When a point of presence (POP) processes a user request to generate a cache key, you can configure it to remove the ? and the query string that follows the ?, such as user identity information and access channel source, from the request URL. This enables request URLs with different parameters to reference the same cache file, improving the cache hit ratio and reducing page load time.
Introduction
How it works: Remove the ? character and all parameters after the ? from the request URL. This ensures that different users accessing the same file can hit the same cache file, even when using different URL parameters. As a result, the cache hit ratio improves, origin fetches decrease, and file delivery efficiency increases.
Use case: Ignore query strings when user request URLs contain parameters unrelated to resource content, such as user identity information or access channel source. For example:
A user: http://example.com/1.jpg?uid=123
B user: http://example.com/1.jpg?uid=654
If you do not ignore query strings, the POP treats the two URLs as different requests. This requires an origin fetch for each request. After you set to ignore query strings, the POP removes parameters after the ? in the URL. It then uses only http://example.com/1.jpg to match cache files.
Procedure
In the ESA console, select Site Management. In the Website column, click the name of the target site.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
In the Query String area, click Configure, select a filtering mode and complete the configuration based on your requirements, and click OK to save.
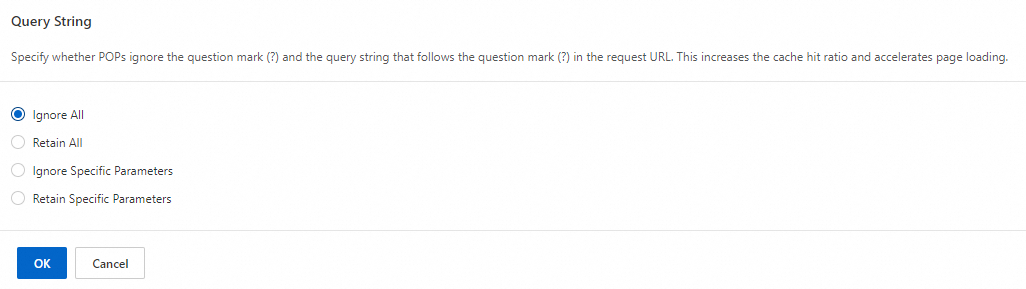
Filtering modes
Assume the original URL is http://example.com/1.jpg?key1=1&key2=2&key3=3. Depending on the rule settings, ESA processes the original URL as follows:
Parameter | Description | Example |
Ignore All | Removes the | The cache key is |
Retain All | You can retain the | The cache key is |
Ignore Specific Parameters | Deletes specified parameters after the | If you enter |
Retain Specific Parameters | To retain only specified query strings after the | If you enter |
Site-level and rule-based settings mapping
Site-level feature configurations apply to all requests for the site. If you want to enable this feature for only specific requests, you can use rule-based features instead. Rule-based features use conditions to detect specific parameters in user requests. This lets you apply configurations with greater precision. The rule-based feature that corresponds to the site-wide query string feature is Custom Cache Key.