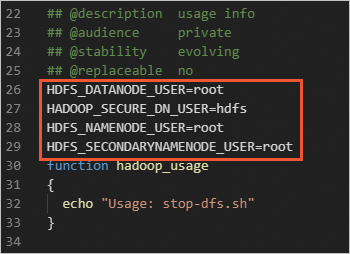
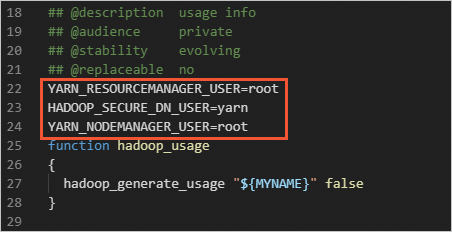
Hadoop is an open source, distributed, Java-based software framework that is developed by the Apache Foundation. This topic describes how to quickly build a distributed Hadoop environment and a pseudo-distributed Hadoop environment on Linux Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances.
Background information
The Apache Hadoop software library is a framework that allows you to process large data sets across clusters of computers in a distributed manner by using simple programming models. The framework can scale up from a single server to thousands of machines that provide local computation and storage capabilities. Hadoop does not rely on hardware to deliver high availability. It is designed to detect and handle failures at the application layer to deliver a highly available service on top of a cluster of computers that are prone to failures.
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and MapReduce are vital components of Hadoop.
HDFS is a distributed file system that is used for distributed storage of application data and provides access to application data.
MapReduce is a distributed computing framework that distributes computing jobs across servers in a Hadoop cluster. Computing jobs are split into map tasks and reduce tasks. JobTracker schedules the tasks for distributed processing.
Item | Pseudo-distributed mode | Distributed mode |
Number of nodes | Single node. A single node hosts all services. | Multiple nodes. Services are distributed across multiple nodes. |
Resource utilization | Use the resources of a single machine. | Utilize the computing and storage resources of multiple machines. |
Fault tolerance | Low. A single point of failure makes the cluster unavailable. | High. Data replication and high availability configurations are supported. |
Scenarios |
|
|
Prerequisites
An ECS instance that meets the requirements described in the following table is created.
Environment | Requirement | |
Instance | Pseudo-distributed mode | One instance |
Distributed mode | Three or more instances Note To improve availability, disaster recovery, and Hadoop cluster management, we recommend that you add the instances to a deployment set that uses the High Availability strategy. | |
Operating system | Linux | |
Public IP address | Each ECS instance is assigned a public IP address by the system or is associated with an elastic IP address (EIP). | |
Instance security group | Inbound rules are added to the security groups associated with the ECS instances to open ports 22, 443, 8088, and 9870. Port 8088 is the default web UI port for Hadoop Yet Another Resource Negotiator (YARN). Port 9870 is the default web UI port for Hadoop NameNode. Note If you deploy a distributed Hadoop environment, you must also open port 9868, which is the Hadoop Secondary NameNode custom Web UI port. For more information, see Manage security group rules. | |
Java Development Kit (JDK) In this topic, Hadoop 3.2.4 and Java 8 are used. To use other Hadoop and Java versions, visit the official Hadoop website for instructions. For more information, see Hadoop Java Versions. | Hadoop version | Java version |
Hadoop 3.3 | Java 8 and Java 11 | |
Hadoop 3.0.x~3.2.x | Java 8 | |
Hadoop 2.7.x~2.10.x | Java 7 and Java 8 | |
Procedure
Distributed mode
You must plan nodes before you deploy Hadoop. In this example, three instances are used to deploy Hadoop. The hadoop001 node serves as the master node, and the hadoop002 and hadoop003 nodes serve as worker nodes.
Functional component | hadoop001 | hadoop002 | hadoop003 |
HDFS |
| DataNode |
|
YARN | NodeManager |
| NodeManager |
Step 1: Install JDK
The JDK environment must be installed on all nodes.
Connect to each ECS instance that you created.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
ImportantTo ensure system security and stability, Apache does not recommend that you start Hadoop as the root user. You may fail to start Hadoop as the root user due to a permissions issue. You can start Hadoop as a non-root user, such as
ecs-user.Run the following command to download the JDK 1.8 installation package:
wget https://download.java.net/openjdk/jdk8u41/ri/openjdk-8u41-b04-linux-x64-14_jan_2020.tar.gzRun the following command to decompress the downloaded JDK 1.8 installation package:
tar -zxvf openjdk-8u41-b04-linux-x64-14_jan_2020.tar.gzRun the following command to move and rename the folder to which the JDK installation files are extracted.
