To enable public and private IPv6 communication within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), create an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance with an IPv6 address in an IPv6-enabled VPC and vSwitch. This topic describes how to assign, configure, and use an IPv6 address for an ECS instance.
Note The scarcity of IPv4 addresses often forces network engineers to spend significant time resolving issues like address conflicts. In contrast, IPv6, with its vast address space, solves the network address scarcity problem and removes many barriers for devices connecting to the internet.
Limitations
Regions that support IPv6 Gateway
Note IPv6 Gateway is a gateway for IPv6 traffic in a VPC. By default, an assigned IPv6 address only provides private network access. You can enable public network communication by purchasing IPv6 Internet Bandwidth for the IPv6 address in an IPv6 Gateway. For more information, see IPv6 Gateway.
Area | Regions |
Asia Pacific - China | China (Qingdao), China (Beijing), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Hohhot), China (Ulanqab), China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Fuzhou - Local Region), China (Shenzhen), China (Heyuan), China (Guangzhou), China (Chengdu), and China (Hong Kong) |
Asia Pacific - Others | Philippines (Manila), Singapore, Japan (Tokyo), South Korea (Seoul), Indonesia (Jakarta), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), and Thailand (Bangkok) |
Europe & Americas | US (Virginia), US (Silicon Valley), Germany (Frankfurt), UK (London), and Mexico |
Middle East | SAU (Riyadh - Partner Region) |
ECS instance families that do not support IPv6
The ic5 intensive-computing instance family
The se1 memory-optimized instance family
The d1 big data instance family
The i2g and i1 local SSD-equipped instance families
The hfc5 (high-frequency compute-optimized) and hfg5 (high-frequency general-purpose) instance families
The ebmg5 (general-purpose) and ebmr5s (memory-optimized network-enhanced) ECS Bare Metal Instance families
The xn4, n4, mn4, and e4 previous-generation shared instance families
The scch5 high-frequency Super Computing Cluster instance family
The gn5 GPU-accelerated computed optimized instance family
The n1, n2, and e3 shared instance families
The sn2 and sn1 general-purpose instance families
Limits on the number of assignable IPv6 addresses for an ECS instance
The number of assignable IPv6 addresses per instance depends on two factors: the number of attachable ENIs and the number of IPv6 addresses allowed per ENI:
The number of IPv6 addresses that can be assigned to a single ENI depends on the instance type. For more information, see the Number of IPv6 addresses per ENI column in Instance families.
The number of ENIs that can be attached to a single instance depends on the instance type. For more information, see the Elastic Network Interface column in Instance families.
Procedure
Note You can use one-click deployment to quickly complete the following operations.
Step 2: Assign an IPv6 address
To allow an ECS instance to communicate with other instances or external networks over the IPv6 protocol, assign an IPv6 address to it.
Assign an IPv6 address to an existing instance
-
Go to ECS console - Instances.
-
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage. 
Locate the target ECS instance and click its instance ID to open the instance details page. In the All Actions section, choose .

In the Manage Secondary Private IP Addresses dialog box, click Increase in the IPv6 section.
If you do not need to specify an IPv6 address, you can leave the IPv6 address field empty. The system automatically assigns an address.
Click Confirm.
Assign an IPv6 address when creating an instance
When creating an instance, note the following settings. For information about other configurations, see Create an instance using the custom launch tab:
Network and Zone: Select a VPC and a vSwitch that have IPv6 enabled.
Instance: Click View more specification parameters, filter for instance types that support IPv6-supported, and then select an instance type.
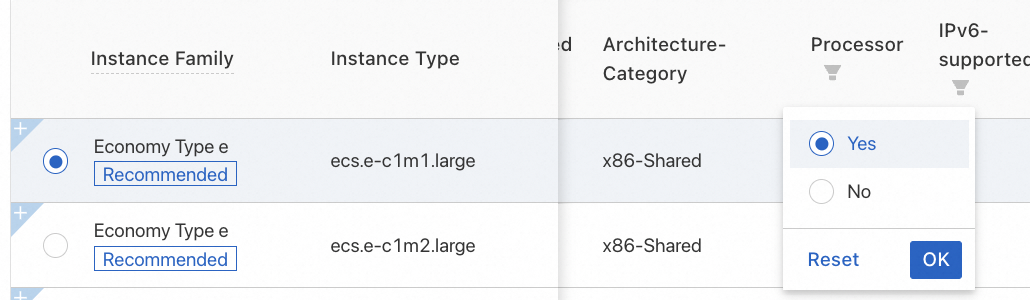
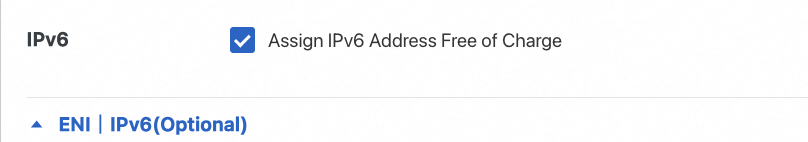
Network and Security Groups: Click Elastic ENI | IPv6(Optional) and select Assign IPv6 Address Free of Charge.
