Delta Lake is an open-source storage framework that builds a Lakehouse architecture on top of data lakes. Delta Lake provides atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID) transactions, scalable metadata processing, and combines stream processing with batch processing on existing data lakes, such as OSS, Amazon S3, and Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). Delta Lake also supports multiple engines, such as Spark, PrestoDB, and Flink, and provides APIs for various programming languages, including Scala, Java, Rust, and Python.
Prerequisites
A workspace is created. For more information, see Create a workspace.
Procedure
Step 1: Create an SQL session
Go to the Sessions page.
Log on to the EMR console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Spark page, click the name of the workspace that you want to manage.
In the left-side navigation pane of the EMR Serverless Spark page, choose Operation Center > Sessions.
On the SQL Sessions tab, click Create SQL Session.
On the Create SQL Session page, configure the parameters in the Spark Configuration section and click Create. For more information, see Manage SQL sessions.
The default catalog of the current workspace is used for metadata. If you want to change the default catalog to an external Hive Metastore, see Connect to an external Hive Metastore service.
spark.sql.extensions io.delta.sql.DeltaSparkSessionExtension spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog org.apache.spark.sql.delta.catalog.DeltaCatalog
Step 2: Read from and write to a Delta Lake table
Navigate to the SQL development page.
On the EMR Serverless Spark page, in the navigation pane on the left, click Development.
On the Development tab, click the
 icon.
icon.In the New dialog box, enter a name, such as users_task, leave the type as the default SparkSQL, and click OK.
Copy the following code to the new SparkSQL tab (users_task).
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS ss_delta_db; CREATE TABLE ss_delta_db.delta_tbl (id INT, name STRING) USING delta; INSERT INTO ss_delta_db.delta_tbl VALUES (1, "a"), (2, "b"); SELECT id, name FROM ss_delta_db.delta_tbl ORDER BY id;From the database drop-down list, select a database. From the session drop-down list, select the SQL session that you created.
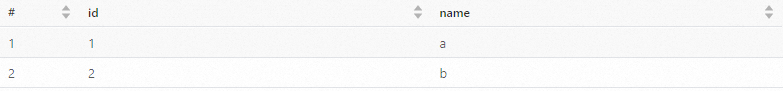
Click Run to execute the task. The following information is returned.
Step 3: Update data
Delta Lake supports various data update operations, including Update, Delete, and Merge Into. The following code provides an example.
-- Update operation
UPDATE ss_delta_db.delta_tbl SET name = "a_v2" WHERE id = 1;
-- Delete operation
DELETE FROM ss_delta_db.delta_tbl WHERE id = 2;
-- Merge Into operation
-- Create a temporary table and insert data.
CREATE TABLE ss_delta_db.tmp_tbl(id INT, name STRING) USING delta;
INSERT INTO ss_delta_db.tmp_tbl VALUES (1, "a_v3"), (3, "c");
-- Execute the Merge Into operation.
MERGE INTO ss_delta_db.delta_tbl AS target
USING ss_delta_db.tmp_tbl AS source
ON target.id = source.id
WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET *
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT *;
-- Verify the result.
SELECT * FROM ss_delta_db.delta_tbl ORDER BY id;The following information is returned.

Step 4: Clean up resources
After the test is complete, run the following commands to clean up the test resources and avoid storage consumption.
DROP TABLE ss_delta_db.delta_tbl;
DROP TABLE ss_delta_db.tmp_tbl;
DROP DATABASE ss_delta_db;The preceding commands permanently delete the tables and the database. Make sure that the data is backed up or no longer needed.
References
For a complete example of the SQL task development and orchestration process, see Quick Start for SparkSQL development.
For more information about the usage and configurations of Delta Lake, see the official Delta Lake documentation.