In this example, the folder is renamed
java8. You can specify a different name for the folder based on your business requirements.sudo mv java-se-8u41-ri/ /usr/java8Run the following commands to configure Java environment variables.
If the name you specified for the folder to which the JDK installation files are extracted is not java8, replace
java8in the following commands with the actual folder name.sudo sh -c "echo 'export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java8' >> /etc/profile" sudo sh -c 'echo "export PATH=\$PATH:\$JAVA_HOME/bin" >> /etc/profile' source /etc/profileRun the following command to check whether JDK is installed:
java -versionThe following command output indicates that JDK is installed.

Step 2: Configure password-free SSH logon
Perform this step on all instances.
The password-free SSH logon feature allows nodes to seamlessly connect to each other, without the need to enter a password to verify identity. This allows you to manage and maintain Hadoop clusters in a more convenient and efficient manner.
Configure hostnames and a communication method.
sudo vim /etc/hostsAdd
<Primary private IP-address> <Hostname>of each instance to the/etc/hostsfile. Examples:<Primary private IP address> hadoop001 <Primary private IP address> hadoop002 <Primary private IP address> hadoop003Run the following command to create a public key and a private key:
ssh-keygen -t rsa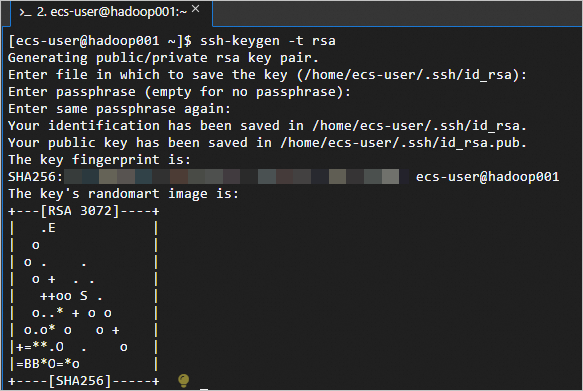
Run the
ssh-copy-id <Hostname>command to replace the hostname with the actual hostname of each instance. Examples:Run the
ssh-copy-id hadoop001,ssh-copy-id hadoop002, andssh-copy-id hadoop003commands in sequence on thehadoop001node. After you run each command, enter yes and the password of the corresponding ECS instance.ssh-copy-id hadoop001 ssh-copy-id hadoop002 ssh-copy-id hadoop003If the following command output is returned, the password-free logon configuration is successful.
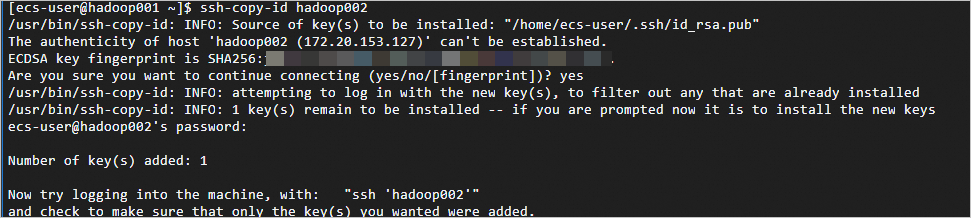
Step 3: Install Hadoop
Run the following commands on all ECS instances.
Run the following command to download the Hadoop installation package:
wget http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/apache/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.2.4/hadoop-3.2.4.tar.gzRun the following commands to decompress the Hadoop installation package to the
/opt/hadooppath:sudo tar -zxvf hadoop-3.2.4.tar.gz -C /opt/ sudo mv /opt/hadoop-3.2.4 /opt/hadoopRun the following commands to configure Hadoop environment variables:
sudo sh -c "echo 'export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/hadoop' >> /etc/profile" sudo sh -c "echo 'export PATH=\$PATH:/opt/hadoop/bin' >> /etc/profile" sudo sh -c "echo 'export PATH=\$PATH:/opt/hadoop/sbin' >> /etc/profile" source /etc/profileRun the following commands to modify the
yarn-env.shandhadoop-env.shconfiguration files:sudo sh -c 'echo "export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java8" >> /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-env.sh' sudo sh -c 'echo "export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java8" >> /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh'Run the following command to check whether Hadoop is installed:
hadoop versionThe following command output indicates that Hadoop is installed.