After the address is assigned, you can view the IP address details in the ECS console. For more information, see IP addresses.
Step 3: Configure the IPv6 address
To allow the operating system to recognize and use the IPv6 address, configure it on the instance's network interface card (NIC).
Some images automatically configure and recognize IPv6 addresses. Follow these steps to check if the operating system has already recognized the IPv6 address.
Linux instances
Connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Connect to Linux.
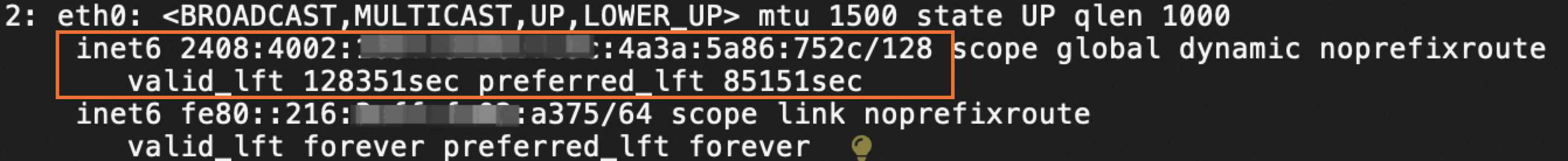
Run the ip -6 addr show or ifconfig command.
If the output shows one global unicast address and one link-local address, as in the figure below, the address is recognized, and you can skip the rest of this step. Otherwise, continue with the following steps.
Windows instances
Connect to the Windows instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Windows instance using Workbench.
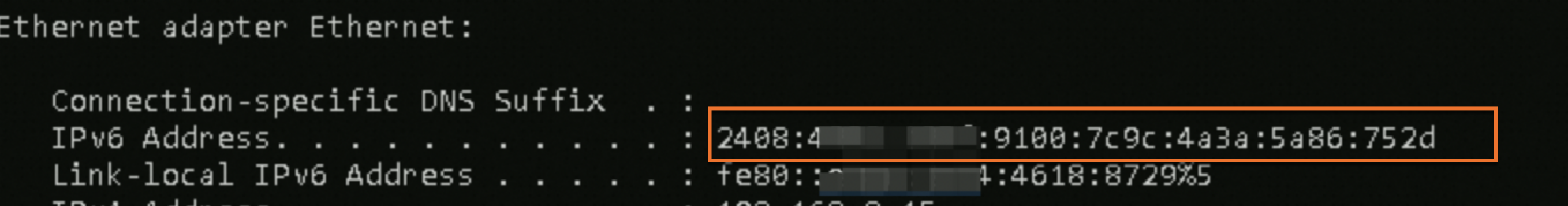
Open the command line interface and run the ipconfig command.
If the output shows one global unicast address and one link-local address, as in the figure below, the address is recognized, and you can skip the rest of this step. Otherwise, continue with the following steps.
Configure the IPv6 address.
Important Automatic configuration requires Cloud Assistant to be installed. If your instance does not support Cloud Assistant or you prefer not to install it, configure the IPv6 address manually.
(Recommended) Automatically configure the IPv6 address
Prerequisites
Ensure the Cloud Assistant agent is installed on the instance. If not, see Install the Cloud Assistant Agent.
This method applies only to the following operating systems: Alibaba Cloud Linux 2/3, CentOS 6/7/8, Red Hat 6/7, Anolis OS, Fedora, Ubuntu 14/16/18/20, Debian 8/9/10/11, SUSE 11/12/15, OpenSUSE 15/42, and FreeBSD 11.
Important This configuration process uses Cloud Assistant and may restart the network interface or services, causing a brief network interruption. Proceed with caution.
Procedure
Connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using Workbench.
Run the following command to configure the IPv6 address.
Note By default, running this command checks if the ecs-utils-ipv6 plugin is installed locally and if it is the latest version. If it is not installed or the version is outdated, the system automatically downloads and installs the latest plugin version.
sudo acs-plugin-manager --exec --plugin=ecs-utils-ipv6
Manual configuration (Linux)
Connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Connect to Linux.
Run the ip addr | grep inet6 or ifconfig | grep inet6 command to check whether the IPv6 service is enabled on the instance.
If no inet6 information is returned, the IPv6 service is disabled and must be enabled.
How to enable the IPv6 service
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2/3
Edit the /etc/sysctl.conf configuration file.
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
Press I to enter edit mode. Find the following parameters and change the value from 1 to 0.
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1
To enable a specific network interface, modify the settings as shown in the following example.
net.ipv6.conf.eth0.disable_ipv6 = 0
After making the changes, press Esc to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press Enter to save and exit.
