This topic describes how to configure and use JindoFS, and its use scenarios.
Overview
JindoFS is a cloud-native file system that combines the advantages of Object Storage Service (OSS) and local storage. JindoFS is also a next-generation storage system that provides efficient and reliable storage services for cloud computing in E-MapReduce (EMR).
JindoFS supports the block storage mode and cache mode.
JindoFS adopts a heterogeneous multi-backup mechanism. Storage Service provides the data storage capability. Data is stored in OSS to ensure high reliability. Redundant backups are stored in the local cluster to accelerate read operations. Namespace Service manages metadata of JindoFS. In this case, metadata is queried from Namespace Service instead of OSS, which improves query performance. This query method of JindoFS is similar to that of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
- EMR V3.20.0 and later support JindoFS. To use JindoFS, select the related services when you create an EMR cluster.
- This topic describes how to use JindoFS in EMR V3.20.0 to V3.22.0 (V3.22.0 excluded). For more information about how to use JindoFS in EMR V3.22.0 or later, see Use JindoFS in EMR V3.22.0 to V3.26.3.
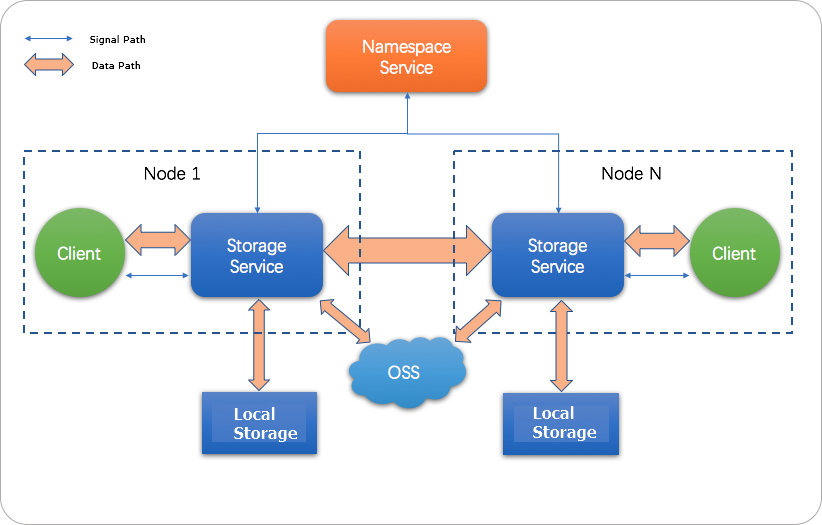
Scenarios
EMR has three storage systems: EMR OssFileSystem, EMR HDFS, and EMR JindoFS. Among them, OssFileSystem and JindoFS store data in the cloud. The following table compares the features of three EMR storage systems and Hadoop support for Alibaba Cloud OSS.
| Feature | Hadoop support for Alibaba Cloud OSS | E-MapReduce OssFileSystem | E-MapReduce HDFS | E-MapReduce JindoFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage capacity | Tremendous | Tremendous | Depending on the EMR cluster scale | Tremendous |
| Reliability | High | High | High | High |
| Factor that affects throughput | Server | I/O performance of caches on disks in the EMR cluster | I/O performance of disks in the EMR cluster | I/O performance of disks in the EMR cluster |
| Metadata query efficiency | Low | Medium | High | High |
| Scale-out operation | Easy | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| Scale-in operation | Easy | Easy | Node decommission required | Easy |
| Data locality | None | Weak | Strong | Medium |
The block storage mode of JindoFS has the following features:
- JindoFS offers tremendous and scalable storage capacity by using OSS as the storage backend. The storage capacity is independent of the EMR cluster scale. The local cluster can be scaled in or out as required.
- JindoFS stores some backup data in the local cluster to accelerate read operations. This improves the throughput by using limited local storage capacity, especially for Write Once Read Many (WORM) solutions.
- JindoFS provides efficient metadata query similar to HDFS. Compared with OssFileSystem, JindoFS saves much time in metadata query. In addition, JindoFS avoids system instability when data and metadata are frequently accessed.
