Alibaba Cloud Enterprise SSDs (ESSDs) use 25 Gigabit Ethernet and Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) technologies to deliver up to 1,000,000 random read/write IOPS per disk and reduce one-way latency. This topic describes how to test the IOPS performance of a raw ESSD based on the test conditions that are described in the following section.
Test conditions
Test tool: Use flexible I/O tester (fio).
Notefio is an open source, powerful I/O performance benchmarking tool that can test the performance metrics of block storage devices, such as random read and write operations and sequential read and write operations.
Instance type: We recommend that you use the ecs.g7se.32xlarge instance type. For information about the instance type, see General-purpose instance families (g series).
Image: Use a later version of a Linux public image provided by Alibaba Cloud. In the following examples, Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 is used.
NoteTest results show that ESSDs may not achieve the expected IOPS performance in specific Linux distribution images. We recommend that you attach ESSDs to Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances that use Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 images.
ESSD:
Tests on raw disks help you obtain real disk performance. We recommend that you use the fio tool to test the IOPS performance of a raw disk.
We recommend that you use an ESSD at performance level 3 (PL3 ESSD). For more information about ESSDs, see ESSDs.
ImportantTests on raw disks help you obtain real block storage performance. If a block storage device contains partitions, file systems, and data, direct use of the fio tool may cause exceptions on the file systems and result in data loss. To prevent the preceding issues, we recommend that you create snapshots for the block storage devices that you want to test to back up disk data before you use the fio tool to test the devices. For more information, see Create a snapshot.
To prevent data loss, we recommend that you do not use the system disk on which the operating system resides or a data disk that contains data as the test object. We recommend that you use the fio tool to test the performance of new empty data disks.
Performance test results are obtained in a test environment and are only for reference. In a production environment, the performance of cloud disks may vary due to factors such as the network environment and concurrency access.
Procedure
Connect to an ECS instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
Query the names of block storage devices:
sudo fdisk -lu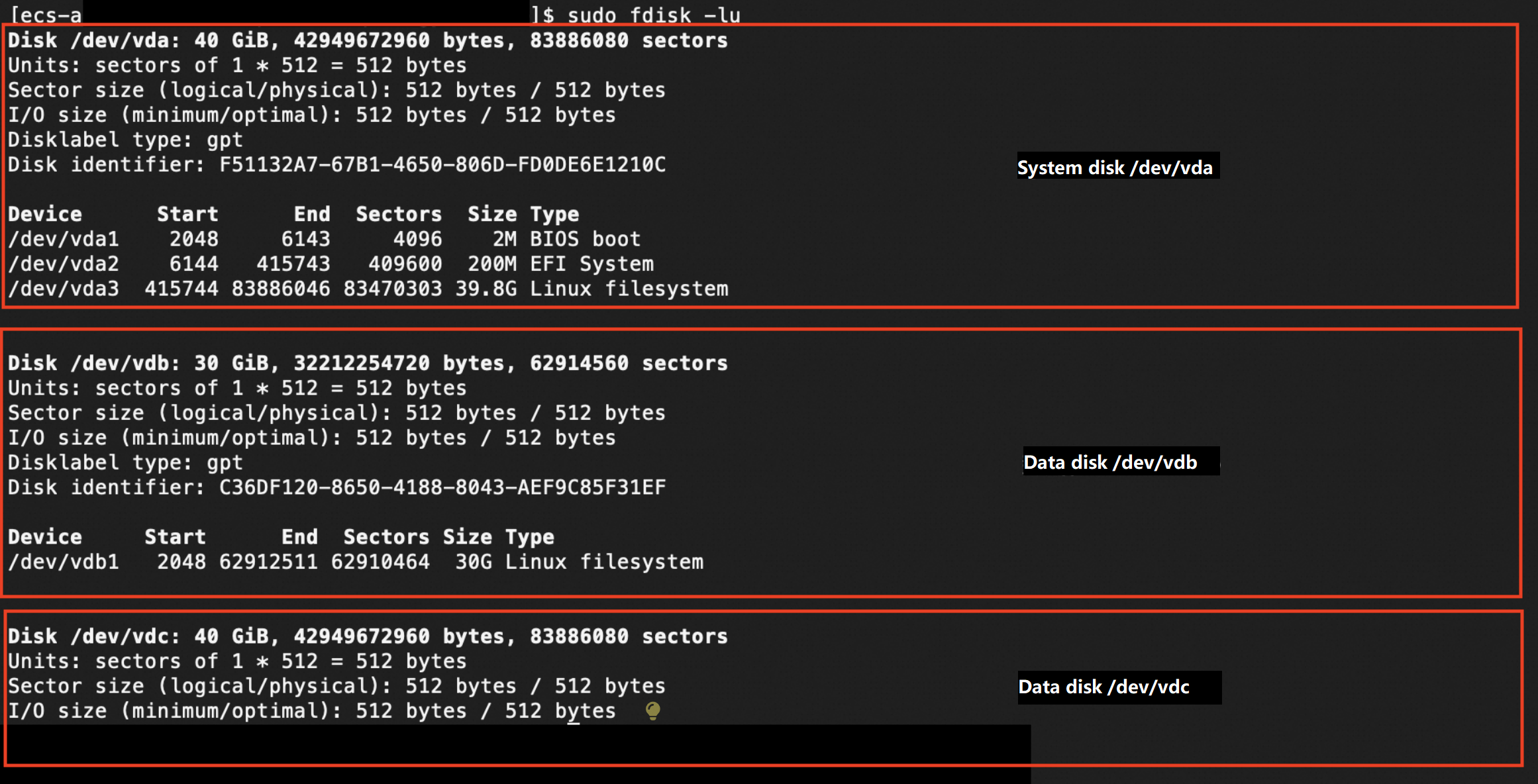 The preceding figure shows that the instance has three block storage devices: the system disk named /dev/vda and two data disks named /dev/vdb and /dev/vdc.
