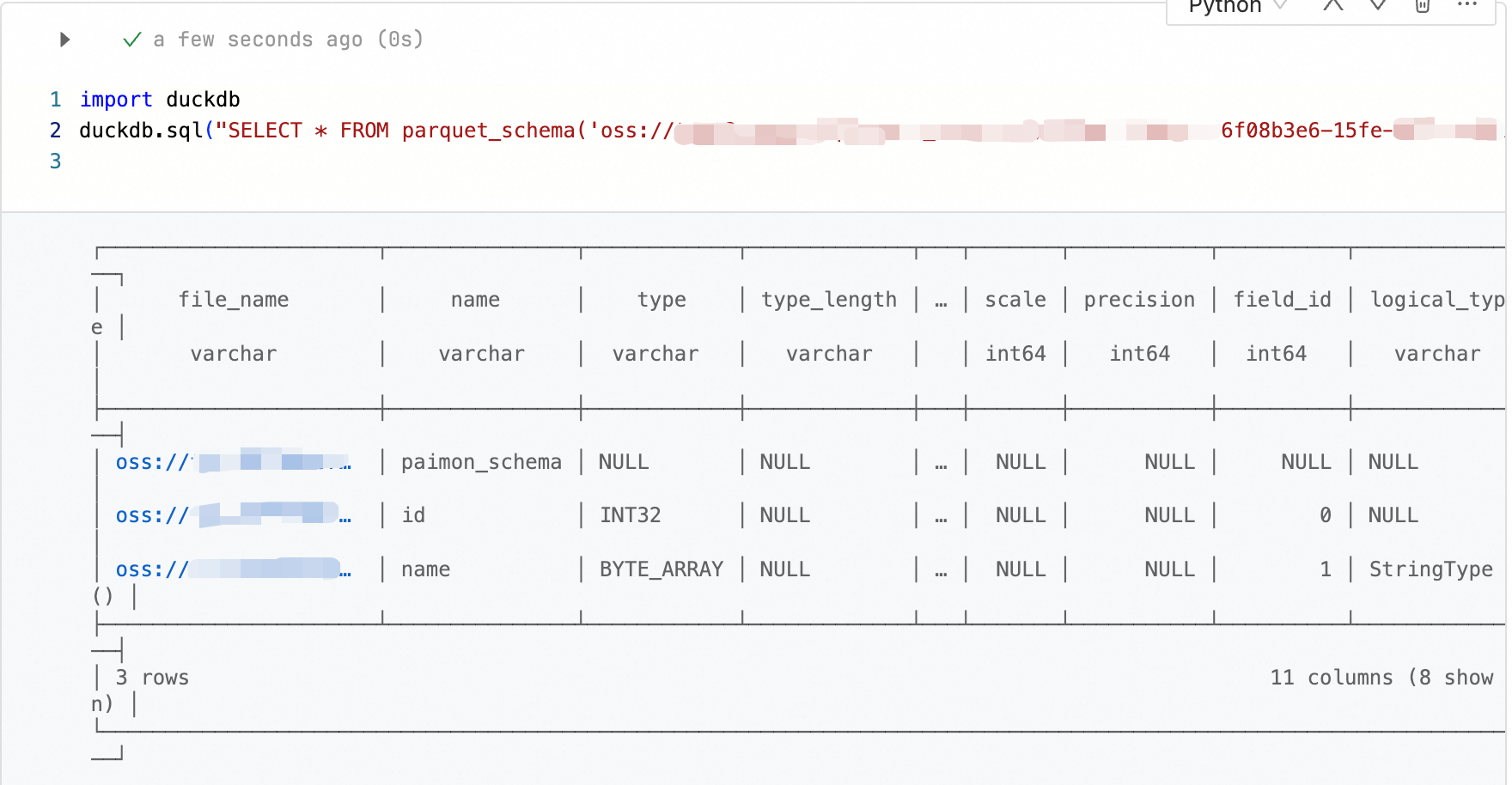
Export the content of a Parquet file to a CSV file.
import duckdb # Export the content of a Parquet file to a CSV file duckdb.sql("COPY (SELECT * FROM 'oss://bucket/path/to/test.parquet') TO 'oss://bucket/path/to/output.csv' (HEADER, DELIMITER ',');")
NoteBefore you read from or write to OSS files, you must activate OSS, create a bucket, and confirm that you have the required access permissions for the bucket.
Access a DLF catalog
NoteDLF catalogs created by data sharing are not supported.
View the DLF catalogs that are mounted in the current workspace. For more information about DLF data catalogs, see Manage data catalogs.
import duckdb duckdb.sql("show databases")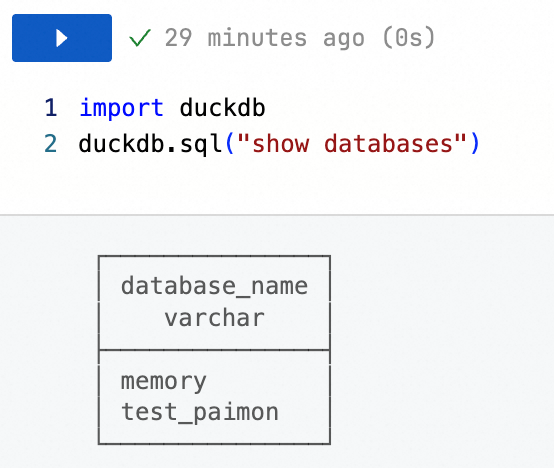
Query table data in a DLF catalog.
import duckdb duckdb.sql("use <catalogName>.<databaseName>") duckdb.sql("select * from <tableName> limit 10")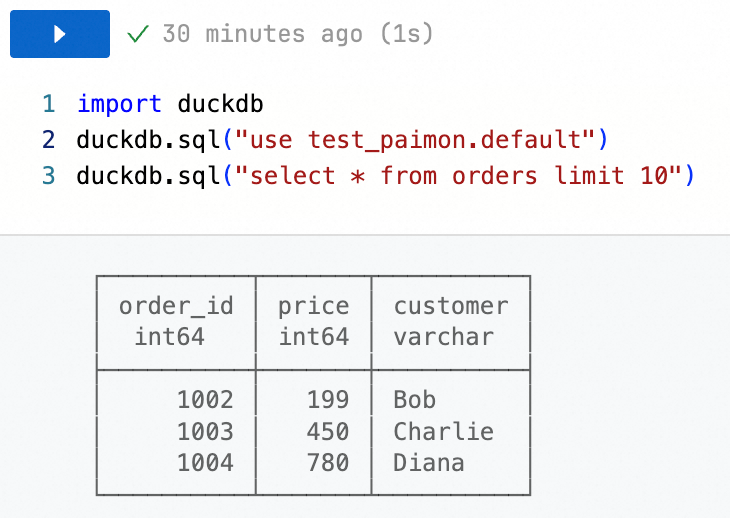
For more information, see the official DuckDB documentation.