cloud-init is an open source tool that initializes Linux operating systems by performing tasks such as setting an initial password, configuring the hostname, and running custom scripts. If you plan to migrate a local custom image to Alibaba Cloud and the image does not have cloud-init, you must install it manually. Otherwise, Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances created from the image cannot automatically perform initialization tasks, such as setting the hostname and configuring the network. This can hinder automated instance deployment and configuration. This topic describes how to install cloud-init on a Linux operating system.
For more information about cloud-init, see the official cloud-init documentation.
Use cases
cloud-init is installed on all Alibaba Cloud public images by default. To ensure that ECS instances created from your local custom images can automatically initialize system configurations, follow the suggestions for your scenario.
Linux servers without cloud-init that you plan to migrate to the cloud
If you plan to migrate a server that does not have cloud-init to Alibaba Cloud, install cloud-init before the migration. This ensures that the resulting ECS instance can automatically run initialization tasks at startup.
NoteFor servers that you do not plan to migrate to the cloud, installing cloud-init might add unnecessary complexity or use extra resources. You can decide whether to install it based on your specific environment.
Linux servers with cloud-init versions earlier than 0.7.9
Newer versions of cloud-init typically include more features and bug fixes to improve compatibility with the latest cloud platform features. If your server has an older version of cloud-init, you should upgrade it to a later version to ensure optimal compatibility and security.
ECS instances on Alibaba Cloud that do not have cloud-init installed
If your ECS instance does not have cloud-init, you can manually install it on the instance to ensure that it can complete its initialization configuration.
Step 1: Check whether to install or upgrade cloud-init
Log on to the source server.
Check whether cloud-init is installed.
CentOS series
rpm -qa | grep -i cloud-init pip list | grep -i cloud-initUbuntu series
dpkg -l | grep -i cloud-init pip list | grep -i cloud-initIf no output is returned or the version is earlier than 0.7.9: Proceed to Step 2: Install cloud-init.
ImportantVersion 0.7.9 is an early community version of cloud-init that is not suitable for initializing ECS instances. You must upgrade it to a later version.
If the version is 18 or later: You do not need to install cloud-init. However, cloud-init automatically configures the network during instance initialization. If the default configuration does not meet your needs, you can disable the network initialization feature. For more information, see Disable automatic network initialization by Alibaba Cloud.
If the version is 19.1.21: Upgrade to Alibaba Cloud cloud-init 23.2.2. Alibaba Cloud cloud-init 23.2.2 provides the following improvements and new features compared with version 19.1.21:
Instances that use cloud-init 23.2.2 support access to metadata in security hardening mode. For more information about instance metadata, see Instance metadata.
Other changes include feature enhancements, performance improvements, bug fixes, and community contributions. For more information, see the ChangeLog file.
Other versions: You do not need to install cloud-init. Proceed to What to do next.
To prevent data loss from incorrect operations during the installation, we recommend that you first back up your source server data. For example, you can create a snapshot.
Step 2: Install cloud-init
(Recommended) Alibaba Cloud cloud-init 23.2.2: Requires Python 3.6 or later. The data source is
Aliyun.Alibaba Cloud cloud-init 19.1.21: Requires Python 3.6 or later. The data source is
Aliyun.Alibaba Cloud cloud-init 0.7.6a17: This version is required for some earlier operating systems, such as CentOS 6, Debian 9, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12. It requires Python 2.7. The data source is
Aliyun.ImportantBecause the Python community no longer provides technical support for Python 2.7, we recommend that you use a later version of cloud-init to avoid potential issues with dependency libraries.
Community version of cloud-init: The community version is maintained by the cloud-init community. The latest version of Alibaba Cloud cloud-init is 23.2.2. If you need a later version, you can install the community version. For more version information, see the official cloud-init website.
The community version of cloud-init is the official version from the project. The Alibaba Cloud version is optimized for the Alibaba Cloud platform and provides better support for its services. Therefore, we recommend that you use the Alibaba Cloud version of cloud-init. You can select a version to install based on your needs.
(Recommended) cloud-init 23.2.2
The latest version of Alibaba Cloud cloud-init is 23.2.2. This version is maintained as a software package. You can install the package for your operating system or install it from the source package.