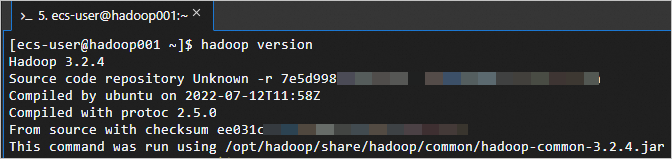
Step 4: Configure Hadoop
Modify the configuration files of Hadoop on all instances.
Modify the
core-site.xmlconfiguration file of Hadoop.Run the following command to open the core-site.xml configuration file:
sudo vim /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xmlIn the
<configuration></configuration>section, add the following content:!" -- Specify the address of the namenode. --> <property> <name>fs.defaultFS</name> <value>hdfs://hadoop001:8020</value> </property> <! -- Specify the directory in which files generated when you use Hadoop are stored. --> <property> <name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name> <value>/opt/hadoop/data</value> </property> <! -- Configure hadoop as the static user for HDFS web page logon. --> <property> <name>hadoop.http.staticuser.user</name> <value>hadoop</value> </property>
Modify the
hdfs-site.xmlconfiguration file of Hadoop.Run the following command to open the hdfs-site.xml configuration file:
sudo vim /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xmlIn the
<configuration></configuration>section, add the following content:<!-- The NameNode web address.--> <property> <name>dfs.namenode.http-address</name> <value>hadoop001:9870</value> </property> <! -- The web address of the secondary NameNode.--> <property> <name>dfs.namenode.secondary.http-address</name> <value>hadoop003:9868</value> </property>
Modify the
yarn-site.xmlconfiguration file of Hadoop.Run the following command to open the yarn-site configuration file:
sudo vim /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xmlIn the
<configuration></configuration>section, add the following content:<!--Specify the shuffle mode in which NodeManager obtains data.--> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name> <value>mapreduce_shuffle</value> </property> <! -- Specify the address of YARN (ResourceManager). --> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.hostname</name> <value>hadoop002</value> </property> <! -- Specify a whitelist of environment variables that NodeManager allows to pass to containers. --> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.env-whitelist</name> <value>JAVA_HOME,HADOOP_COMMON_HOME,HADOOP_HDFS_HOME,HADOOP_CONF_DIR,CLASSPATH_PREPEND_DISTCACHE,HADOOP_YARN_HOME,HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME</value> </property>
Modify the
mapred-site.xmlconfiguration file of Hadoop.Run the following command to open the mapred-site.xml configuration file:
sudo vim /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xmlIn the
<configuration></configuration>section, add the following content:<!--Instruct Hadoop to run Map/Reduce (MR) on YARN.--> <property> <name>mapreduce.framework.name</name> <value>yarn</value> </property>
Modify the
workersconfiguration file of Hadoop.Run the following command to open the workers configuration file:
sudo vim /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/workersIn the
workersfile, add the instance information.hadoop001 hadoop002 hadoop003
Step 5: Start Hadoop
Run the following command to initialize
NameNode:WarningThe
NameNodeinitialization is required only for the first Hadoop startup. Perform this step on all instances.hadoop namenode -formatStart Hadoop.
ImportantTo ensure system security and stability, Apache does not recommend that you start Hadoop as the root user. You may fail to start Hadoop as the root user due to a permissions issue. You can start Hadoop as a non-root user, such as
ecs-user.If you want to start Hadoop as the root user, you must be familiar with the instructions for managing Hadoop permissions and the associated risks and modify the following configuration files.
Take note that when you start Hadoop as the root user, severe security risks may arise. The security risks include but are not limited to data leaks, vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malware to obtain the highest system permissions, and unexpected permissions issues or operations. For information about Hadoop permissions, see Hadoop in Secure Mode.
Run the
start-dfs.shcommand on thehadoop001node to start HDFS.The start-dfs.sh command starts the HDFS service by starting components, such as NameNode, SecondaryNameNode, and DataNode.
start-dfs.shRun the
jpscommand. The following command output indicates that HDFS is started.
