An Alibaba Cloud account is the core identity credential used to log on to and manage cloud resources. Leaked credentials pose a high security risk. You must protect your account credentials to prevent unauthorized access and misuse.
Security risks
The main security threats to an Alibaba Cloud account include brute-force attacks on passwords and the leakage of long-term credentials, such as AccessKeys and Security Token Service (STS) tokens for RAM roles. If an attacker obtains these credentials, they can impersonate a legitimate user to log on, manage resources, or access sensitive data. This can lead to serious consequences:
Unauthorized use of resources, which can result in direct financial losses.
Infrastructure damage or service interruptions that affect business availability.
Sensitive data leakage or encryption, which can lead to information disclosure and ransomware risks.
Installation of malicious programs or back doors, which pose long-term threats to system security and data integrity.
Best practices
Protect account passwords and enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Set complex passwords: Weak passwords are a primary cause of account breaches. To prevent passwords from being guessed or cracked through brute-force attacks, avoid using weak passwords.
Change passwords regularly: Change your password every 90 days to reduce the risk of leakage that can result from long-term use.
Enable MFA: Attach or detach a virtual MFA device for your Alibaba Cloud account. MFA adds a dynamic verification code, such as a mobile token or a hardware-protected key, as an additional layer of security on top of password authentication. This helps prevent unauthorized access if your password is leaked.
Use ECS RAM roles instead of AccessKeys
If an application deployed on an ECS instance needs to call Alibaba Cloud service APIs, such as for ECS scaling, use a RAM role instead of an AccessKey.
Create a RAM user and attach a role
The current account must have the sts:AssumeRole permission to attach a role to an instance. This requirement helps prevent permission abuse.
Console
Create and authorize a Resource Access Management (RAM) user.
Attach a RAM role to an ECS instance.
Attach a role during instance creation
When you create an instance on the instance purchase page, select Instance RAM Role in the Advanced Settings(Optional) section.
We recommend that you select Security Hardening Mode for Metadata Access Mode to prevent Security Token Service token leakage that can be caused by instance vulnerabilities or configuration errors. For more information, see Access instance metadata using the enforced mode.
Attach a role to an existing instance
Go to the ECS console - Instances page and switch to the desired destination region.
Find the target ECS instance and click the instance ID to go to the instance details page.
In the Other Information section, click Attach/Detach RAM Role.
In the dialog box that appears, select the RAM role and click Confirm.
ImportantAn ECS instance can be attached to only one RAM role. If your application requires multiple permissions, you must grant all of them to that single role.
For example, if an instance is already attached to the
AliyunECSDiskEncryptDefaultRolerole and also needs network interface management permissions, you can add theAliyunECSNetworkInterfaceManagementAccesspolicy to the role in the RAM console.
API
You can use API operations to attach and detach roles:
Attach a role during instance creation: When you call RunInstances or CreateInstance to create an instance, specify the
RamRoleNameparameter.Attach a role to an existing instance: Call AttachInstanceRamRole to grant a RAM role to an instance.
Detach a role: Call DetachInstanceRamRole to revoke the RAM role granted to an instance.
Use a RAM role to access Alibaba Cloud services from an application
An application that runs on an ECS instance can automatically obtain a temporary STS token from the instance metadata service. The application can then use this token to call Alibaba Cloud service APIs.
Protect AccessKeys and reduce leakage risks
If you must use an AccessKey, you need to strengthen its security management throughout its lifecycle, from creation and storage to distribution and use.
Creation: Follow the principle of "one AccessKey per person, one AccessKey per application." Do not share an AccessKey among multiple users or programs. If an AccessKey is leaked, this practice lets you quickly identify the responsible party, limit the impact, and rotate the key promptly.
Permission management: Follow the principle of least privilege and grant only the necessary permissions. Use RAM users and assign permissions based on their responsibilities. Avoid using the AccessKey of your Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Avoid using your Alibaba Cloud account and grant different permissions to RAM users with different responsibilities.
Secure storage: Store AccessKeys on trusted devices. Examples include the following:
A file that only the root user or a specific user can read.
A database or a Key Management Service (KMS) with access control.
