If a catastrophic event occurs on your Elasticsearch cluster, such as a service interruption caused by a hardware failure, software error, data center failure, or natural disaster, you can use the cross-cluster replication (CCR) feature to implement cross-region or cross-resource disaster recovery. This topic describes how to implement CCR in both new and original network architectures.
Background information
CCR is a commercial feature released in open source Elasticsearch of the Platinum edition. After you purchase an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster and make a few simple configurations, you can use this feature free of charge.
You can use CCR in disaster recovery scenarios to back up data among Elasticsearch clusters that reside in the same virtual private cloud (VPC) but different zones. If a cluster (remote cluster) fails, you can retrieve its data from another cluster (local cluster) and restore the data to the remote cluster. This feature helps prevent data loss.
To use CCR, you must prepare two types of clusters: local clusters and remote clusters. Remote clusters provide source data, which is stored in leader indexes. Local clusters replicate the data and store it in follower indexes. You can also use CCR to migrate large volumes of data at a time. For more information, see Cross-cluster replication.
Scenarios
Choose a solution based on your business scenario:
Environment | Solution |
Two Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters are deployed in the new network architecture. Note Only Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters of V7.7 or later are supported. | |
Two Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters are deployed in the original network architecture and reside in the same VPC. Note Only single-zone Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters of V6.7.0 or later are supported. |
The preceding use scenarios are also applicable to the cross-cluster search (CCS) feature. For more information, see modules-cross-cluster-search.
The CCR feature cannot be used to back up data between an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster and a self-managed Elasticsearch cluster.
Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters created before October 2020 are deployed in the original network architecture. Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters created in October 2020 or later are deployed in the new network architecture.
Use NLB and PrivateLink to implement CCR
Preparations
Create two Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters of V7.7 or later in the same region and zone.
NoteThe two clusters are used in the following way:
One is used as a remote cluster and provides source data.
The other is used as a local cluster and replicates data from one or more indexes in the remote cluster.
Establish a private connection between the two clusters. For more information, see Use NLB and PrivateLink to establish a private connection between Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters.
NoteAdd the private IP address of the remote cluster to a Network Load Balancer (NLB) server group to establish a private connection between the two clusters.
Create indexes (leader indexes) in the remote cluster.
Log on to the Kibana console of the remote cluster. For more information, see Log on to the Kibana console.
On the page that appears, click the
 icon in the upper-left corner and choose Management > Dev Tools).
icon in the upper-left corner and choose Management > Dev Tools).Run the following command to create a leader index in the remote cluster:
PUT /leader-new { "settings": { "number_of_shards": 1, "number_of_replicas": 0 }, "mappings": { "properties": { "name": { "type": "text" }, "age": { "type": "integer" } } } }
Scenario 1: Implement CCR for a specific index
Step 1: Connect the remote cluster to the local cluster
Log on to the Kibana console of the local cluster. For more information, see Log on to the Kibana console.
On the page that appears, click the
 icon in the upper-left corner and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner and choose .In the left-side navigation pane of the Management page, click Remote Clusters.
Click Add A Remote Cluster.
On the page that appears, specify information about the remote cluster.
Name: the name of the remote cluster. The name must be unique.
Connection Mode: Turn on Use Proxy Mode.
Proxy Address: the address of the proxy server. The address must be in the
Endpoint domain name:9300format. The endpoint domain name is the domain name of the endpoint that corresponds to your PrivateLink endpoint service.NoteDuring CCR, Kibana uses the IP addresses of data nodes to access clusters over TCP port 9300. HTTP port 9200 is not supported.
Click Save.
After saving, the system automatically connects to the Leader cluster. After the connection is successful, the connection status displays Connected (Connected).
API usage examples
PUT /_cluster/settings
{
"persistent": {
"cluster": {
"remote": {
"<remote_cluster>": {
"mode": "PROXY",
"proxy_address": "Endpoint domain name:9300"
}
}
}
}
}Parameter | Description |
persistent | Specifies that settings are permanently stored even if the clusters are restarted. |
<remote_cluster> | Replace it with the name of the remote cluster. |
mode | Only the proxy mode is supported. The local cluster uses the configured proxy address to access the remote cluster. All requests to the remote cluster are sent to this proxy address and forwarded by the proxy server to the appropriate node in the remote cluster. |
proxy_address | The address of the proxy server. The address must be in the Note In this example, CCR or CCS uses the transport layer of Elasticsearch and needs to use port 9300 for communication. |
Step 2: Configure CCR
Go to the Management page in the Kibana console of the local cluster. In the left-side navigation pane, click Cross-Cluster Replication.