Check for differences between /etc/sysctl.conf and the version in initramfs.
diff -u /etc/sysctl.conf <(lsinitrd -f /etc/sysctl.conf)
Note Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 uses an initial RAM file system (initramfs). If the /etc/sysctl.conf file in initramfs differs from the main IPv6 configuration file, the system may apply an unintended configuration.
If the two files differ, run the following command to regenerate initramfs.
sudo dracut -v -f
Restart the ECS instance for the changes to take effect. For more information, see Restart an instance.
Run ip addr | grep inet6 or ifconfig | grep inet6 to verify that IPv6 is enabled.
If inet6 information is returned, the IPv6 service is successfully enabled.
CentOS 6/7
To modify the /etc/modprobe.d/disable_ipv6.conf configuration file, run the following command.
vi /etc/modprobe.d/disable_ipv6.conf
Press I to enter edit mode and change options ipv6 disable=1 to options ipv6 disable=0.
After making the changes, press Esc to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press Enter to save and exit.
Modify the /etc/sysconfig/network file.
vi /etc/sysconfig/network
Press I to enter edit mode and change NETWORKING_IPV6=no to NETWORKING_IPV6=yes.
After making the changes, press Esc to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press Enter to save and exit.
(Optional) Run the following commands in sequence to reload the IPv6 module.
Note This step is required for CentOS 6. You can skip it for other versions.
modprobe ipv6 -r
modprobe ipv6
lsmod | grep ipv6
If the output is similar to the following, the IPv6 module is loaded successfully.
ipv6 xxxxx 8
Note The value in the third column cannot be 0. If it is, you must re-enable the IPv6 service.
Run the following command to modify the /etc/sysctl.conf file.
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
Press I to enter edit mode. Find the following parameters and change the values from 1 to 0.
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1
After making the changes, press Esc to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press Enter to save and exit.
Run the following command to apply the changes.
sudo sysctl -p
Debian 8/9
Run the following command to modify the /etc/default/grub configuration file.
vi /etc/default/grub
Press the I key to enter edit mode and delete ipv6.disable=1.
After you make the changes, press the Esc key to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press the Enter key to save the file and exit.
Run the following command to modify the /boot/grub/grub.cfg configuration file.
vi /boot/grub/grub.cfg
Press the I key to enter edit mode and delete ipv6.disable=1.
After you make the changes, press the Esc key to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press the Enter key to save the file and exit.
Restart the Linux instance. For more information, see Restart an instance.
Run the following command to modify the /etc/sysctl.conf configuration file.
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
Press the I key to enter edit mode. Find the following parameters and change their values from 1 to 0.
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 0
net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 0
After you make the changes, press the Esc key to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press the Enter key to save the file and exit.
Run the following command for the configuration to take effect.
sudo sysctl -p
Ubuntu 14/16 and OpenSUSE 42
Run the following command to modify the vi /etc/sysctl.conf configuration file.
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
Press the I key to enter edit mode. Find the following parameters and change their values from 1 to 0.
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 0
net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 0
After you make the changes, press the Esc key to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press the Enter key to save the file and exit.
Run the following command for the configuration to take effect.
sysctl -p
FreeBSD 11
Run the following command to modify the /etc/rc.conf configuration file.
vi /etc/rc.conf
Press the I key to enter edit mode and add the ipv6_activate_all_interfaces="YES" line.
After you make the changes, press the Esc key to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press the Enter key to save the file and exit.
Run the following command to restart the network for the configuration to take effect.
/etc/netstart restart
SUSE 11/12
Run the following command to modify the /etc/modprobe.d/50-ipv6.conf configuration file.
vi /etc/modprobe.d/50-ipv6.conf
Press the I key to enter edit mode and delete the install ipv6 /bin/true line.
After you make the changes, press the Esc key to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press the Enter key to save the file and exit.
Run the following command to modify the vi /etc/sysctl.conf configuration file.
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
Press the I key to enter edit mode. Find the following parameters and change their values from 1 to 0.
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 0
net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 0
After you make the changes, press the Esc key to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press the Enter key to save the file and exit.
Run the following command for the configuration to take effect.
sysctl -p
If information related to inet6 is returned, the IPv6 service is enabled. You must configure the IPv6 address.
Configure the IPv6 address.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2/3, CentOS 6/7, and Red Hat 6/7
Run the following command to modify the NIC configuration file.
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
Replace eth0 with the actual NIC name. After you make the changes, save the file and exit.
Press the I key to enter edit mode and add the following configuration lines to the file.
DHCPV6C=yes
IPV6INIT=yes
After you make the changes, press the Esc key to exit edit mode. Then, enter :wq and press the Enter key to save the file and exit.
Restart the ECS instance for the changes to take effect. For more information, see Restart an instance.