The following procedures use Debian 12 and CentOS Stream 9 as examples to demonstrate how to download and install the binary package.
Debian 12
Download the cloud-init package.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloudinit/debian12/cloud-init_23.2.2-5_all.debInstall the package.
sudo apt-get install -y ./cloud-init_23.2.2-5_all.deb(Optional) To prevent the package from being updated or upgraded to a later open source version, you can run the following command to hold the cloud-init package at its current version.
sudo apt-mark hold cloud-initCheck whether the cloud-init version is the expected version.
cloud-init --version
CentOS Stream 9
Download the cloud-init package.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloudinit/centosstream9/cloud-init-23.2.2-5.el9.noarch.rpmInstall the package.
sudo yum install -y ./cloud-init-23.2.2-5.el9.noarch.rpm(Optional) To prevent the package from being updated or upgraded to a later open source version, you can run the following command to lock the cloud-init package at its current version.
sudo sh -c 'echo "exclude=cloud-init" >> /etc/dnf/dnf.conf'Check whether the cloud-init version is the expected version.
cloud-init --version
By default, Alibaba Cloud cloud-init 23.2.2 no longer adds a mapping from the hostname to the private IPv4 address in the /etc/hosts file. If your business requires this configuration, you must configure it yourself. Later operating system versions use the nss-myhostname component to ensure connectivity with the hostname. This component is provided by the systemd-libs package (for Red Hat series) or the libnss-myhostname package (for Debian series) and is enabled through the /etc/nsswitch.conf configuration file. For more information, see the nss-myhostname manual.
cloud-init 19.1.21
Ensure that the Python PIP dependency library is installed on the source server.
The following examples show how to install the
python3-pipdependency library on different Linux distributions.CentOS/Red Hat Enterprise Linux
sudo yum -y install python3-pipUbuntu/Debian
sudo apt-get -y install python3-pipOpenSUSE/SUSE
sudo zypper -n install python3-pipDownload Alibaba Cloud cloud-init.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloudinit/cloud-init-19.1.21.tgzDecompress the cloud-init installation package to the current directory.
tar -zxvf cloud-init-19.1.21.tgzGo to the cloud-init directory and install the dependency libraries.
cd ./cloud-init-19.1.21 pip3 install -r ./requirements.txtGo to the tools subdirectory of the cloud-init directory.
cd ./toolsExecute the deploy.sh script and install cloud-init.
sudo bash ./deploy.sh <issue> <major_version>The following table describes the parameters of the deploy.sh script and provides example values.
Parameter
Description
Example
<issue>
The operating system platform type. Valid values: centos, redhat, rhel, debian, ubuntu, opensuse, and sles. The parameter values are case-sensitive. sles specifies SUSE/SLES.
NoteIf the operating system is CentOS Stream, set this parameter to centos.
centos
<major_version>
The major version number of the operating system platform.
NoteYou cannot install Alibaba Cloud cloud-init 19.1.21 on Ubuntu 14.
The major version number of CentOS 7.6 is 7.
For example, if your current operating system is CentOS 7, run the command
sudo bash ./deploy.sh centos 7.Confirm that cloud-init is installed.
If
"description": "success"is returned, the installation was successful.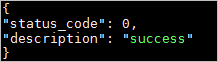
Check whether the cloud-init version is the expected version.
cloud-init --version
The following section provides sample shell scripts to install Alibaba Cloud cloud-init on different Linux distributions for your reference. You can modify the script based on your operating system.
CentOS 7/8
# Check and install python3-pip.
if ! python3 -c 'import setuptools' >& /dev/null; then
yum -y install python3-pip
fi
# Back up the old version of cloud-init.
test -d /etc/cloud && mv /etc/cloud /etc/cloud-old
# Download and decompress the Alibaba Cloud cloud-init package.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloudinit/cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
tar -zxvf ./cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
# Install cloud-init.
issue_major=$( cat /etc/redhat-release | grep -Eo '[0-9]+\.?[0-9]+' | head -1 | awk -F'.' '{printf $1}')
bash ./cloud-init-*/tools/deploy.sh centos "$issue_major"Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7/8