Click Create A Follower Index.
Configure CCR.
Parameter
Description
Remote Cluster
The remote cluster that is connected to the local cluster.
Leader Index
The index that will be migrated.
Follower Index
The index to which you want to back up data. You must specify a unique index name.
Click Create.
After the follower index is created, the index is in the Active state.
API usage examples
When you create a follower index, you must reference the remote cluster and the leader index created in the remote cluster.
The code in this topic is for reference only. When you use the code, replace the cluster and index names with your own.
# Example: leader-new-copy is the name of the follower index created in the local cluster to receive data replicated from the leader index in the remote cluster.
PUT /leader-new-copy/_ccr/follow
{
"remote_cluster": "es-leader",
"leader_index": "leader-old"
}Parameter | Description |
remote_cluster | The name of the remote cluster that is connected to the local cluster. This parameter corresponds to the |
leader_index | The name of the leader index. This parameter controls which index in the remote cluster is used to replicate data. |
Step 3: Verify the data backup result
In the Kibana console of the remote cluster, run the following command to insert data into the leader index:
POST leader-new/_doc/ { "name":"Jack", "age":40 }In the Kibana console of the local cluster, run the following command to check whether the inserted data is backed up to the follower index:
GET leader-new-copy/_searchThe result shown in the following figure is returned. The result shows that data in the leader index leader-new of the remote cluster is backed up to the follower index leader-new-copy of the local cluster.
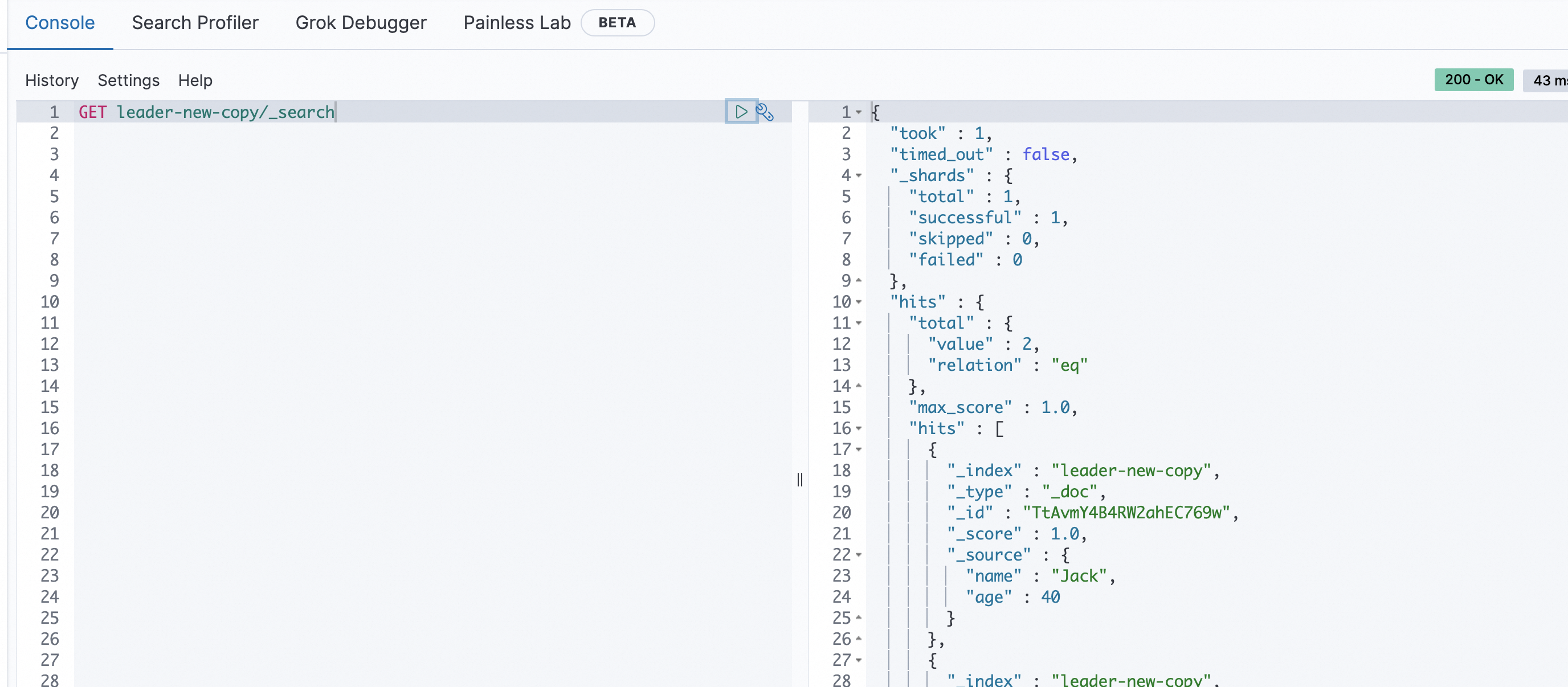
Insert a document into the leader index.