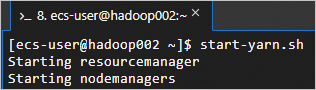
Run the
start-yarn.shcommand on thehadoop002node to start the YARN service.The start-yarn.sh command starts the YARN service by starting components, such as ResourceManager and NodeManager.
start-yarn.shThe following command output indicates that YARN is started.
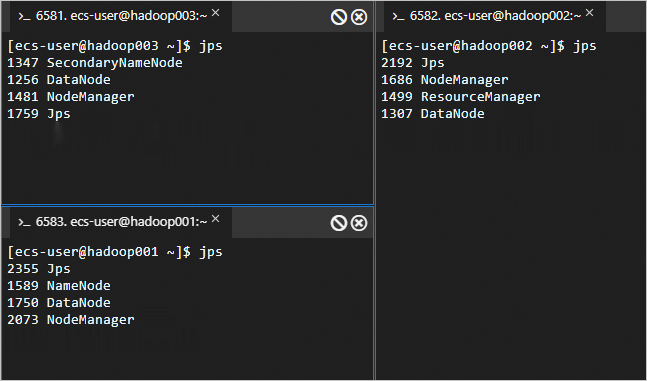
Run the following command to view the processes that are started:
jpsThe processes shown in the following figure are started.
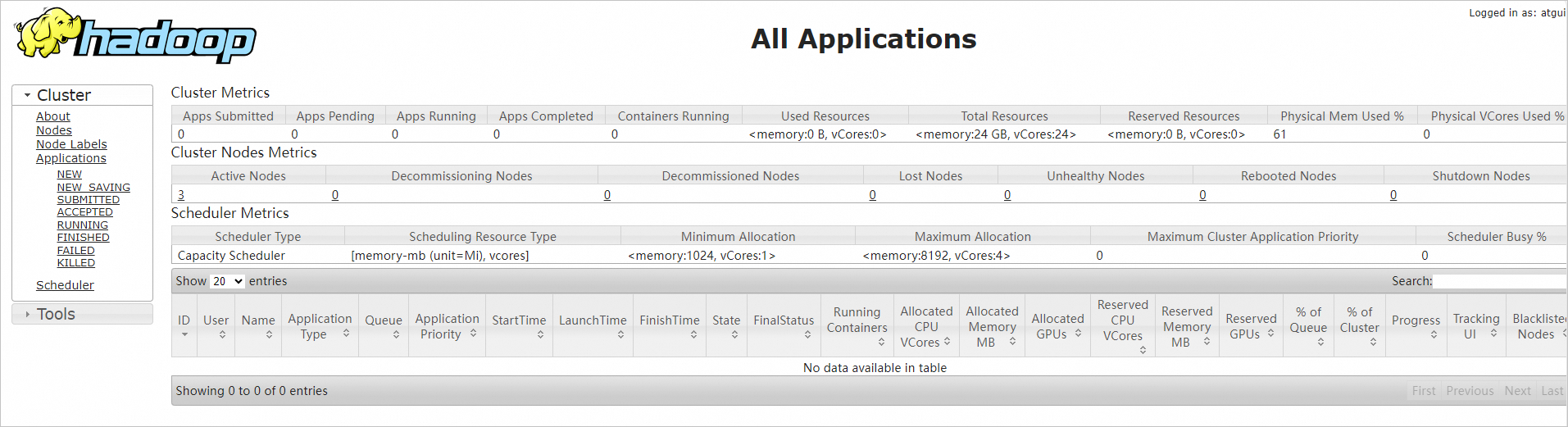
Enter
http://<Public IP address of the hadoop002 node>:8088in the address bar of a web browser on your on-premises computer to access the web UI of YARN.The web UI shows information about the entire cluster, including resource usage, status of applications (such as MapReduce jobs), and queue information.
ImportantMake sure that an inbound rule is added to a security group to which the ECS instance belongs to open port 8088. Otherwise, you cannot access the web UI. For information about how to add a security group rule, see Add a security group rule.