- JindoFS ensures maximal data locality when jobs are executed in the EMR cluster. This reduces the load on network transmission and improves the read performance.
Prepare the environment
- Create an EMR cluster
Select a version from EMR V3.20.0 to V3.22.0 (V3.22.0 excluded). Select SmartData and Bigboot from the optional services. For more information about how to create an EMR cluster, see Create a cluster. Bigboot provides distributed data management and component management services in EMR. Based on Bigboot, SmartData provides JindoFS for the application layer.
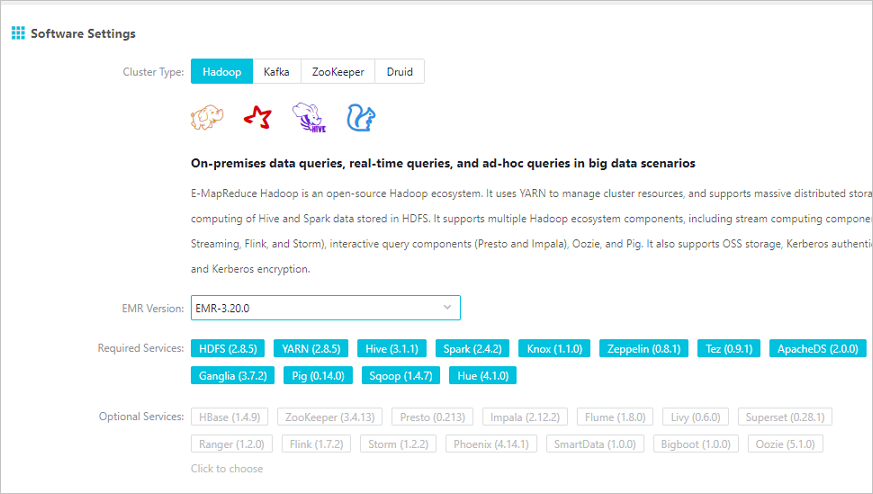
- Configure JindoFS
JindoFS provided by SmartData uses OSS as the storage backend. Therefore, you must configure parameters related to OSS before you use JindoFS. EMR provides the following two configuration methods: 1. Modify parameters related to Bigboot after you create an EMR cluster, and then restart SmartData for the configurations to take effect. 2. Add custom configurations when you create an EMR cluster. In this case, the related services are restarted based on custom parameters after the EMR cluster is created.
- Initialize parameters after the EMR cluster is created
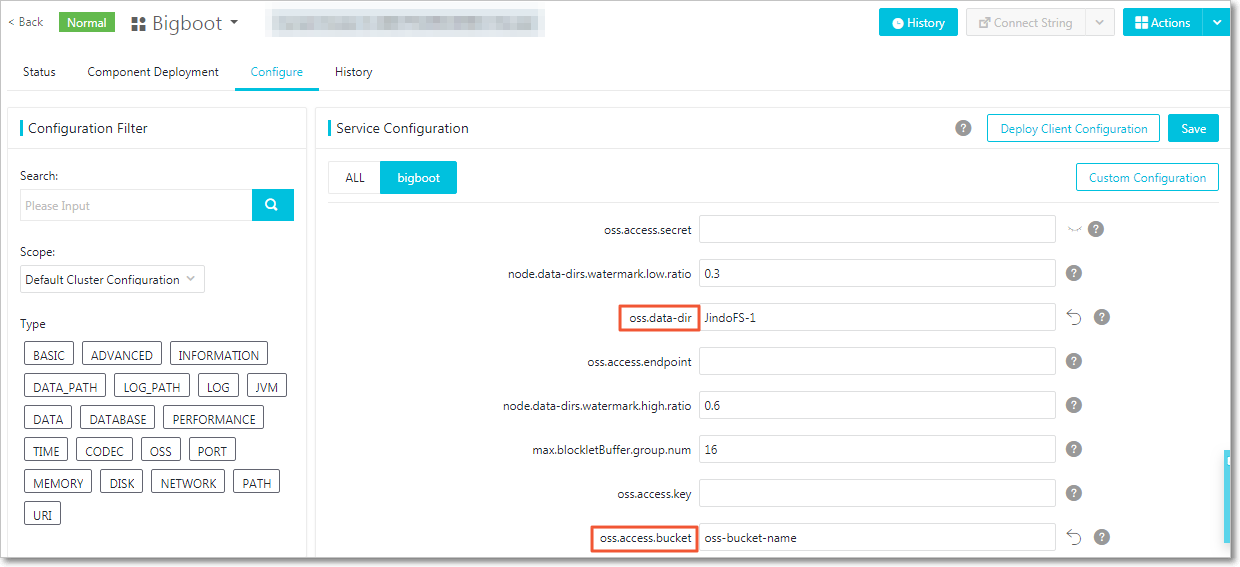
oss.access.bucketspecifies the name of the OSS bucket.oss.data-dirspecifies the directory of JindoFS in the OSS bucket. The directory only serves as the storage backend for JindoFS. The data generated in the directory cannot be damaged. The directory is automatically created when JindoFS writes data. You do not need to create the directory in advance.oss.access.endpointspecifies the region where the OSS bucket resides.oss.access.keyspecifies the AccessKey ID used to access the OSS bucket.oss.access.secretspecifies the AccessKey secret used to access the OSS bucket.