POST leader-new/_doc/ { "name":"Pony", "age":50 }Run the following command on the local cluster to check whether incremental data can be backed up to the follower index in real time:
GET leader-new-copy/_searchThe command output shows that the incremental data is backed up to the follower index.
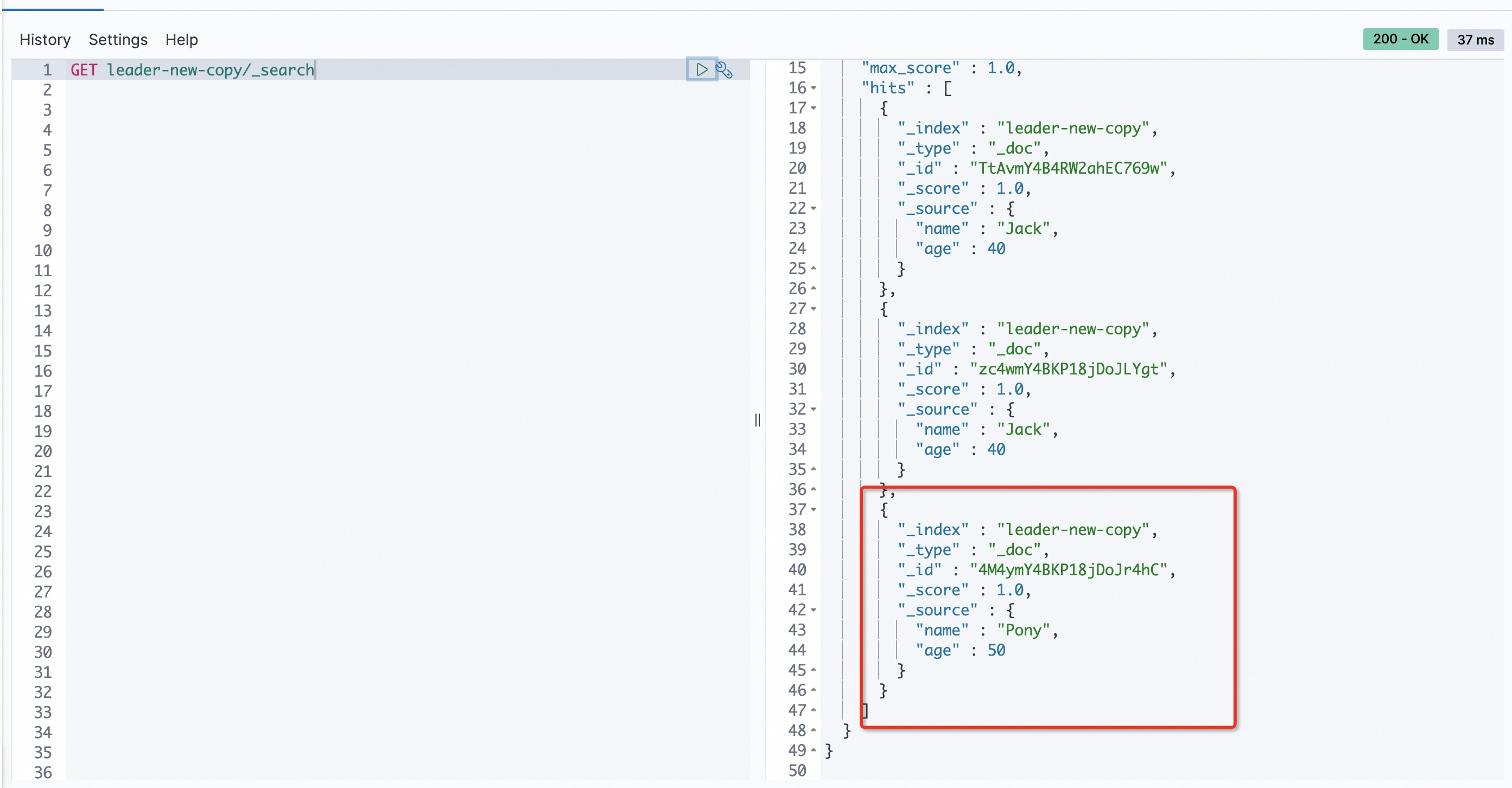
Scenario 2: Specify an index pattern to implement CCR for multiple indexes
Step 1: Connect the remote cluster to the local cluster
Log on to the Kibana console of the local cluster. For more information, see Log on to the Kibana console.
On the page that appears, click the
 icon in the upper-left corner and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner and choose .In the left-side navigation pane of the Management page, click Remote Clusters.
Click Add A Remote Cluster.
On the page that appears, specify information about the remote cluster.
Name: the name of the remote cluster. The name must be unique.
Connection Mode: Turn on Use Proxy Mode.
Proxy Address: the address of the proxy server. The address must be in the
Endpoint domain name:9300format. The endpoint domain name is the domain name of the endpoint that corresponds to your PrivateLink endpoint service.NoteDuring CCR, Kibana uses the IP addresses of data nodes to access clusters over TCP port 9300. HTTP port 9200 is not supported.
Click Save.
After saving, the system automatically connects to the Leader cluster. After the connection is successful, the connection status displays Connected (Connected).
API usage examples