The preceding figure shows that the instance has three block storage devices: the system disk named /dev/vda and two data disks named /dev/vdb and /dev/vdc. Query whether partitions and file systems exist on the block storage devices:
sudo blkid The preceding figure shows that the block storage devices named /dev/vda and /dev/vdb have partitions and file systems. The command output does not contain information about the block storage device named /dev/vdc, which indicates that the block storage device does not have partitions or file systems.
The preceding figure shows that the block storage devices named /dev/vda and /dev/vdb have partitions and file systems. The command output does not contain information about the block storage device named /dev/vdc, which indicates that the block storage device does not have partitions or file systems.
Before you test the performance of the block storage devices, make sure that you back up the data that is stored on the devices to prevent data loss. For more information, see Create a snapshot.
NoteYou are charged for snapshots. For information about the billing of snapshots, see Snapshots.
Install the libaio library and the fio tool based on your operating system.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2, Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, or CentOS 6 or later
NoteCentOS 6 reached end of life (EOL). In accordance with Linux community rules, all content was removed from the following CentOS 6 repository address: http://mirror.centos.org/centos-6/. If you continue to use the default CentOS 6 repository on Alibaba Cloud, an error is reported. To use specific installation packages of CentOS 6, change the CentOS 6 repository address. For more information, see How do I change CentOS 6 repository addresses?
sudo yum install libaio libaio-devel fio -yDebian 9 or later, or Ubuntu 14 or later
ImportantDebian 9 and Debian 10 reached their EOL. If your instance runs Debian 9 or Debian 10, change the repository addresses of the operating system. For more information, see How do I change Debian 9 or Debian 10 repository addresses?
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install libaio* fio -yChange the path:
cd /tmpCreate the test100w.sh script:
sudo vim test100w.shPaste the following content to the test100w.sh script.
For more information, see the Details of the test100w.sh script section of this topic.
#!/bin/bash DEV_NODE=your_device DEV_NAME=/dev/$DEV_NODE function CheckHasFS { local device=$1 # The device path. # Check whether the device exists. if [ ! -b "$device" ]; then echo "Error: The $device device does not exist." exit 1 fi # Run the blkid command to check the partition table and file system type. local pt_type=$(sudo blkid -o value -s PTTYPE "$device") local fs_type=$(sudo blkid -o value -s TYPE "$device") if [ -n "$pt_type" ] || [ -n "$fs_type" ]; then return 1 else return 0 fi } CheckHasFS "$DEV_NAME" if [ $? -eq 1 ]; then echo "The $DEV_NAME device contains a partition table or a file system. The fio script is stopped." exit 1 fi function RunFio { numjobs=$1 # The number of test threads. In this example, the value is 10. iodepth=$2 # The maximum number of concurrent I/O requests. In this example, the value is 64. bs=$3 # The data block size per I/O. In this example, the value is 4k. rw=$4 # The read and write policy. In this example, the value is randwrite. size=$5 filename=$6 # The name of the test file. In this example, the value is /dev/your_device. nr_cpus=`cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep "processor" |wc -l` if [ $nr_cpus -lt $numjobs ];then echo "The value of the numjobs parameter is greater than the number of CPU cores. The test is stopped." exit -1 fi let nu=$numjobs+1 cpulist="" for ((i=1;i<10;i++)) do list=`cat /sys/block/$DEV_NODE/mq/*/cpu_list | awk '{if(i<=NF) print $i;}' i="$i" | tr -d ',' | tr '\n' ','` if [ -z $list ];then break fi cpulist=${cpulist}${list} done spincpu=`echo $cpulist | cut -d ',' -f 2-${nu}` echo $spincpu fio --ioengine=libaio --runtime=30s --numjobs=${numjobs} --iodepth=${iodepth} --bs=${bs} --size=${size} --rw=${rw} --filename=${filename} --time_based=1 --direct=1 --name=test --group_reporting --cpus_allowed=$spincpu --cpus_allowed_policy=split } echo 2 > /sys/block/$DEV_NODE/queue/rq_affinity sleep 5 RunFio 10 128 4k randwrite 1024g $DEV_NAMEModify the parameters in the test100w.sh script based on your business scenario.