Enter
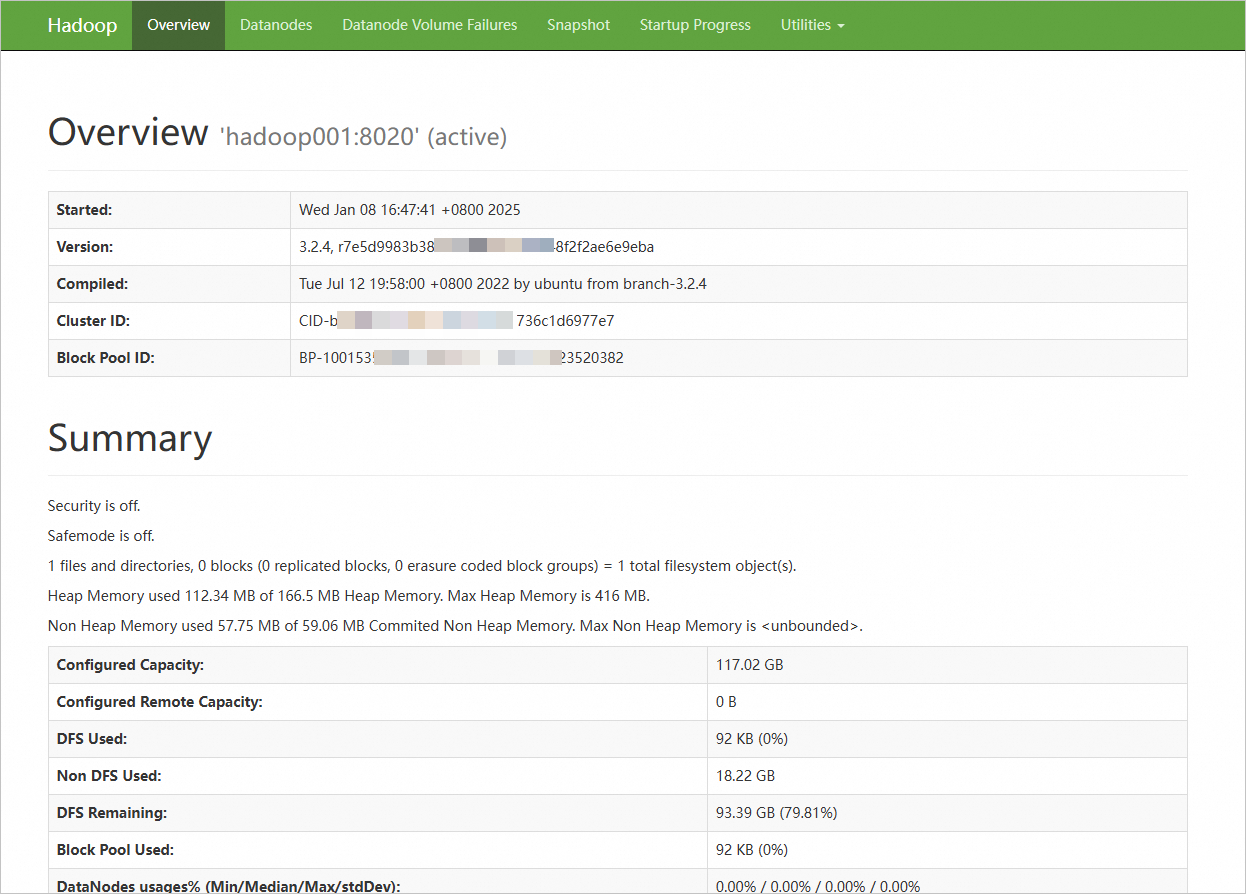
http://<Public IP address of the hadoop001 node>:9870in the address bar of a web browser on your on-premises computer to access the web UI of NameNode. Enterhttp://<Public IP address of the hadoop003 node>:9868to access the web UI of SecondaryNameNode.The web UI shows information about the HDFS file system, including the file system status, cluster health, active nodes, and NameNode logs.
The page shown in the following figure indicates that the distributed Hadoop environment is built.
ImportantMake sure that an inbound rule is added to a security group to which the ECS instance belongs to open port 9870. Otherwise, you cannot access the web UI. For information about how to add a security group rule, see Add a security group rule.