# Check and install python3-pip.
if ! python3 -c 'import setuptools' >& /dev/null; then
yum -y install python3-pip
fi
# Back up the old version of cloud-init.
test -d /etc/cloud && mv /etc/cloud /etc/cloud-old
# Download and decompress the Alibaba Cloud cloud-init package.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloudinit/cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
tar -zxvf ./cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
# Install cloud-init.
issue_major=$( cat /etc/os-release | grep VERSION_ID | grep -Eo '[0-9]+\.?[0-9]+' | head -1 | awk -F'.' '{printf $1}')
bash ./cloud-init-*/tools/deploy.sh rhel "$issue_major"Ubuntu 16/18/20
# Check and install python3-pip.
if ! python3 -c 'import setuptools' >& /dev/null; then
apt-get install python36 python3-pip -y
fi
# Back up the old version of cloud-init.
test -d /etc/cloud && mv /etc/cloud /etc/cloud-old
# Download and decompress the Alibaba Cloud cloud-init package.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloudinit/cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
tar -zxvf ./cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
# Install cloud-init.
issue_major=$( cat /etc/os-release | grep VERSION_ID | grep -Eo '[0-9]+\.?[0-9]+' | head -1 | awk -F'.' '{printf $1}')
bash ./cloud-init-*/tools/deploy.sh ubuntu "$issue_major"Debian 9/10
# Check and install python3-pip.
if ! python3 -c 'import setuptools' >& /dev/null; then
apt-get -y install python3-pip
fi
# Back up the old version of cloud-init.
test -d /etc/cloud && mv /etc/cloud /etc/cloud-old
# Download and decompress the Alibaba Cloud cloud-init package.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloudinit/cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
tar -zxvf ./cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
# Install cloud-init.
issue_major=$( cat /etc/os-release | grep VERSION_ID | grep -Eo '[0-9]+\.?[0-9]+' | head -1 | awk -F'.' '{printf $1}')
bash ./cloud-init-*/tools/deploy.sh debian "$issue_major"SUSE 12/15
# Check and install python3-pip.
if ! python3 -c 'import setuptools'>& /dev/null; then
zypper -n install python3-pip
fi
# Back up the old version of cloud-init.
test -d /etc/cloud && mv /etc/cloud/etc/cloud-old
# Download and decompress the Alibaba Cloud cloud-init package.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloudinit/cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
tar -zxvf ./cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
# Install cloud-init.
issue_major=$( cat /etc/os-release | grep VERSION_ID | grep -Eo '[0-9]+\.?[0-9]+' | head -1 | awk -F'.' '{printf $1}')
bash ./cloud-init-*/tools/deploy.sh sles "$issue_major"OpenSUSE 15
# Check and install python3-pip.
if ! python3 -c 'import setuptools'>& /dev/null; then
zypper -n install python3-pip
fi
# Back up the old version of cloud-init.
test -d /etc/cloud && mv /etc/cloud/etc/cloud-old
# Download and decompress the Alibaba Cloud cloud-init package.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloudinit/cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
tar -zxvf ./cloud-init-19.1.21.tgz
# Install cloud-init.
issue_major=$( cat /etc/os-release | grep VERSION_ID | grep -Eo '[0-9]+\.?[0-9]+' | head -1 | awk -F'.' '{printf $1}')
bash ./cloud-init-*/tools/deploy.sh opensuse"$issue_major"cloud-init 0.7.6a17
By default, Alibaba Cloud public images for CentOS 6, Debian 9, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 have cloud-init-0.7.6a17 installed. To perform a test, you can run the sudo mv /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg_bak command to back up the configuration file first.
Check whether the operating system is CentOS 6, Debian 9, or SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12.
cat /etc/issueEnsure that the Python PIP dependency library is installed on the source server.
The following examples show how to install the
python2-pipdependency library.CentOS 6/SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12
sudo yum -y install python2-pipDebian 9
sudo apt-get -y install python2-pipDownload and decompress Alibaba Cloud cloud-init 0.7.6a17.
wget https://ecs-image-tools.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/cloud-init-0.7.6a17.tgz tar -zxvf cloud-init-0.7.6a17.tgzGo to the tools subdirectory of the cloud-init directory.
cd cloud-init-0.7.6a17/tools/Install cloud-init.
sudo bash ./deploy.sh <issue> <major_version>For example, if your current operating system is CentOS 6, run the command
sudo bash ./deploy.sh centos 6.The following table describes the parameters of the deploy.sh script and provides example values.
