DataWorks is a unified, end-to-end platform for big data development and governance. It integrates with big data engines such as MaxCompute, Hologres, EMR, AnalyticDB, and CDP and supports solutions such as data warehouses, data lakes, and data lakehouses. This topic provides an example of how to use the core features of DataWorks to integrate data, process business logic, schedule recurring tasks, and visualize data.
Introduction
This tutorial uses an E-commerce scenario as an example to show you how to build a complete data pipeline, from raw data integration to data analysis, calculation, and visualization. You will learn how to quickly build a reusable data production pipeline by following a standardized development process. This process ensures scheduling reliability and operational observability. This approach allows business personnel to transform data into value without requiring deep technical knowledge, which lowers the barrier for enterprises to adopt big data applications.
This tutorial helps you quickly learn how to perform the following operations:
Data synchronization: Use the Data Integration module in DataWorks to create an offline sync task. This task synchronizes business data to a big data computing platform, such as MaxCompute.
Data cleansing: Use the DataStudio module in DataWorks to process, analyze, and mine business data.
Data visualization: Use the Data Analysis module in DataWorks to convert analysis results into charts that are easy for business personnel to understand.
Recurring scheduling: Configure recurring schedules for the data synchronization and data cleansing workflows to run them at scheduled times.
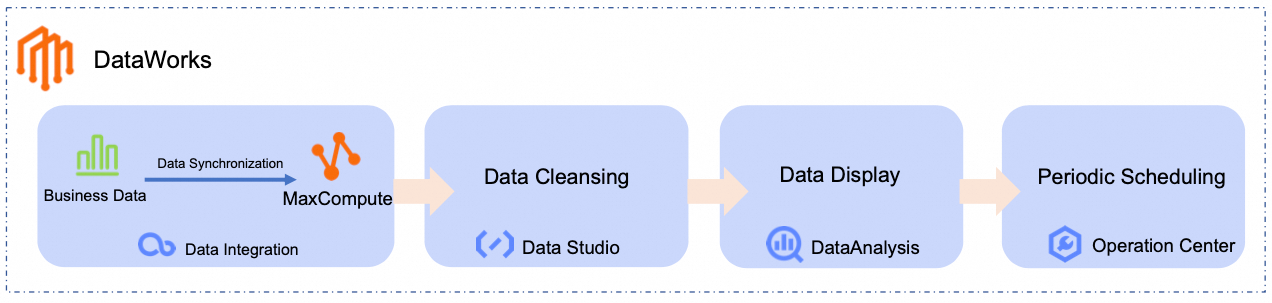
This tutorial synchronizes raw product and order data from a public data source to MaxCompute. It then uses the following data analysis workflow to generate a daily ranking of the best-selling product categories:

Prerequisites
To complete the steps in this tutorial, you must use an Alibaba Cloud account or a RAM user that has the AliyunDataWorksFullAccess permission. For more information, see Prepare an Alibaba Cloud account or Prepare a RAM user.
DataWorks provides a comprehensive access control mechanism that supports permission management at the product and module levels. For finer-grained access control, see Overview of the DataWorks permission model.
Preparations
Activate DataWorks
Create a workspace
Create a resource group and attach it to a workspace
Enable Internet access for the resource group
Create and attach a MaxCompute computing resource
Procedure
This section uses the following scenario as an example to guide you through the features of DataWorks:
Assume an E-commerce platform stores product and order information in a MySQL database. You need to periodically analyze the order data and view a daily ranking of the best-selling product categories in a visual format.
1. Data synchronization
Create a data source
DataWorks connects to data sources and destinations using data source connections. In this step, you need to create a MySQL data source to connect to the source MySQL database that stores the business data. This data source provides the raw data for this tutorial.
You do not need to prepare the raw business data for this tutorial. For testing and learning purposes, DataWorks provides a test dataset. The table data is stored in a public MySQL database that you can connect to by creating a MySQL data source.
Go to the DataWorks Management Center page, switch to the China (Shanghai) region, select the workspace you created from the drop-down list, and then click Go To Management Center.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Data Source to go to the Data Source List page. Click Add Data Source, select the MySQL type, and configure the MySQL data source parameters.
NoteKeep the default values for parameters not mentioned in the table.
The first time you add a data source, you are prompted to complete Cross-service Authorization. Follow the on-screen instructions to grant the AliyunDIDefaultRole service-linked role.
Parameter
Description
Data Source Name
This example uses MySQL_Source.
Configuration Mode
Select Connection String Mode.
Connection Address
Host IP:
rm-bp1z69dodhh85z9qa.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.comPort:
3306.
ImportantThe data provided in this tutorial is for hands-on practice with DataWorks only. All data is test data and can only be read in the Data Integration module.
Database Name
Set to
retail_e_commerce.Username
Enter the username
workshop.Password
Enter the password
workshop#2017.In the Connection Configuration area, switch to the Data Integration tab, find the resource group attached to the workspace, and click Test Connectivity in the Connectivity Status column.
NoteIf the MySQL data source connectivity test fails, perform the following steps:
Follow the instructions in the connectivity diagnosis tool.
Check whether an EIP is configured for the VPC that is attached to the resource group. The MySQL data source requires the resource group to have internet access. For more information, see Enable internet access for the resource group.
Click Complete.
Build a synchronization pipeline
In this step, you build a synchronization pipeline to sync E-commerce product and order data to MaxCompute tables. This prepares the data for subsequent processing.
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner and choose to go to the data development page.
icon in the upper-left corner and choose to go to the data development page.At the top of the page, switch to the workspace created for this tutorial. In the navigation pane on the left, click
 to go to the data development - project directory page.
to go to the data development - project directory page.In the Project Directory area, click
 , select New Workflow, and set the workflow name. This tutorial sets it to
, select New Workflow, and set the workflow name. This tutorial sets it to dw_quickstart.On the workflow orchestration page, drag a Zero Load Node and an Offline Synchronization node from the left onto the canvas, and then set their names.
The example node names and their functions in this tutorial are as follows:
Node Type
Node Name
Node Function
 Virtual node
Virtual nodeworkshopUsed to manage the entire user persona analysis workflow, making the data forwarding path clearer. This node is a Dry-run Task and does not require code editing.
 Offline Synchronization Node
Offline Synchronization Nodeods_item_infoUsed to synchronize the product information source table
item_infofrom MySQL to the MaxCompute tableods_item_info. Offline Synchronization Node
Offline Synchronization Nodeods_trade_orderUsed to synchronize the order information source table
trade_orderfrom MySQL to the MaxCompute tableods_trade_order.Manually connect the nodes by dragging lines between them. Set the
workshopnode as the ancestor node for the two offline synchronization nodes. The result should look like the following figure:Workflow scheduling configuration.
In the right-side panel of the workflow orchestration page, click Scheduling Configuration and configure the parameters. This tutorial requires you to configure the following key parameters. You can keep the default values for all other parameters.
Scheduling Configuration Parameter
Description
Scheduling Parameters
Set scheduling parameters for the entire workflow. Inner nodes in the workflow can use them directly.
This tutorial configures it as
bizdate=$[yyyymmdd-1]to get the previous day's date.NoteDataWorks provides scheduling parameters that allow for dynamic parameter input in code. You can define variables in your SQL code using the format
${variable_name}and assign values to these variables in Scheduling Configuration > Scheduling Parameters. For more information about supported formats for scheduling parameters, see Supported formats for scheduling parameters.Scheduling Cycle
This tutorial configures it as
Daily.Scheduling Time
This tutorial sets the Scheduling Time to
00:30. The workflow will start at00:30every day.Recurring Dependency
The workflow has no upstream dependency, so this can be left unconfigured. For unified management, you can click Use Workspace Root Node to attach the workflow to the workspace root node.
The workspace root node is named in the format:
workspace_name_root.
Configure synchronization tasks
Configure the initial node
Configure the product information synchronization pipeline (ods_item_info)
Configure the order data synchronization pipeline (ods_trade_order)
2. Data cleansing
After the data is synchronized from MySQL to MaxCompute, you have two data tables: the product information table ods_item_info and the order information table ods_trade_order. You can use the DataStudio module in DataWorks to cleanse, process, and analyze the data in these tables to generate a daily ranking of the best-selling product categories.
Build a data transformation pipeline
In the navigation pane on the left of DataStudio, click
 to go to the data development page. Then, in the Project Directory area, find the workflow that you created, open the workflow orchestration page, and drag MaxCompute SQL nodes from the component list on the left to the canvas. Then, name the nodes.
to go to the data development page. Then, in the Project Directory area, find the workflow that you created, open the workflow orchestration page, and drag MaxCompute SQL nodes from the component list on the left to the canvas. Then, name the nodes.The example node names and their functions in this tutorial are as follows:
Node Type
Node Name
Node Function
 MaxCompute SQL
MaxCompute SQLdim_item_infoBased on the
ods_item_infotable, processes product dimension data to produce the product basic information dimension tabledim_item_info. MaxCompute SQL
MaxCompute SQLdwd_trade_orderBased on the
ods_trade_ordertable, performs initial cleansing, transformation, and business logic processing on detailed transaction data of orders to produce the transaction order detail fact tabledwd_trade_order. MaxCompute SQL
MaxCompute SQLdws_daily_category_salesBased on the
dwd_trade_ordertable and thedim_item_infotable, aggregates the cleansed and standardized detailed data from the DWD layer to produce the daily product category sales aggregate tabledws_daily_category_sales. MaxCompute SQL
MaxCompute SQLads_top_selling_categoriesBased on the
dws_daily_category_salestable, produces the daily ranking table of best-selling product categoriesads_top_selling_categories.Manually connect the nodes by dragging lines between them and configure the ancestor node for each node. The result should look like the following figure:
NoteIn a workflow, you can set the upstream and downstream dependencies of each node by manually connecting them. You can also use code parsing in a child node to automatically identify node dependencies. This tutorial uses the manual connection method. For more information about code parsing, see Automatic dependency parsing.
Configure data transformation nodes
Configure the dim_item_info node
Configure the dwd_trade_order node
Configure the dws_daily_category_sales node
Configure the ads_top_selling_categories node
3. Debug and run
After you configure the workflow, you must run the entire workflow to verify that the configuration is correct before you publish it to the production environment.
In the navigation pane on the left of DataStudio, click
 to go to the data development page. Then, in the Project Directory area, find the workflow you created.
to go to the data development page. Then, in the Project Directory area, find the workflow you created.In the toolbar, click Run. For Current Run Value, enter the date for the day before the current date (for example,
20250416).NoteIn the workflow node configuration, scheduling parameters provided by DataWorks are used to enable dynamic parameter input in the code. When you debug the node, you must assign a constant value to this parameter for testing.
Click OK to go to the debug run page.
Wait for the run to complete. The expected result is shown in the following figure:

