This document describes the cost components and billing methods for Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance types.
Cost components
The cost of an instance type includes charges for its compute resources (vCPUs, memory, and GPUs), local disks (storage devices that cannot be detached from the instance), and components for enhanced instance types.
Billing methods
Instance types support three billing methods: subscription, pay-as-you-go, and spot instance.
Billing method | |||
Features | A prepaid model where you pay upfront for one or more months to receive a discount. | A postpaid, per-second billing model. You can create and release instances at any time. The unit price is higher than that of the Subscription model. | A postpaid model where the price fluctuates with market supply and demand, with discounts of up to 90% off the pay-as-you-go price. The system automatically reclaims the instance if the market price exceeds your bid or when computing resources are scarce. |
Scenarios |
|
| Interruption-insensitive workloads, such as tasks that can be resumed from a checkpoint, including movie rendering, scientific computing, and big data analytics. |
Billing formula The unit price of an instance type varies by region. For details, see the ECS pricing page. | Instance type unit price × Billing duration. | Instance type unit price × Billing duration. Important For the pay-as-you-go billing method, a minimum billing duration applies during the instance's final billing cycle:
For more information, see Minimum billing duration examples. |
The cost of a spot instance fluctuates with market prices. You can refer to the Billing example to estimate the actual cost. |
Billing duration | Purchase duration. | Billing starts when the instance is created and ends when it is released. Usage is measured per second. Billing for the instance type continues even if the instance is stopped. To stop billing without releasing the instance, you can enable economical mode. | Billing starts when the instance is created and ends when it is released. Usage is measured per second. |
Billing example
The following example shows how to calculate the cost for an ecs.g7.large instance created in the Singapore region.
The prices in this example are for reference only. For current pricing, see the Elastic Compute Service pricing page. This example covers only the cost of the instance type and does not include costs for Images, Elastic Block Storage, public bandwidth, or Snapshots.
Billing method | Billing conditions | Calculation | Total cost (USD) |
Subscription | The Subscription price for an ecs.g7.large instance is | 69.21 USD/month × 1 month | 69.21 |
Pay-as-you-go | The pay-as-you-go price for an ecs.g7.large instance is | 0.1188 USD/hour × 24 hours/day × 30 days | 85.536 |
Minimum billing duration examples
For pay-as-you-go instances, Alibaba Cloud generates a billable item for each one-hour billing cycle (for example, from 00:00:00 on January 1, 2025, to 01:00:00 on January 1, 2025). During the cycle in which an instance is released, if its actual usage is less than the minimum billing duration, it is billed for the minimum duration.
Example scenario | Instance creation and release time | Pay-as-you-go billing duration |
Create and release an instance within the same billing cycle | Created: 00:01:00 on January 1, 2025 Released: 00:02:00 on January 1, 2025 | The actual usage duration is shorter than the minimum billing duration, so the instance is billed for the minimum billing duration as follows:
|
Create and release an instance across billing cycles | Created: 00:59:00 on January 1, 2025 Released: 02:00:20 on January 1, 2025 |
|
Switch billing methods
You can switch the billing method for instances between Subscription and pay-as-you-go. Spot instances do not support switching billing methods. Switching the billing method may result in a refund. For more information, see Switch from subscription to pay-as-you-go and Switch from pay-as-you-go to subscription.
Cost optimization
To optimize your instance type costs, you can switch billing methods or use one of the following strategies:
Release or unsubscribe from an instance
If a Subscription instance is no longer needed, you can request to unsubscribe from it. Alibaba Cloud reclaims the resources and issues a refund based on the unsubscribe rules. For information about the resource release time and refund rules, see Unsubscribe rules.
If a pay-as-you-go or spot instance is no longer needed, you can manually release the instance. After release, billing for the instance type stops. For instructions on how to release an instance, see Release an instance.
Note: Data on a released instance is permanently deleted and cannot be recovered. If you need to save the data, create a snapshot to back it up before you release the instance. This action incurs snapshot costs. For instructions, see Create a snapshot.
Stop instances in economical mode
Only pay-as-you-go instances and spot instances support economical mode.
Normally, you are still charged for the instance type when a pay-as-you-go instance is stopped. After you enable economical mode, billing for the instance type and image license fees stops. However, you are still charged for other resources such as Elastic Block Storage (System Disk and Data Disk), Elastic IP Addresses, and Snapshots.
Downgrade the instance type configuration
If instance monitoring data shows your instance type is over-provisioned, you can downgrade its configuration to reduce costs.
For Subscription instances, you can downgrade the instance type by changing the instance type of a subscription instance or using the downgrade on renewal feature.
For pay-as-you-go instances, you can downgrade the instance type by changing the instance type of a pay-as-you-go instance.
Use discounts and savings
You can use the following discounts to reduce the cost of pay-as-you-go instances:
Savings Plan: Similar to a spending commitment, you commit to a certain amount of hourly spending (for example, 1 USD/hour) and pay for this commitment in advance to receive a discount. Savings Plans are flexible and apply to various instance types.
