Alibaba Cloud enterprise SSDs (ESSDs) use 25 Gigabit Ethernet and remote direct memory access (RDMA) to reduce latency and deliver up to 1,000,000 random read/write IOPS per disk. This topic provides general information about ESSDs, such as performance levels (PLs), use scenarios, and performance specifications.
Specifications
The API parameter value cloud_essd indicates ESSDs. ESSDs are classified into four PLs based on the maximum performance per disk.
ESSD attribute | Performance level | |||
PL3 | PL2 | PL1 | PL0 | |
Performance description | Ultra-high I/O performance and low I/O latency | High I/O performance and low I/O latency | Moderate I/O performance and relatively low I/O latency | Moderate I/O performance and relatively low I/O latency |
Capacity range (GiB) | 1,261 to 65,536 | 461 to 65,536 | 20 to 65,536 | 1 to 65,536 |
Data durability | 99.9999999% | 99.9999999% | 99.9999999% | 99.9999999% |
Maximum IOPS per disk | 1,000,000 | 100,000 | 50,000 | 10,000 |
Maximum throughput per disk (MB/s) | 4,000 | 750 | 350 | 180 |
Formula for calculating the IOPS per disk | min{1,800 + 50 × Capacity, 1,000,000} | min{1,800 + 50 × Capacity, 100,000} | min{1,800 + 50 × Capacity, 50,000} | min{1,800 + 12 × Capacity, 10,000} |
Formula for calculating the throughput per disk (MB/s) | min{120 + 0.5 × Capacity, 4,000} | min{120 + 0.5 × Capacity, 750} | min{120 + 0.5 × Capacity, 350} | min{100 + 0.25 × Capacity, 180} |
Example scenario | Large and medium-sized relational databases for core business and NoSQL databases, and large SAP and Oracle databases | Medium-sized relational databases and NoSQL databases, medium-sized Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana (ELK) log clusters, and enterprise-level commercial software such as SAP and Oracle | Small and medium-sized MySQL and SQL Server databases, small and medium-sized ELK log clusters, enterprise-level commercial software such as SAP and Oracle, and container applications | Small and medium-sized MySQL and SQL Server databases, small and medium-sized ELK log clusters, enterprise-level commercial software such as SAP and Oracle, and container applications |
Recommended system or data disks to be replaced with ESSDs in recommended business scenarios | Data disks of instance families that are equipped with local SSDs and have 16 or more vCPUs (i1, i2, and i2g) | Standard SSDs and data disks of instance families that are equipped with local SSDs (i1, i2, and i2g) | Standard SSDs | System disks |
For information about how to test the IOPS performance of an ESSD, see Test the IOPS performance of an ESSD.
Billing methods
ESSDs support the pay-as-you-go and subscription billing methods.
For information about the pricing of ESSDs at different PLs, see the Pricing tab on the Elastic Compute Service page.
Scenarios
ESSDs are suitable for the following latency-sensitive applications or I/O intensive business scenarios:
Large online transaction processing (OLTP) databases: relational databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server databases
NoSQL databases: non-relational databases such as MongoDB, HBase, and Cassandra databases
Elasticsearch distributed logs: ELK log analysis
Support for the NVMe protocol
You can attach ESSDs to Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances by using the Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) protocol and enable the multi-attach feature to allow an ESSD to be attached to multiple ECS instances. For more information, see NVMe disks and Multi-attach for cloud disks.
Capacity and PLs
The performance of a storage device is closely related to the capacity of the device. A storage device that has a larger capacity provides higher data processing capabilities. All ESSDs have the same I/O performance per unit of capacity. However, the overall performance of an ESSD increases linearly with its capacity until the maximum performance per disk at the PL is reached.