4. Query and visualize data
You have processed the raw test data from MySQL and aggregated it into the ads_top_selling_categories table. You can now query this table to view the analysis results.
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner. In the pop-up page, click .
icon in the upper-left corner. In the pop-up page, click .After My Files, click . Enter a custom File Name and click OK.
On the SQL Query page, configure the following SQL.
SELECT * FROM ads_top_selling_categories WHERE pt=${bizdate};In the upper-right corner, select the MaxCompute data source and click OK.
Click the Run button at the top. On the Cost Estimation page, click Run.
In the query results, click
 to view the results as a chart. You can click
to view the results as a chart. You can click  in the upper-right corner of the chart to customize the chart style.
in the upper-right corner of the chart to customize the chart style. You can also click Save in the upper-right corner of the chart to save it as a card. Then, in the navigation pane on the left, you can click Card (
 ) to view the saved card.
) to view the saved card.
5. Recurring scheduling
By completing the previous steps, you have obtained the sales data for various product categories from the previous day. To retrieve the latest sales data every day, you can publish the workflow to the production environment to run it periodically at a scheduled time.
When you configured the data synchronization and data transformation tasks, you also configured the scheduling parameters for the workflow and its nodes. You do not need to configure them again. You only need to publish the workflow to the production environment. For more information about scheduling configurations, see Node scheduling configuration.
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner. In the pop-up page, click .
icon in the upper-left corner. In the pop-up page, click .In the navigation pane on the left of DataStudio, click
 to go to the data development page. Switch to the project space used in this case. Then, in the Project Directory area, find the workflow you created.
to go to the data development page. Switch to the project space used in this case. Then, in the Project Directory area, find the workflow you created.In the toolbar, click Publish. In the publish panel, click Start Publishing To Production. Wait for the Deployment Package Build and Production Checker steps to complete, and then click Confirm Publish.
After the Publish To Production Environment status changes to Completed, click Go To O&M to go to the Operation Center.

In , you can see the auto-triggered task for the workflow (named
dw_quickstartin this tutorial).To view the details of the auto-triggered tasks for the child nodes in the workflow, right-click the auto-triggered task for the workflow and select View Inner Tasks.

The expected result is as follows:

What to do next
For more information about the operations and parameters for the modules used in this tutorial, see Data Integration, DataStudio (new version), Data Analysis, and Node scheduling configuration.
In addition to the modules introduced in this tutorial, DataWorks also provides other modules, such as Data Modeling, Data Quality, Data Security Guard, and DataService Studio, to offer one-stop data monitoring and O&M.
You can also try other DataWorks tutorials. For more information, see More scenario-based cases/tutorials.