EMR Serverless Spark lets you edit and run jobs using SQL code. This topic describes how to create, start, and maintain SQL jobs.
Prerequisites
You have an Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Sign up for an account.
The required roles have been granted. For more information, see Grant roles to an Alibaba Cloud account.
A workspace and a session instance have been created. For more information, see Create a workspace and Manage SQL sessions.
Step 1: Create and publish development jobs
A job must be published before it can be used in a workflow.
Go to the Data Development page.
Log on to the EMR console.
In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Spark page, click the target workspace name.
On the EMR Serverless Spark page, in the navigation pane on the left, click Development.
Create the users_task job.
On the Development tab, click the
 icon.
icon.In the New dialog box, enter a name, such as users_task, leave the type as the default SparkSQL, and click OK.
Copy the following code to the new Spark SQL tab (users_task).
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS students ( name VARCHAR(64), address VARCHAR(64) ) USING PARQUET PARTITIONED BY (data_date STRING) OPTIONS ( 'path'='oss://<bucketname>/path/' ); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE students PARTITION (data_date = '${ds}') VALUES ('Ashua Hill', '456 Erica Ct, Cupertino'), ('Brian Reed', '723 Kern Ave, Palo Alto');The following table describes the supported date variables. The default value is the previous day.
Variable
Data type
Description
{data_date}
str
A variable that indicates the date. The format is
YYYY-MM-DD.Example: 2023-09-18.
{ds}
str
{dt}
str
{data_date_nodash}
str
A variable that indicates the date. The format is
YYYYMMDD.Example: 20230918.
{ds_nodash}
str
{dt_nodash}
str
{ts}
str
A variable that indicates the timestamp. The format is
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.Example: 2023-09-18T16:07:43.
{ts_nodash}
str
A variable that indicates the timestamp. The format is
YYYYMMDDHHMMSS.Example: 20230918160743.
From the database and session drop-down lists, select a database and a running session instance.
You can also select Connect to SQL Session from the drop-down list to create a new session. For more information, see Manage SQL sessions.
Click Run to execute the job.
Results are displayed on the Execution Results tab. If an exception occurs, you can view the details on the Execution Issues tab.
Publish the users_task job.
NoteParameters specified for a job are published with it and are used when the job runs in a pipeline. Session parameters are used when the job runs in the SQL editor.
On the new Spark SQL tab, click Publish.
In the dialog box, enter a description for the publication and click OK.
Create the users_count job.
On the Development tab, click the
 icon.
icon.In the New dialog box, enter a name such as users_count, accept the default type, SparkSQL, and click OK.
Copy the following code to the new Spark SQL job tab (users_count).
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM students;From the database and session drop-down lists, select a database and a running session instance.
You can also select Connect to SQL Session from the drop-down list to create a new session. For more information about session management, see Manage SQL sessions.
Click Run to execute the job.
The Execution Results tab displays the results. If an exception occurs, you can view it on the Execution Issues tab.
Publish the users_count job.
NoteParameters specified for a job are published with it and are used when the job runs in a pipeline. Session parameters are used when the job runs in the SQL editor.
On the new Spark SQL job tab, click Publish.
In the dialog box that appears, enter a description for the publication and click OK.
Step 2: Create a workflow and its nodes
In the left navigation pane, click Workflows.
On the Workflows page, click Create Workflow.
In the Create Workflow panel, enter a Name such as spark_workflow_task, and then click Next.
You can configure the parameters in the Other Settings section as needed. For more information about the parameters, see Manage workflows.
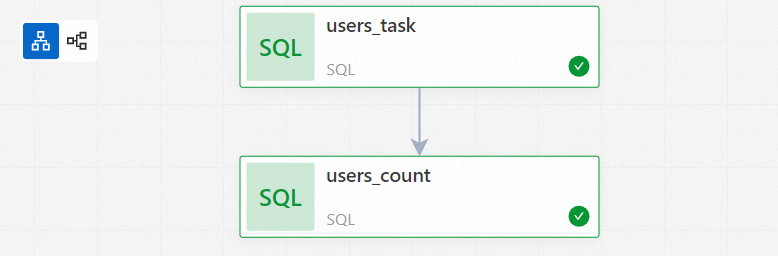
Add the users_task node.
On the new node canvas, you can click Add Node.
In the Add Node panel, select the published users_task job from the Source Path drop-down list, and then click Save.
Add the users_count node.
Click Add Node.
In the Add Node panel, select the published users_count job from the Source Path drop-down list and users_task from the Upstream Nodes drop-down list, and then click Save.
On the new node canvas, click Publish Workflow.