Reserved Instance: Similar to a membership card for a specific product, you purchase a voucher for a specific instance type (such as ecs.g8i) and operating system. This voucher then offsets the costs of eligible pay-as-you-go instances.
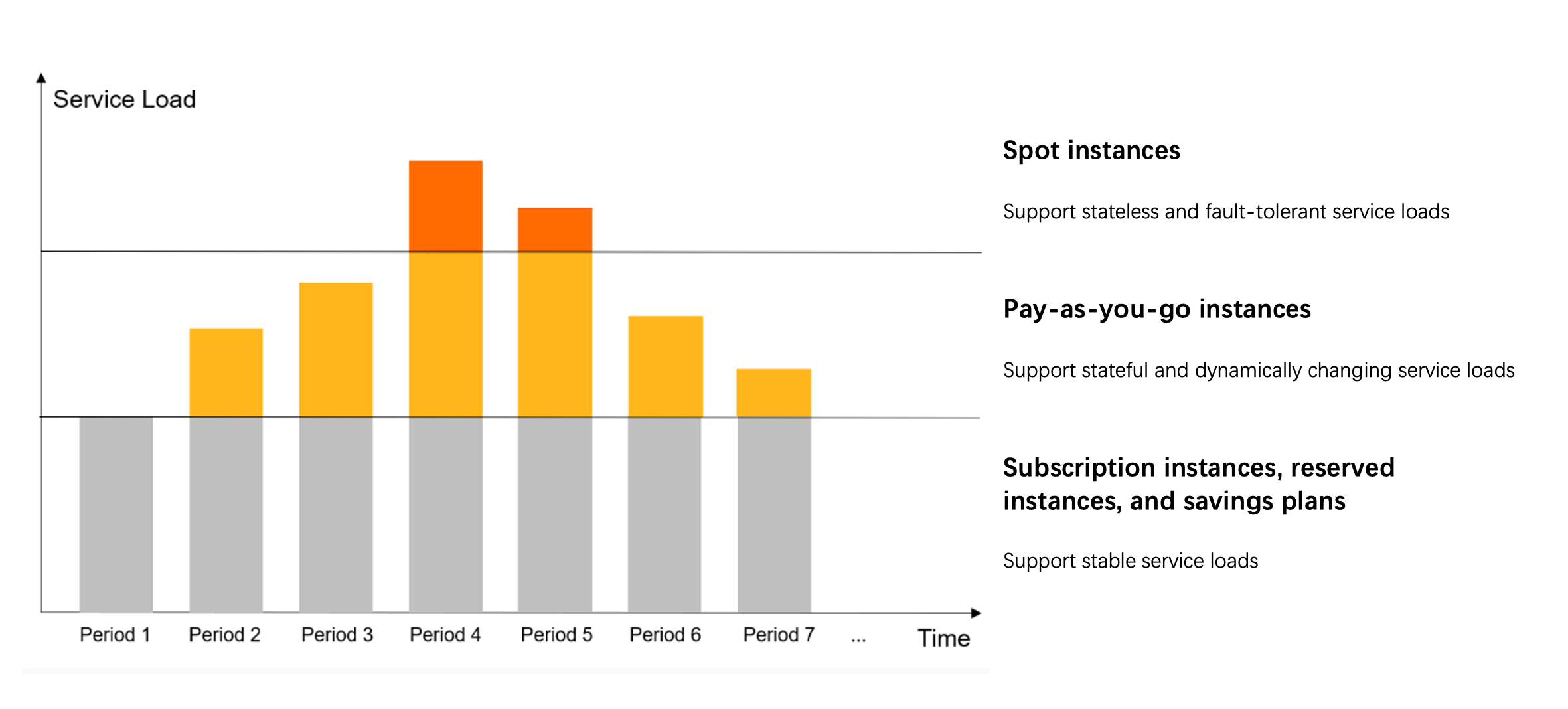
Combine billing methods
To optimize your instance costs, you can combine different billing methods when you have multiple ECS instances. The recommended combination of billing methods is shown in the following figure.
Query bills
To view your bills, you can follow the steps in Query bills. The billable item for an Instance type is named Cloud Server Configuration in the billing details.
FAQ
What costs are included in my total ECS bill besides the instance type fee?
The total cost of an ECS instance is not limited to the instance type fee. It also includes charges for other resources that are often required to run a server. You can review all billable items for an instance on the purchase page. Common additional costs include:
Elastic Block Storage: Charges for the system disk and any attached data disks. Note that the cost of a Local Disk is already bundled into the instance type fee.
Public bandwidth: If your instance needs to be accessible from the internet, you will be charged for outbound data transfer.
Image: Costs can vary based on the image you use, such as certain public images, stored custom images, or images from the Cloud Marketplace.
Additionally, if you configure an automatic snapshot policy or manually create snapshots for backup, you will incur snapshot costs.