PUT /_cluster/settings
{
"persistent": {
"cluster": {
"remote": {
"<remote_cluster>": {
"mode": "PROXY",
"proxy_address": "Endpoint domain name:9300"
}
}
}
}
}Parameter | Description |
persistent | Specifies that settings are permanently stored even if the clusters are restarted. |
<remote_cluster> | Replace it with the name of the remote cluster. |
mode | Only the proxy mode is supported. The local cluster uses the configured proxy address to access the remote cluster. All requests to the remote cluster are sent to this proxy address and forwarded by the proxy server to the appropriate node in the remote cluster. |
proxy_address | The address of the proxy server. The address must be in the Note In this example, CCR or CCS uses the transport layer of Elasticsearch and needs to use port 9300 for communication. |
Step 2: Configure CCR
Go to the Management page in the Kibana console of the local cluster. In the left-side navigation pane, click Cross-Cluster Replication.
Click Auto-follow Patterns.
Click Create Auto-follow Pattern.
Configure CCR. The following table describes the key parameters.
Parameter
Description
Remote Cluster
The remote cluster that is connected to the local cluster.
Index Patterns
The pattern of indexes whose data you want to back up.
NoteAn index pattern is a rule or template used to match a set of index names (for example, leader-*). These patterns are typically defined using wildcards or regular expressions. Indexes that match the pattern will be automatically replicated to the local cluster.