Pseudo-distributed mode
Step 1: Install JDK
Connect to the ECS instance that you created.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
ImportantTo ensure system security and stability, Apache does not recommend that you start Hadoop as the root user. You may fail to start Hadoop as the root user due to a permissions issue. You can start Hadoop as a non-root user, such as
ecs-user.Run the following command to download the JDK 1.8 installation package:
wget https://download.java.net/openjdk/jdk8u41/ri/openjdk-8u41-b04-linux-x64-14_jan_2020.tar.gzRun the following command to decompress the downloaded JDK 1.8 installation package:
tar -zxvf openjdk-8u41-b04-linux-x64-14_jan_2020.tar.gzRun the following command to move and rename the folder to which the JDK installation files are extracted.
In this example, the folder is renamed
java8. You can specify a different name for the folder based on your business requirements.sudo mv java-se-8u41-ri/ /usr/java8Run the following commands to configure Java environment variables.
If the name you specified for the folder to which the JDK installation files are extracted is not java8, replace
java8in the following commands with the actual folder name.sudo sh -c "echo 'export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java8' >> /etc/profile" sudo sh -c 'echo "export PATH=\$PATH:\$JAVA_HOME/bin" >> /etc/profile' source /etc/profileRun the following command to check whether JDK is installed:
java -versionThe following command output indicates that JDK is installed.

Step 2: Configure password-free SSH logon
You must configure SSH password-free logon for the single node. Otherwise, a Permission Denied error occurs when you start NameNode and DataNode.
Run the following command to create a public key and a private key:
ssh-keygen -t rsa
Run the following commands to add the public key to the
authorized_keysfile:cd .ssh cat id_rsa.pub >> authorized_keys
Step 3: Install Hadoop
Run the following command to download the Hadoop installation package:
wget http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/apache/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.2.4/hadoop-3.2.4.tar.gzRun the following commands to decompress the Hadoop installation package to the
/opt/hadooppath:sudo tar -zxvf hadoop-3.2.4.tar.gz -C /opt/ sudo mv /opt/hadoop-3.2.4 /opt/hadoopRun the following commands to configure Hadoop environment variables:
sudo sh -c "echo 'export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/hadoop' >> /etc/profile" sudo sh -c "echo 'export PATH=\$PATH:/opt/hadoop/bin' >> /etc/profile" sudo sh -c "echo 'export PATH=\$PATH:/opt/hadoop/sbin' >> /etc/profile" source /etc/profileRun the following commands to modify the
yarn-env.shandhadoop-env.shconfiguration files:sudo sh -c 'echo "export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java8" >> /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-env.sh' sudo sh -c 'echo "export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java8" >> /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh'Run the following command to check whether Hadoop is installed:
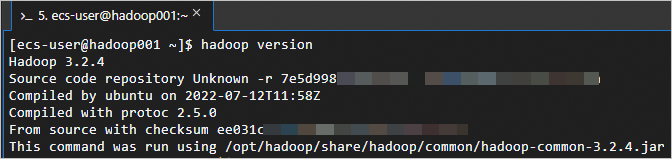
hadoop versionThe following command output indicates that Hadoop is installed.
Step 4: Configure Hadoop
Modify the
core-site.xmlconfiguration file of Hadoop.Run the following command to open the core-site.xml configuration file:
sudo vim /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xmlIn the
<configuration></configuration>section, add the following content:<property> <name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name> <value>file:/opt/hadoop/tmp</value> <description>location to store temporary files</description> </property> <property> <name>fs.defaultFS</name> <value>hdfs://localhost:9000</value> </property>
Modify the
hdfs-site.xmlconfiguration file of Hadoop.Run the following command to open the hdfs-site.xml configuration file:
sudo vim /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xmlIn the
<configuration></configuration>section, add the following content:<property> <name>dfs.replication</name> <value>1</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name> <value>file:/opt/hadoop/tmp/dfs/name</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name> <value>file:/opt/hadoop/tmp/dfs/data</value> </property>
Step 5: Start Hadoop
Run the following command to initialize
NameNode:hadoop namenode -formatStart Hadoop.
ImportantTo ensure system security and stability, Apache does not recommend that you start Hadoop as the root user. You may fail to start Hadoop as the root user due to a permissions issue. You can start Hadoop as a non-root user, such as
ecs-user.If you want to start Hadoop as the root user, you must be familiar with the instructions for managing Hadoop permissions and the associated risks and modify the following configuration files.
Take note that when you start Hadoop as the root user, severe security risks may arise. The security risks include but are not limited to data leaks, vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malware to obtain the highest system permissions, and unexpected permissions issues or operations. For information about Hadoop permissions, see Hadoop in Secure Mode.