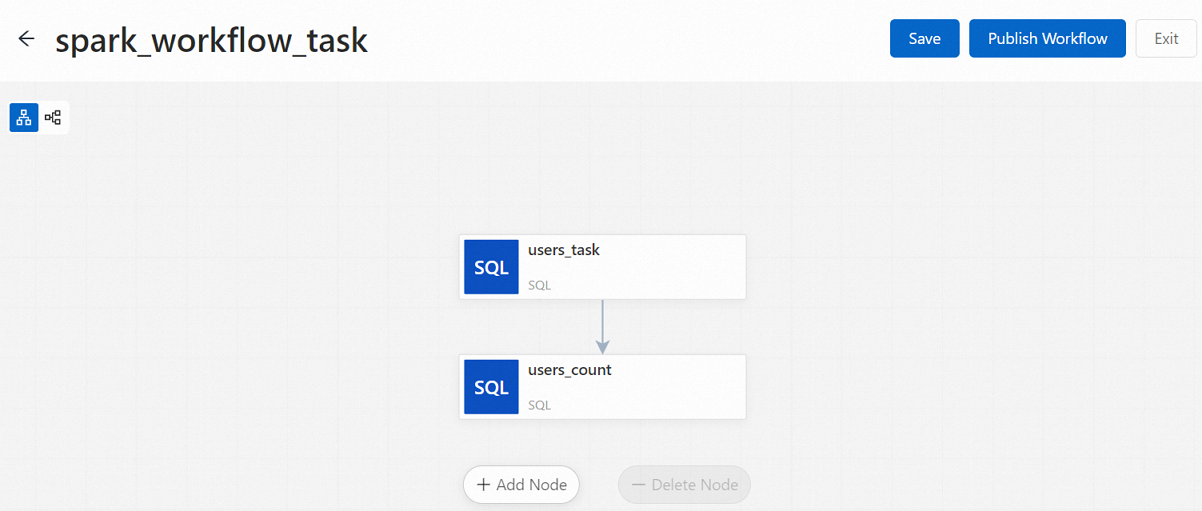
In the Publish dialog box, enter a description for the publication and click OK.
Step 3: Run the workflow
On the Workflows page, in the Name column, click the name of the new workflow (for example, spark_workflow_task).
On the Workflow Runs page, click Run.
NoteAfter you configure a scheduling cycle, you can also start the schedule on the Workflows page by turning on the switch on the left.
In the Start Workflow dialog box, click OK.
Step 4: View the instance status
On the Workflows page, click the target workflow, such as spark_workflow_task.
On the Workflow Runs page, you can view all workflow instances and the runtime and status of each.
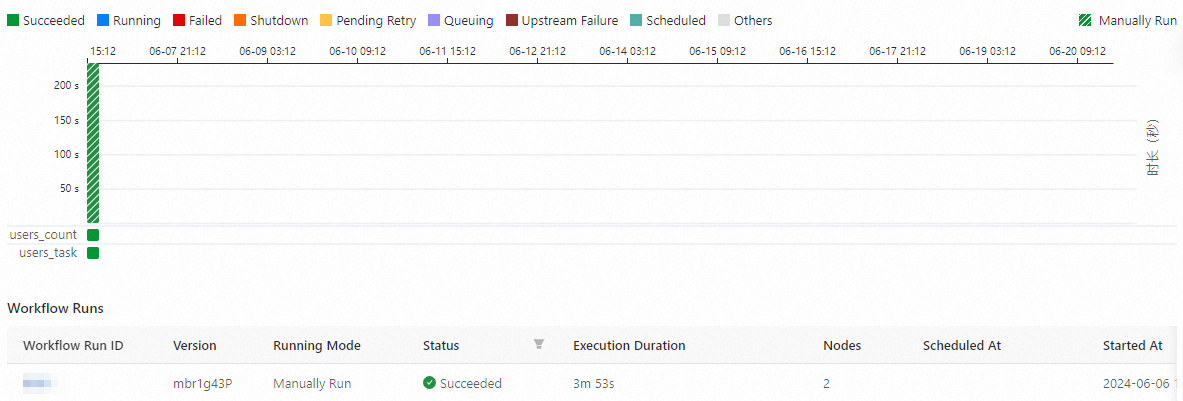
Click the Workflow Run ID in the Workflow Runs section or the Workflow Runs Diagram tab to view the workflow instance graph.
Click a target node instance. In the node information dialog box that appears, you can perform operations or view information as needed.
For more information about related operations and details, see View node instances.