Do not store AccessKeys in local notes, cloud notes, code repositories, chat records, or personal signatures or statuses.
Secure distribution: Distribute AccessKeys in encrypted files. Send the encrypted AccessKey file through one channel, such as email, and send the decryption password through a separate channel, such as a text message.
Secure use: Do not hard-code AccessKeys in your code. Instead, store the AccessKey in a separate configuration file, encrypt the file, and save it on a trusted server. Decrypt the file only after it is distributed to the server, and then set the file permissions so that only the owner can read it.
Network access control: Configure a network access control policy for the AccessKey in the RAM console. For more information, see Network access control policy for an AccessKey.
Regular rotation and cleanup
Rotate regularly: Rotate your AccessKey every 90 days. Generate a new AccessKey and notify users to update to the new key. For more information, see Rotate the AccessKey of a RAM user.
Clean up regularly: Check the operation records of your AccessKeys in the RAM console and promptly revoke any keys that have not been used for a long time. For more information, see Delete the AccessKey of a RAM user.
Monitor for AccessKey leakage risks: Use the AccessKey leakage detection feature in Security Center to identify whether an AccessKey has been leaked. This feature supports alert notifications for leaked AccessKeys. In addition, if an AccessKey is leaked, Alibaba Cloud provides restrictive protection for the AccessKey to prevent the risk from escalating.
Compliance capabilities
Check: Determine if an ECS instance uses an AccessKey to access Alibaba Cloud services
You can query AccessKey logs to find basic information about an AccessKey, the Alibaba Cloud services it accessed, and related IP addresses and resources.
Prerequisite: You have created an ActionTrail trail and delivered logs to a Simple Log Service (SLS) Logstore.
Query AccessKey calls initiated from a VPC Endpoint:
* | SELECT "event.eventid","event.sourceipaddress", "event.userIdentity.accessKeyId", "event.vpcId" WHERE "event.userIdentity.accessKeyId" LIKE 'LTA%' and "event.vpcId" LIKE 'vpc%'The result is similar to the following example:
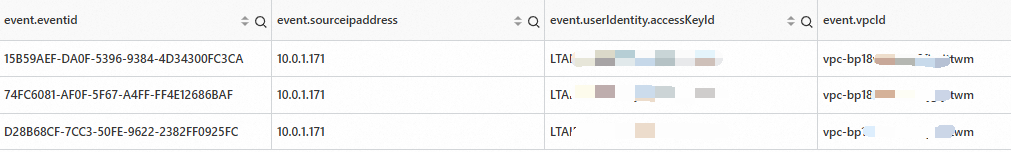
Use the
vpcIdandsourceipaddressto identify the ECS instance that initiated the call. Then, investigate which programs are using theaccessKeyIdto call the OpenAPI.Query AccessKey calls initiated from an Internet Endpoint:
* | SELECT "event.eventid","event.sourceipaddress", "event.userIdentity.accessKeyId" WHERE "event.userIdentity.accessKeyId" LIKE 'LTA%' and "event.vpcId" IS NULLThe result is similar to the following example:
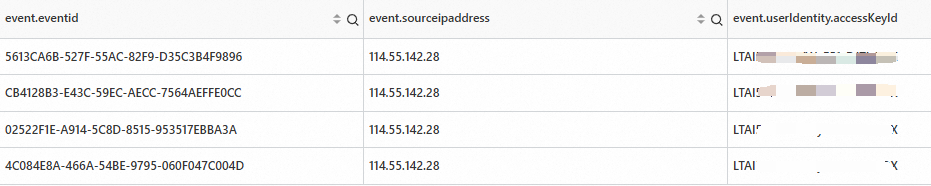
Determine whether the
sourceipaddressis a public IP address of an ECS instance. First, retrieve the elastic IP addresses (EIPs) and public IP addresses under your account. Then, check whether thesourceipaddressin the result belongs to you. If an EIP or public IP address is directly attached to an ECS instance, you can locate the specific instance and modify its configuration.
Remediation: Replace the AccessKey with an instance RAM role
To fix this issue, see Use ECS RAM roles instead of AccessKeys. For more information, see Solutions for AccessKey leakage.