API usage examples
PUT /_ccr/auto_follow/beats
{
"remote_cluster": "es-leader",
"leader_index_patterns":
[
"leader-*"
],
"follow_index_pattern": "{{leader_index}}-copy"
}Parameter | Description |
remote_cluster | The name of the remote cluster that is connected to the local cluster. This parameter corresponds to the |
leader_index_patterns | The index pattern, which is a rule or template used to match a set of index names, to determine which indexes in the remote cluster need to be replicated. |
follow_index_pattern | The pattern of indexes to be created in the local cluster. The system creates indexes in the local cluster based on the pattern and backs up data to the indexes. |
Step 3: Verify the data backup result
In the Kibana console of the remote cluster, run the following command to add an index:
PUT /leader-new { "settings": { "number_of_shards": 1, "number_of_replicas": 0 }, "mappings": { "properties": { "name": { "type": "text" }, "age": { "type": "integer" } } } }In the Kibana console of the local cluster, run the following command to check whether data in the added index is backed up to the local cluster:
get _cat/indices?v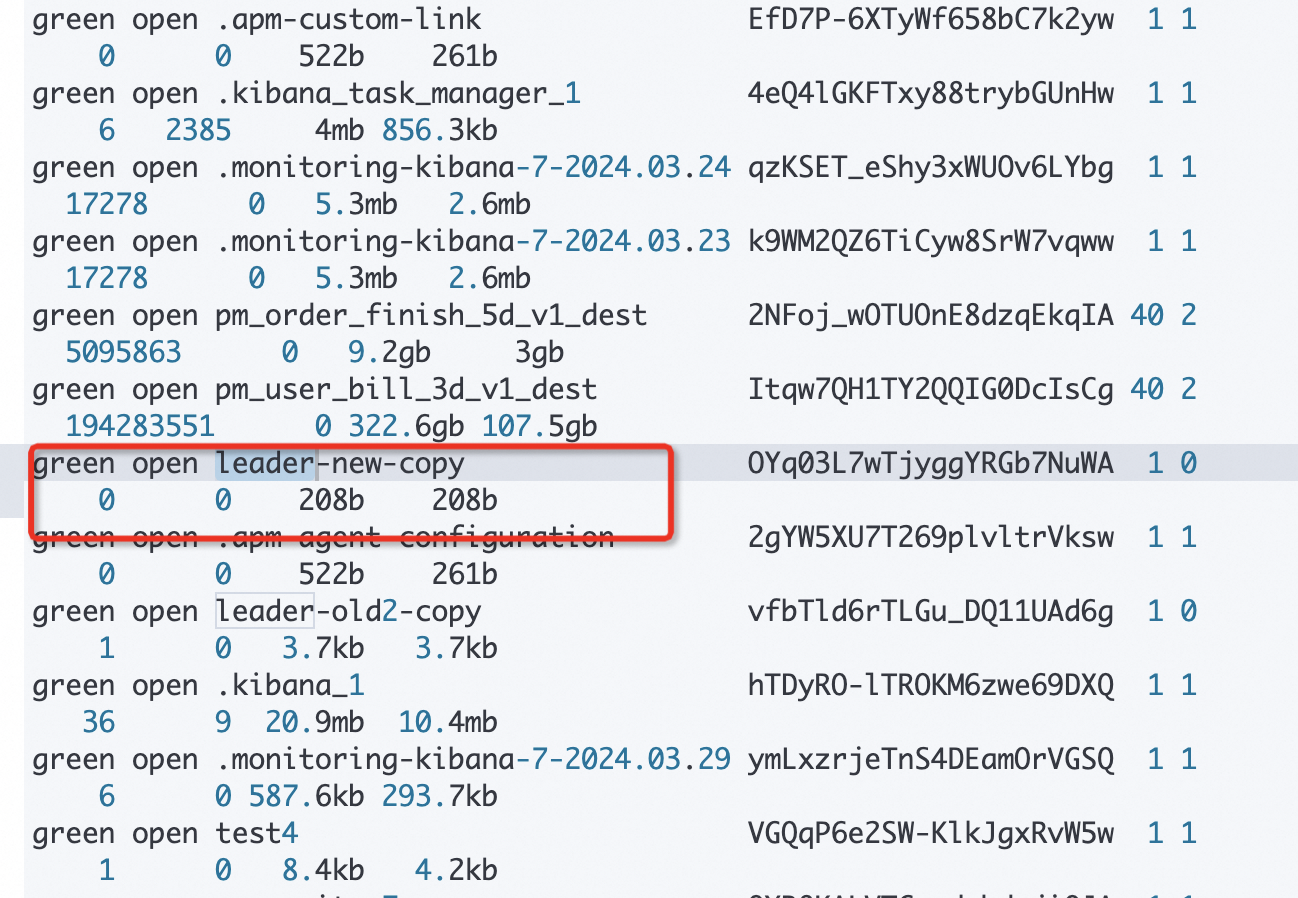
Connect Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters to enable CCR
Preparations
Create two Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters of the same version (6.7 or later). Make sure that the two clusters are deployed in the same VPC and belong to the same vSwitch.