We recommend that you store data in an OSS bucket that is in the same region as your EMR cluster. This ensures high performance and stability. In this case, you do not need to configure the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret because the OSS bucket allows password-free access from the EMR cluster.
You can configure all parameters related to JindoFS in Bigboot, as shown in the following figure. The parameters framed in red are required.
 Note JindoFS supports multiple namespaces. A namespace named test is used in this topic.
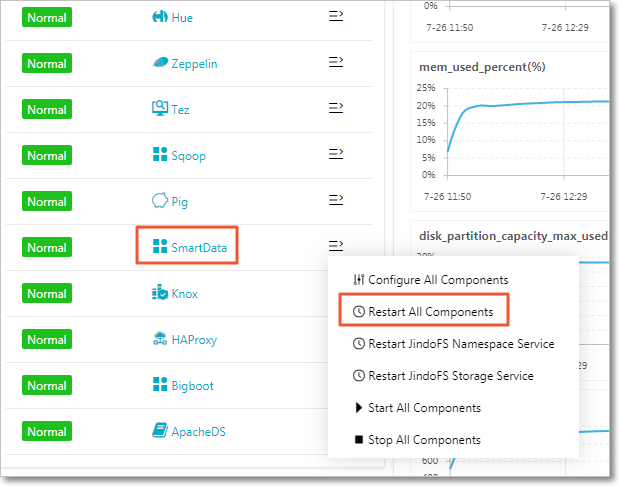
Note JindoFS supports multiple namespaces. A namespace named test is used in this topic.Save and deploy the JindoFS configuration. Restart all components in SmartData to use JindoFS.
- Add custom configurations when you create an EMR cluster
You can add custom configurations when you create an EMR cluster. Assume that you want to create an EMR cluster in the same region as an OSS bucket to access OSS without using an AccessKey pair. Turn on Custom Software Settings as shown in the following figure. Add the following configurations including
oss.data-dirandoss.access.bucketto the field in the Advanced Settings section:[ { "ServiceName":"BIGBOOT", "FileName":"bigboot", "ConfigKey":"oss.data-dir", "ConfigValue":"jindoFS-1" }, { "ServiceName":"BIGBOOT", "FileName":"bigboot", "ConfigKey":"oss.access.bucket", "ConfigValue":"oss-bucket-name" } ]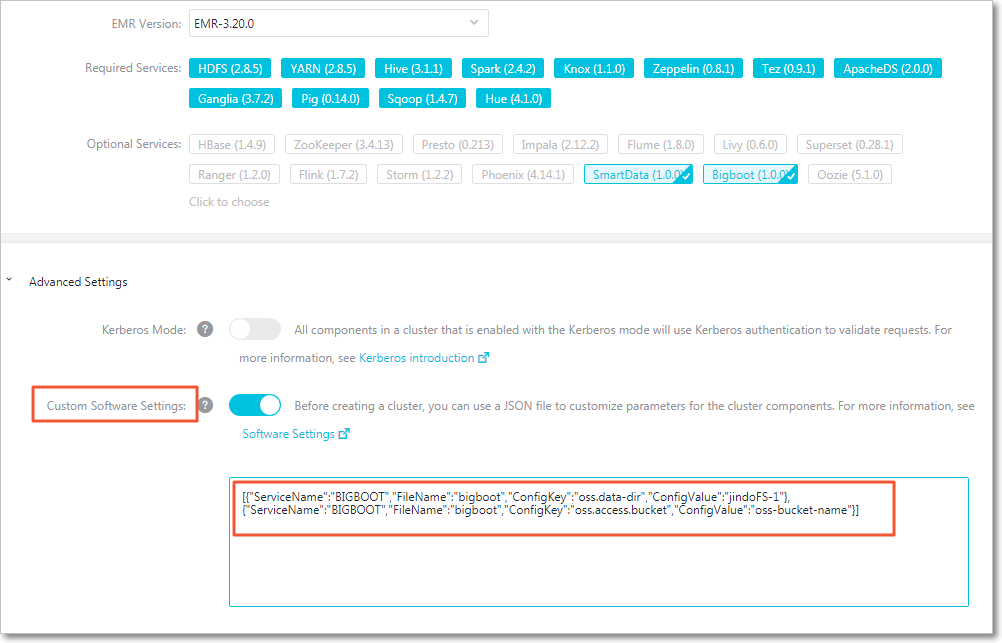
- Initialize parameters after the EMR cluster is created
Use JindoFS
hadoop fs -ls jfs:/// hadoop fs -mkdir jfs:///test-dirhadoop fs -put test.log jfs:///test-dir/Control disk space usage
JindoFS uses OSS as the data storage backend, which allows you to store large volumes of data. However, the capacity of local disks is limited. JindoFS automatically deletes cold data in local disks. Alibaba Cloud uses the node.data-dirs.watermark.high.ratio and node.data-dirs.watermark.low.ratio parameters to adjust the space usage of local disks. The values of both parameters are in the range of 0 to 1 to indicate the percentage of space usage. JindoFS uses the total storage capacity of all data disks by default. The node.data-dirs.watermark.high.ratio parameter specifies the upper limit of space usage on each disk. Less frequently accessed data stored