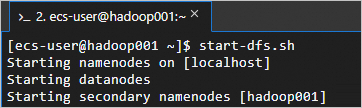
Run the following command to start the HDFS service.
The start-dfs.sh command starts the HDFS service by starting components, such as NameNode, SecondaryNameNode, and DataNode.
start-dfs.shThe following command output indicates that the HDFS service is started.
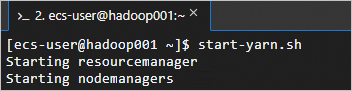
Run the following command to start the YARN service.
The start-yarn.sh command starts the YARN service by starting components, such as ResourceManager, NodeManager, and ApplicationHistoryServer.
start-yarn.shThe following command output indicates that YARN is started.
Run the following command to view the processes that are started:
jpsThe processes shown in the following figure are started.

Enter
http://<Public IP address of the ECS instance>:8088in the address bar of a web browser on your on-premises computer to access the web UI of YARN.The web UI shows information about the entire cluster, including resource usage, status of applications (such as MapReduce jobs), and queue information.
ImportantMake sure that an inbound rule is added to a security group to which the ECS instance belongs to open port 8088. Otherwise, you cannot access the web UI. For information about how to add a security group rule, see Add a security group rule.
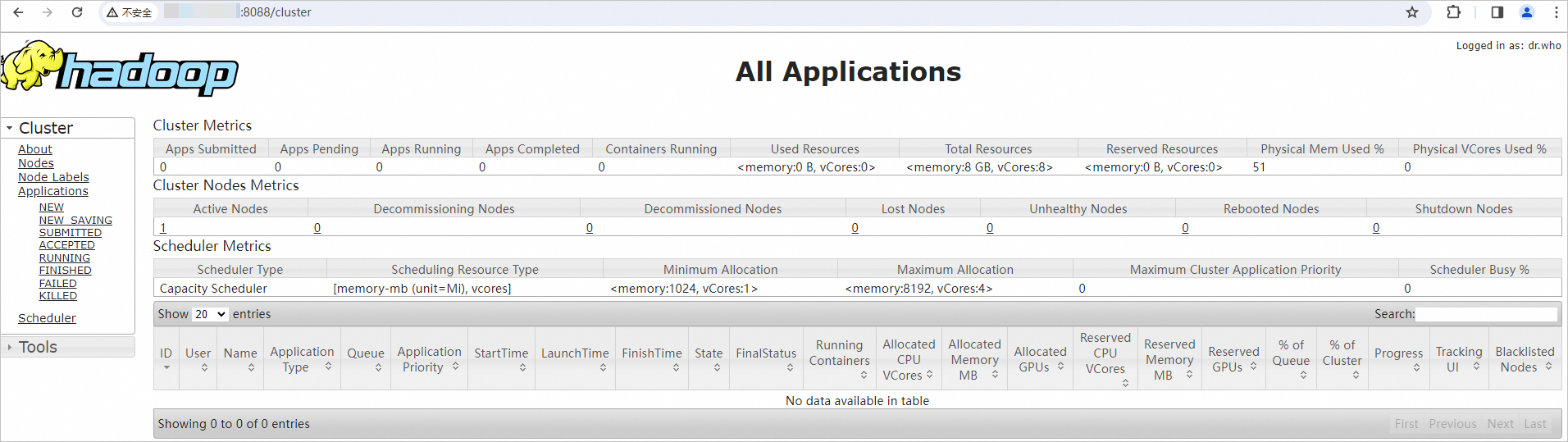
Enter
http://<Public IP address of the ECS instance>:9870in the address bar of a web browser on your on-premises computer to access the web UI of NameNode.The web UI shows information about the HDFS file system, including the file system status, cluster health, active nodes, and NameNode logs.
The page shown in the following figure indicates that the distributed Hadoop environment is built.
ImportantMake sure that an inbound rule is added to a security group to which the ECS instance belongs to open port 9870. Otherwise, you cannot access the web UI. For information about how to add a security group rule, see Add a security group rule.