Replace
your_devicewith the actual device name of the device that you want to test. Example: nvme1n1.Replace 10 (numjobs), 64 (iodepth), 4k (bs), randwrite (rw), and /dev/your_device in the
RunFio 10 64 4k randwrite /dev/your_deviceline with actual values.The value of the numjobs parameter cannot exceed the number of CPU cores. You can run the following command to query the number of CPU cores:
cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep "processor" |wc -l
Test the performance of the ESSD:
sudo sh test100w.shThe following figure shows the sample command output, in which the
IOPS=***parameter indicates the IOPS of the ESSD.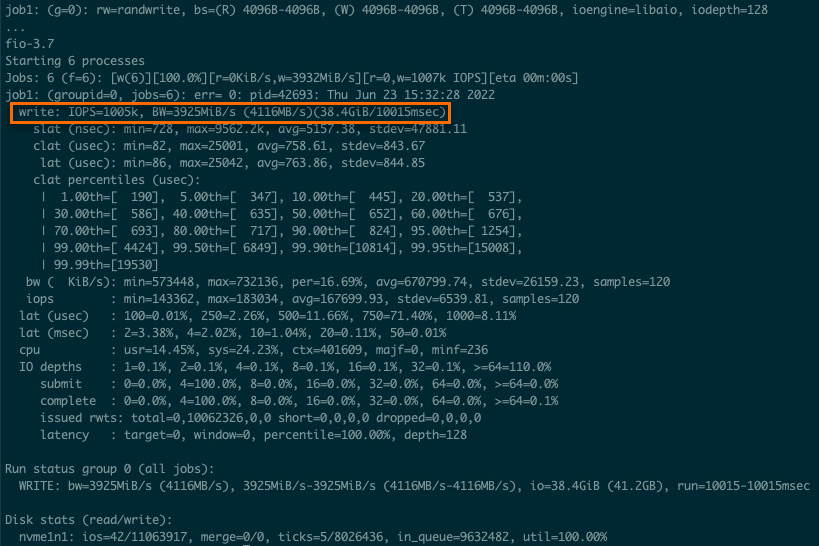
If the result shown in the following sample code is returned, the test object contains partitions or file systems. To ensure data security, the fio script is stopped. We recommend that you create an empty data disk to conduct the test.
[[ecs-user@ecs tmp]$ sudo sh test100w.sh The /dev/vdb device contains a partition table or a file system. The fio script is stopped.WarningIf the test object contains partitions, file systems, and data, direct use of the fio tool may cause exceptions on the file systems and result in data loss. If your data disk has partitions and file systems, we recommend that you create an empty data disk and test the new disk.
You can create a pay-as-you-go disk that has the same specifications as your data disk and attach the new disk to your instance for testing. For more information, see Create an empty data disk.
After the test is completed, you can detach and release the pay-as-you-go disk based on your business requirements. For more information, see Detach a data disk and Release a disk.
Details of the test100w.sh script
In the test100w.sh script, the following command sets the
rq_affinityparameter to 2:echo 2 > /sys/block/your_device/queue/rq_affinityValue of rq_affinity
Description
1
Indicates that the block device delivers received I/O completion events to the group of the vCPUs that submit the corresponding I/O requests. In scenarios where multiple threads concurrently run, I/O completion events may be delivered only to one vCPU and cause a performance bottleneck.
2
Indicates that the block device delivers received I/O completion events to the vCPUs that submit the corresponding I/O requests. In scenarios where multiple threads concurrently run, each vCPU can deliver its maximum performance.
The following command runs
jobsto bind queues to different CPU cores:fio -ioengine=libaio -runtime=30s -numjobs=${numjobs} -iodepth=${iodepth} -bs=${bs} -rw=${rw} -filename=${filename} -time_based=1 -direct=1 -name=test -group_reporting -cpus_allowed=$spincpu -cpus_allowed_policy=splitNoteIn normal mode, a device has a single request queue. The request queue becomes a performance bottleneck when multiple threads concurrently process I/O requests. In multi-queue mode, a device can have multiple request queues to process I/O requests and deliver the maximum backend storage performance. For example, assume that you have four I/O threads. To make full use of multi-queue mode and improve storage performance, you must bind the I/O threads to the CPU cores that correspond to different request queues.
Parameter
Description
Example value
numjobsThe number of I/O threads.
10
/dev/your_deviceThe device name of the ESSD.
/dev/nvme1n1
cpus_allowed_policyThe parameter provided by the fio tool to bind vCPUs. The fio tool provides the
cpus_allowed_policyandcpus_allowedparameters to bind vCPUs.split
The preceding command runs
jobsto bind queues that have different queue IDs to different CPU cores. To view the ID of the CPU core to which a queue is bound, run the following commands:Run the
ls /sys/block/your_device/mq/command. In the command, replace theyour_deviceparameter with the actual device name. Example: nvme1n1. The command returns the ID of the queue for an ESSD whose device name is in the /dev/vd* format.Run the cat /sys/block/your_device/mq/cpu_list command. In the command, replace the
your_deviceparameter with the actual device name. Example: nvme1n1. The command returns the ID of the CPU core to which the queue for an ESSD is bound. The device name of the ESSD is in the /dev/vd* format.