Parameter
Description
Example
<issue>
The operating system platform type. Valid values: centos, debian, and sles. The parameter values are case-sensitive. sles specifies SUSE/SLES.
centos
<major_version>
The major version number of the operating system platform.
The major version number of CentOS 6.5 is 6.
Check whether the cloud-init version is the expected version.
cloud-init --version
Community version of cloud-init
Ensure that the Git, Python, and Python PIP dependency libraries are installed on the source server.
The following examples show how to install the Git, Python 3.6, and
python3-pipdependency libraries on different Linux distributions.CentOS/Red Hat Enterprise Linux
sudo yum -y install git python36 python3-pipUbuntu/Debian
sudo apt-get -y install git python36 python3-pipOpenSUSE/SUSE
sudo zypper -n install git python36 python3-pipDownload the cloud-init source package using Git.
git clone https://git.launchpad.net/cloud-initGo to the cloud-init directory.
cd ./cloud-initInstall all dependency libraries.
sudo pip3 install -r ./requirements.txtInstall cloud-init.
python3 setup.py installModify the cloud.cfg configuration file.
Open the configuration file.
sudo vi /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
Replace the configuration before
cloud_init_modules:with the following content.# Example datasource config # The top level settings are used as module # and system configuration. # A set of users which may be applied and/or used by various modules # when a 'default' entry is found it will reference the 'default_user' # from the distro configuration specified below users: - default user: name: root lock_passwd: False # If this is set, 'root' will not be able to ssh in and they # will get a message to login instead as the above $user disable_root: false # This will cause the set+update hostname module to not operate (if true) preserve_hostname: false syslog_fix_perms: root:root datasource_list: [ AliYun ] # Example datasource config datasource: AliYun: support_xen: false timeout: 5 # (defaults to 50 seconds) max_wait: 60 # (defaults to 120 seconds) # metadata_urls: [ 'blah.com' ] # The modules that run in the 'init' stage cloud_init_modules:
Check whether the cloud-init version is the expected version.
cloud-init --version
(Optional) Step 3: Configure cloud-init
Disable automatic network initialization by Alibaba Cloud
If your cloud-init version is 18 or later, it automatically completes network initialization with the following configuration: BOOTPROTO=dhcp DEVICE=eth0 ONBOOT=yes STARTMODE=auto TYPE=Ethernet USERCTL=no. If the default network configuration does not meet your business needs, you can modify the cloud-init configuration file to customize the network configuration.
Open the default cloud-init configuration file. Then, press the
ikey to enter insert mode.sudo vim /etc/cloud/cloud.cfgBefore
Example datasource config, add the disabled configuration to disable the automatic network configuration feature of cloud-init.network: config: disabled
After you add this configuration, cloud-init no longer manages network configuration files, such as
ifcfg-eth0, in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory. You must manage these files yourself.Press the
Esckey, enter:wq, and press theEnterkey to save and close the file.As needed, you can customize the network configurations in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory, such as the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway.
Disable automatic hostname setting by Alibaba Cloud
By default, cloud-init automatically sets the hostname and updates the /etc/hostname file when the instance starts. If you do not want the hostname to be changed, you can modify the cloud-init configuration file as follows.
Open the default cloud-init configuration file. Then, press the
ikey to enter edit mode.sudo vim /etc/cloud/cloud.cfgIn the configuration file, change
preserve_hostname: falsetopreserve_hostname: true.
Press the
Esckey, enter:wq, and press theEnterkey to save and close the file.
What to do next
For Linux servers that you plan to migrate to the cloud, you can use Server Migration Center (SMC) for the migration. For more information, see Migrate servers to Elastic Compute Service (ECS).
For ECS instances that are already running a Linux custom image on Alibaba Cloud, you can restart the system to verify the result. If the hostname, network, and Network Time Protocol (NTP) are automatically configured, cloud-init was installed successfully. For example, you can run the following command to view the network configuration file:
sudo reboot cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0The following output indicates that the system has automatically configured network settings, such as the DHCP protocol, network device, and device type, using cloud-init.
BOOTPROTO=dhcp DEVICE=eth0 ONBOOT=yes STARTMODE=auto TYPE=Ethernet USERCTL=no