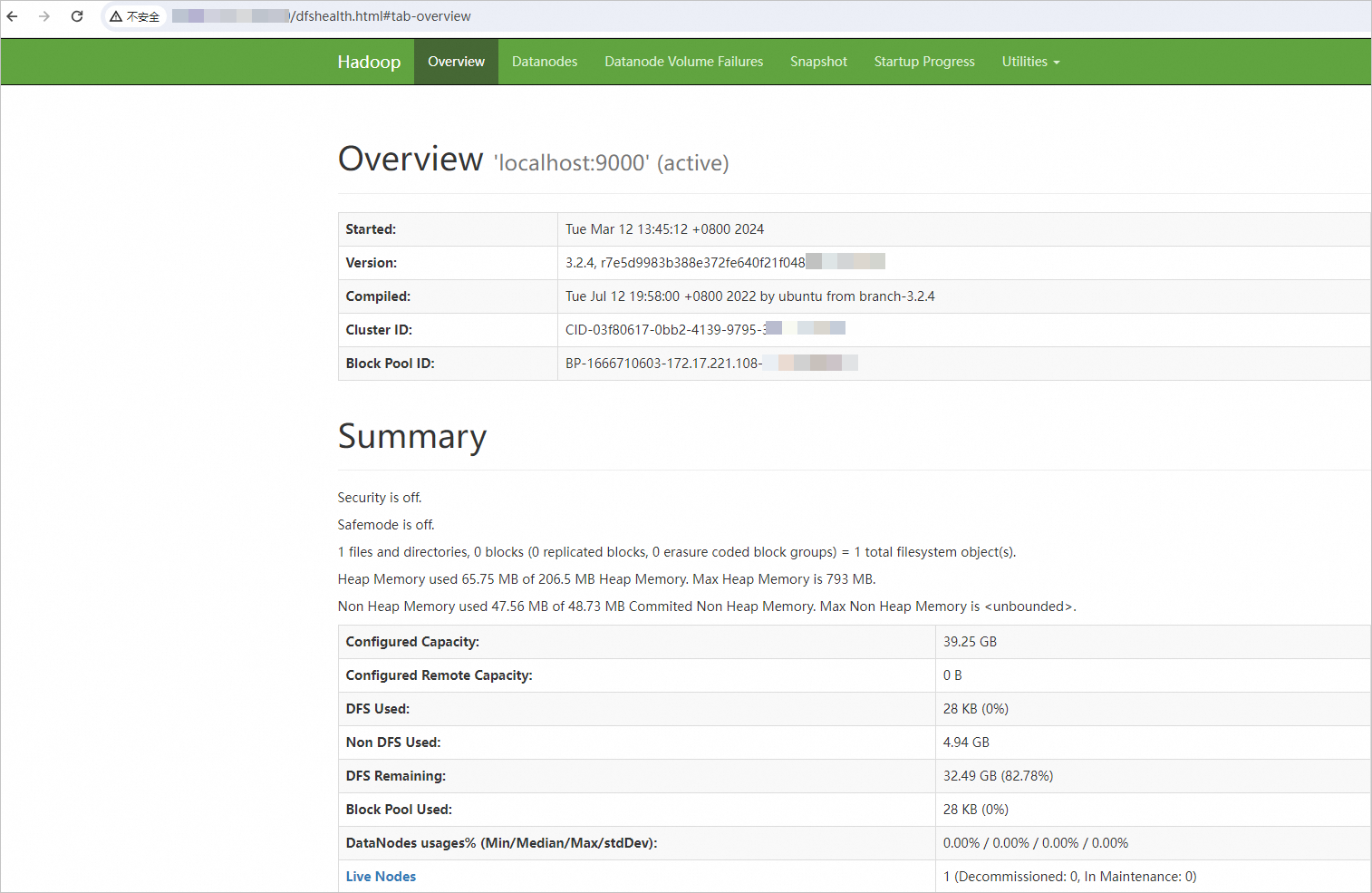
Related operations
Create a snapshot-consistent group
If you use distributed Hadoop, we recommend that you create a snapshot-consistent group to ensure data consistency and reliability in the Hadoop cluster and provide a stable environment for subsequent data processing and analysis. For more information, see Create a snapshot-consistent group.
Hadoop-related operations
For information about how to use HDFS components, see Common HDFS commands.
References
For information about how to use the big data environment that is integrated with Alibaba Cloud ECS, see Getting started with EMR.
For information about how to use the data lake development and governance environment, see Getting started with DataWorks.