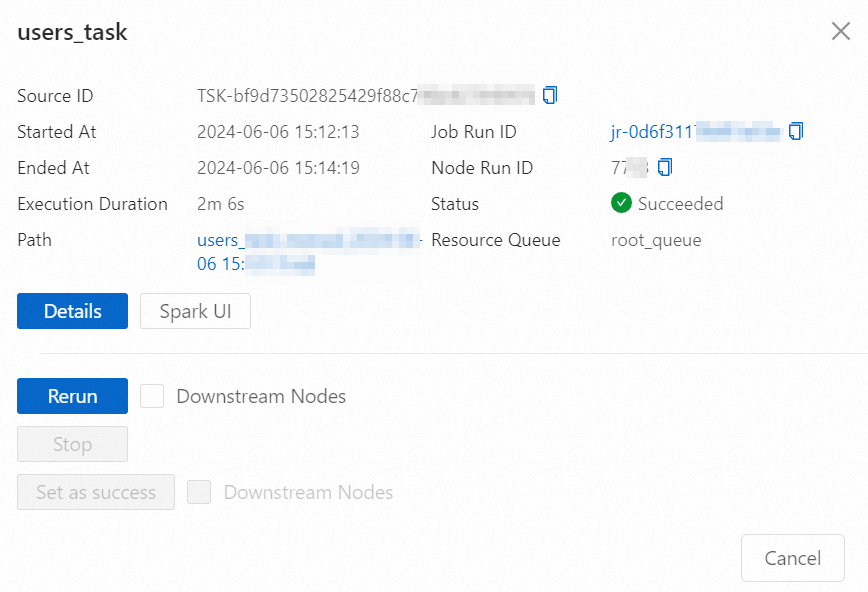
For example, click Spark UI to open the Spark Jobs page, where you can view real-time information about Spark tasks.
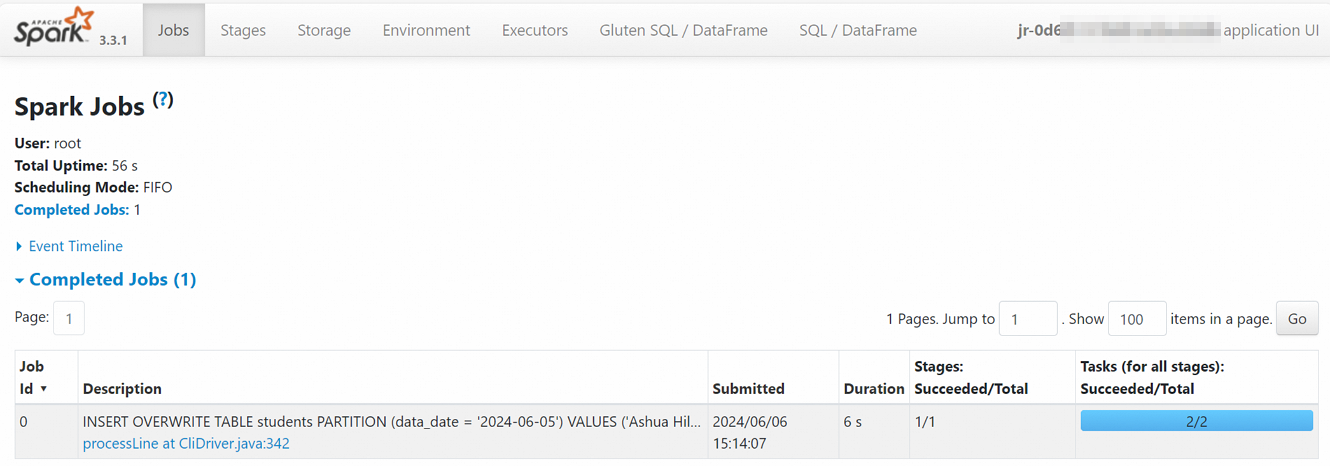
Click the Name to open the Job History page. On this page, you can view metrics, diagnostics, and logs.

Step 5: Workflow O&M
On the Workflows page, click the name of the target workflow to open the Workflow Runs page. You can:
In the Workflow Information section, you can edit some parameters.
The Workflow Runs section lists all workflow instances. Click a Workflow Run ID to open the corresponding workflow instance graph.
Step 6: View data
In the left navigation pane, click Development.
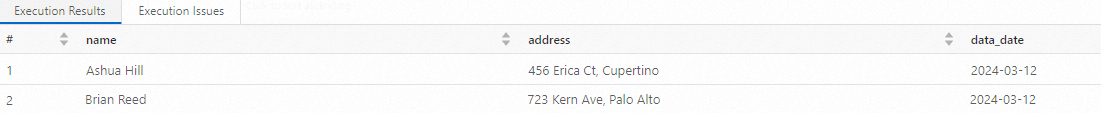
Create a SparkSQL development job. Then, enter and run the following command to view the table details:
SELECT * FROM students;The following information is returned:
References
For more information about how to create a resource queue, see Manage resource queues.
For more information about how to create an SQL session, see Manage SQL sessions.