on a disk is released if the space used by JindoFS reaches the upper limit. The node.data-dirs.watermark.low.ratio parameter specifies the lower limit of space usage on each disk. After the space usage of a disk reaches the upper limit, less frequently accessed data is released until the space usage of the disk reaches the lower limit. You can configure the upper limit and lower limit to adjust and assign disk space to JindoFS. Make sure that the upper limit is greater than the lower limit.
Configure the storage policy
JindoFS provides multiple storage policies to meet different storage needs. The following table lists four available storage policies for a directory.
| Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| COLD | Data has a backup in OSS but no backups in the local cluster. This policy is suitable for storing cold data. |
| WARM |
The default storage policy. Data has a backup in OSS and a backup in the local cluster. The local backup can accelerate read operations. |
| HOT | Data has a backup in OSS and multiple backups in the local cluster. Local backups can accelerate read operations on hot data. |
| TEMP | Data has a backup in the local cluster but no backups in OSS. This policy is suitable for storing temporary data. The local backup can accelerate read and write operations on the temporary data. However, this may lower data reliability. |
JindoFS provides a command-line tool Admin to configure the storage policy of a directory. The default storage policy is WARM. New files are stored based on the storage policy configured for the parent directory. Run the following command to configure the storage policy:
jindo dfsadmin -R -setStoragePolicy [path] [policy]Run the following command to obtain the storage policy configured for a directory:
jindo dfsadmin -getStoragePolicy [path]The Admin tool provides the archive command to archive cold data.
This command allows you to explicitly evict local blocks. Assume that Hive partitions a table by day. If the data generated a week ago in partitioned tables is infrequently accessed, you can run the archive command on the directory that stores such data on a regular basis. Then, the backups stored in the local cluster are evicted, whereas the backups in OSS are retained.
Run the following archive command:
jindo dfsadmin -archive [path]