NoteThe two clusters are used in the following way:
One is used as a remote cluster and provides source data.
The other is used as a local cluster and replicates data from one or more indexes in the remote cluster.
If you have uploaded a synonym file to the remote cluster, you must upload the synonym file to the local cluster.
Configure the remote cluster to connect it to the local cluster. For more information, see Connect Elasticsearch clusters to enable cross-cluster searches.
Create indexes (leader indexes) in the remote cluster.
Log on to the Kibana console of the remote cluster. For more information, see Log on to the Kibana console.
On the page that appears, click the
 icon in the upper-left corner and choose Management > Dev Tools).
icon in the upper-left corner and choose Management > Dev Tools).Run the following command to create a leader index in the remote cluster:
PUT myindex { "settings": { "index.soft_deletes.retention.operations": 1024, "index.soft_deletes.enabled": true } }NoteIf you create an index in an Elasticsearch cluster of V7.0 or earlier, you must enable the soft_deletes attribute for the index. Otherwise, an error is reported. You can run the
GET /<yourIndexName>/_settings?prettycommand to check whether the soft_deletes attribute is enabled. If the soft_deletes attribute is enabled, the configuration of the soft_deletes attribute is displayed in the command output.If you want to back up data in an existing index, you can call the reindex API to enable the soft_deletes attribute.
Disable the physical replication feature for the leader index.
NoteThe physical replication feature is automatically enabled for indexes in Elasticsearch V6.7.0 clusters. Before you use CCR, you must disable the physical replication feature.
Disable the index.
POST myindex/_closeUpdate the settings configuration of the index to disable the physical replication feature.
PUT myindex/_settings { "index.replication.type" : null }Enable the index.
POST myindex/_open
Step 1: Connect the remote cluster to the local cluster
Log on to the Kibana console of the local cluster. For more information, see Log on to the Kibana console.
On the page that appears, click the
 icon in the upper-left corner and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner and choose .In the left-side navigation pane of the Management page, click Remote Clusters.
Click Add A Remote Cluster.
On the page that appears, specify information about the remote cluster.
Name: the name of the remote cluster. The name must be unique.
Proxy Address: The address must be in the
IP address of a node in the remote cluster:9300format. To obtain the IP addresses of nodes, log on to the Kibana console of the remote cluster and run theGET /_cat/nodes?vcommand on the Console tab of the Dev Tools page. The nodes you specify must include a dedicated master node of the remote cluster. We recommend that you specify multiple nodes. This ensures that you can still use CCR if the specified dedicated master node fails.NoteDuring CCR, Kibana uses the IP addresses of data nodes to access clusters over TCP port 9300. HTTP port 9200 is not supported.
Click Save.
After you save the settings, the system automatically connects to the remote cluster. When the connection is successful, the connection status displays Connected (Connected).
Step 2: Configure CCR
Go to the Management page in the Kibana console of the local cluster. In the left-side navigation pane, click Cross-Cluster Replication.
Click Create A Follower Index.
Configure CCR.
Parameter
Description
Remote cluster
The remote cluster that is connected to the local cluster.
Leader index
The index whose data you want to back up. In this example, the myindex index that is created in Preparations is used.
Follower index
The index to which you want to back up data. You must specify a unique index name.
Click Create.
After the follower index is created, the index is in the Active state.
Step 3: Verify the data backup result
In the Kibana console of the remote cluster, run the following command to insert data into the remote cluster:
POST myindex/_doc/ { "name":"Jack", "age":40 }In the Kibana console of the local cluster, run the following command to check whether the inserted data is backed up to the local cluster:
GET myindex_follow/_searchThe result shown in the following figure is returned. The result shows that data in the leader index myindex of the remote cluster is backed up to the follower index myindex_follow of the local cluster.