Performance level | ESSD capacity range (GiB) | Maximum IOPS | Maximum I/O throughput (MB/s) |
PL0 | 1 to 65,536 | 10,000 | 180 |
PL1 | 20 to 65,536 | 50,000 | 350 |
PL2 | 461 to 65,536 | 100,000 | 750 |
PL3 | 1,261 to 65,536 | 1,000,000 | 4,000 |
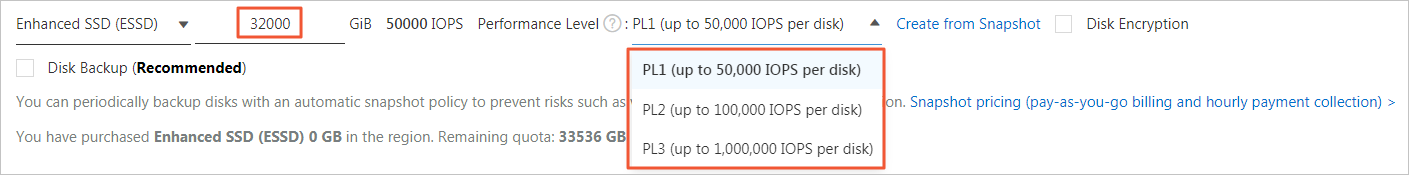
Example 1: If Alex selects 20 GiB as the disk capacity when Alex creates an ESSD in the ECS console, Alex can select PL0 or PL1 as the PL of the ESSD. A PL0 ESSD delivers up to 10,000 IOPS. A PL1 ESSD delivers up to 50,000 IOPS.

Example 2: If Alex selects 32,000 GiB of storage capacity when Alex creates an ESSD in the ECS console, all PLs are available. A maximum of 10,000 IOPS is delivered for PL0, 50,000 IOPS for PL1, 100,000 IOPS for PL2, and 1,000,000 IOPS for PL3.
Storage I/O performance of instance types
The storage I/O performance of instances of specific new-generation instance families is proportional to the specifications of the instance types. For example, in the g7se storage-enhanced instance family, a higher-specification instance type can deliver higher storage IOPS and throughput. For more information, see Storage I/O performance.
The following section describes the relationship between instance types and ESSDs in terms of performance:
If the total performance of ESSDs of an instance does not exceed the storage I/O performance of the instance type, the total performance of the ESSDs prevails.
If the total performance of ESSDs of an instance exceeds the storage I/O performance of the instance type, the storage I/O performance of the instance type prevails.
The actual storage performance differs when instances of different instance types have ESSDs at different PLs attached. In the following examples, the g7se instance family is used.
Example 1: Alex creates an instance of the ecs.g7se.xlarge instance type that has 16 GiB of memory and can deliver a maximum of 60,000 IOPS. Alex attaches a PL2 ESSD to the instance. The ESSD has a capacity of 2,000 GiB and can deliver a maximum of 100,000 IOPS. The maximum IOPS of the instance is limited by the maximum IOPS of the instance type to 60,000.
Example 2: Alex creates an instance of the ecs.g7se.4xlarge instance type that has 64 GiB of memory and can deliver a maximum of 150,000 IOPS. Alex attaches three PL2 ESSDs to the instance. Each ESSD has a capacity of 2,000 GiB and can deliver a maximum of 100,000 IOPS. The total maximum IOPS that these ESSDs can deliver is 300,000. The maximum IOPS of the instance is limited by the maximum IOPS of the instance type to 150,000.
Example 3: Alex creates an instance of the ecs.g7se.4xlarge instance type that has 64 GiB of memory and can deliver a maximum of 150,000 IOPS. Alex attaches a PL3 ESSD to the instance. The ESSD has a capacity of 2,000 GiB and can deliver a maximum of 101,800 IOPS. The maximum IOPS of the instance is limited by the maximum IOPS of the ESSD to 101,800.
Instance families supported by ESSDs
For information about instance families supported by ESSDs at PL0, PL1, PL2, and PL3, see Overview of instance families.
References
If the performance requirements of your applications or workloads change or if the storage capacity is insufficient, you may need to change the disk categories. For more information, see Change the category of a disk.
ESSDs at the four PLs have different performance limits. You can choose or change a performance level based on your application requirements. For more information, see Change the performance level of an ESSD.