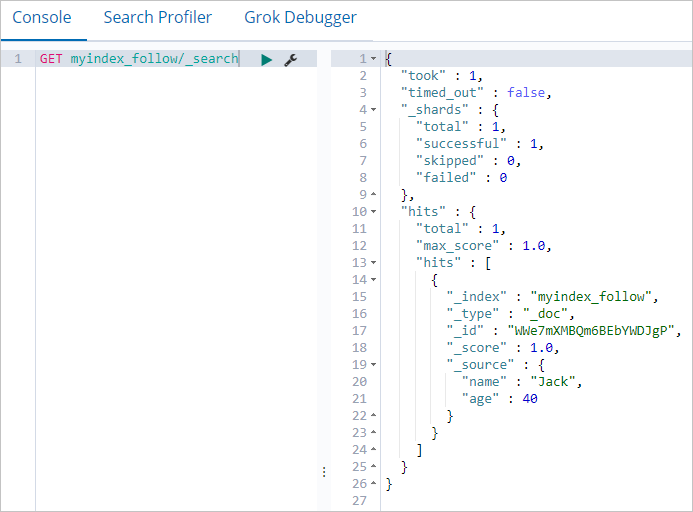 Note
NoteThe follower index myindex_follow is read-only. If you want to write data to the follower index, convert the follower index into a common index first. For more information, see Use Elasticsearch CCR to migrate data across data centers.
In the remote cluster, insert a new data record to verify if the incremental data is synchronized.
POST myindex/_doc/ { "name":"Pony", "age":50 }Query the inserted document in the local cluster. The following figure shows the document.
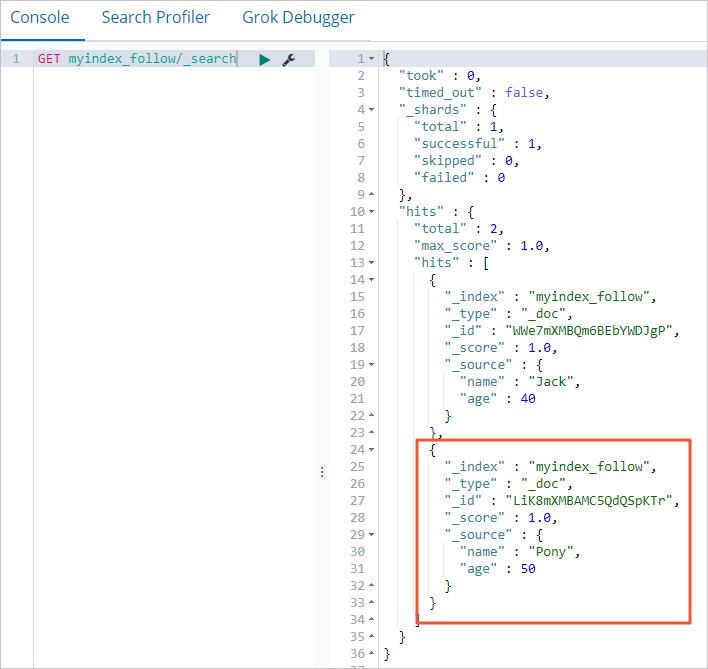
The preceding figure shows that the CCR feature can implement backup of incremental data.
NoteYou can also call the APIs for the CCR feature to perform cross-cluster replication operations. For more information, see Cross-cluster replication APIs.
FAQ
Q: I can use port 9300 to add a remote cluster. Why is only port 9200 accessible when I use a domain name to access an Elasticsearch cluster?
A: Port 9300 is an open port. However, when you access a cluster over the Internet, Server Load Balancer (SLB) enables only port 9200 during port verification for security purposes.
Q: How do I view the status of CCR-based data synchronization?
A: Run the
GET /_ccr/statscommand in the Kibana console of the cluster that stores the follower index and view the value of thenumber_of_failed_follow_indicesparameter. This parameter indicates the number of failed shards.If the value of the parameter is 0, the synchronization is normal.
If the value of the parameter is not 0, run the following commands for the cluster that stores the follower index to pause and then resume the synchronization:
POST /<follower_index>/_ccr/pause_follow POST /<follower_index>/_ccr/resume_follow