CentOS 8
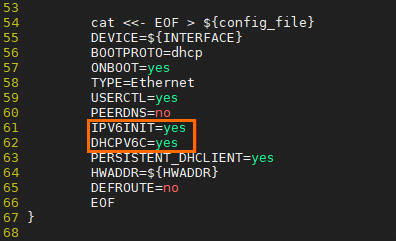
Check whether the NIC configuration file contains the IPV6INIT=yes and DHCPV6C=yes lines. If the file does not contain these lines, you must manually add them before you proceed to the next step.
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
Replace eth0 with the actual NIC identifier. After you make the changes, save the file and exit.
Disable the cloud-init feature that modifies the NIC configuration file in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory.
Note An assigned IPv6 address is automatically configured. However, the configuration may be lost after a restart. To prevent this issue, you must disable the cloud-init feature that modifies the NIC configuration file.
Run vi /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg to open the NIC configuration file.
vi /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
Add the following information before the Example datasource config section:
network:
config: disabled
After you make the changes, save the file and exit.
Restart the ECS instance for the changes to take effect. For more information, see Restart an instance.
Debian 8/9/10/11 and Ubuntu 16
Run vi /etc/network/interfaces to open the NIC configuration file and add the following lines to the file:
iface eth0 inet6 dhcp
Replace eth0 with the actual NIC name. After you make the changes, save the file and exit.
Restart the ECS instance for the changes to take effect. For more information, see Restart an instance.
Ubuntu 18/20
Disable the cloud-init feature that modifies the NIC configuration file in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory.
Note An assigned IPv6 address is automatically configured. However, the configuration may be lost after a restart. To prevent this issue, you must disable the cloud-init feature that modifies the NIC configuration file.
Run vi /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg to open the NIC configuration file.
vi /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
Add the following information before the Example datasource config section:
network:
config: disabled
After you make the changes, save the file and exit.
Restart the ECS instance for the changes to take effect. For more information, see Restart an instance.
Ubuntu 14
Run vi /etc/network/interfaces to open the NIC configuration file and add the following lines to the file:
iface eth0 inet6 dhcp
Replace eth0 with the actual NIC name. After you make the changes, save the file and exit.
Restart the ECS instance for the changes to take effect. For more information, see Restart an instance.
FreeBSD 11
Run the vi /etc/rc.conf command to open the NIC configuration file and add the following lines to the file:
ipv6_enable="YES"
ipv6_ifconfig_vtnet0="<IPv6 address> <Subnet prefix length>"
Replace vtnet0 with the actual NIC name. After you make the changes, save the file and exit.
Add the following lines to the file. After you make the changes, save the file and exit.
ip6addrctl_enable="YES"
ipv6_activate_all_interfaces="YES"
ipv6_network_interfaces="auto"
After the modification, the configuration file is similar to the following example:
hostname="Aliyun"
sshd_enable="YES"
dumpdev="NO"
ipv6_enable="YES"
ip6addrctl_enable="YES"
ip6addrctl_policy="ipv4_prefer"
ipv6_activate_all_interfaces="YES"
ipv6_network_interfaces="auto"
ifconfig_lo0="inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0"
ifconfig_vtnet0="inet 192.168.XX.XX netmask 255.255.255.0"
ipv6_ifconfig_vtnet0="2001:XXXX:4:4:4:4:4:4 prefixlen 64"
defaultrouter="192.168.XX.XX"
hostname="freebsd"
Restart the ECS instance for the changes to take effect. For more information, see Restart an instance.
Anolis OS 7.9/8.4, CentOS Stream, and Fedora
Check whether the NIC configuration file contains the IPV6INIT=yes and DHCPV6C=yes lines. If the file does not contain these lines, you must manually add them.
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
Replace eth0 with the actual NIC name. After you make the changes, save the file and exit.
Restart the ECS instance for the changes to take effect. For more information, see Restart an instance.
Manual configuration (Windows)
Remotely connect to the Windows instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Windows instance using Workbench.
Open the command line interface and run the ipconfig command to check whether the IPv6 service is enabled on the instance.
If no information related to inet6 is returned, the IPv6 service is disabled. You must enable the IPv6 service.
How do I enable the IPv6 service?
Choose .
Click the current network connection name to open the status dialog box. Then, click Properties.
Select Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6).
For Windows Server 2008/2012/2016/2019/2022, perform the following steps:
If the IPv6 protocol checkbox is not selected, select it and click OK.
For Windows Server 2003, perform the following steps:
The steps vary based on whether the IPv6 protocol exists.
If the IPv6 protocol exists:
Select Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) and click OK.
If the IPv6 protocol does not exist:
On the Local Area Connection Properties page, click Install. On the Network Component Type page, select .
On the Select Network Protocol page, select to complete the installation.
Select Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) and click OK.
If information related to inet6 is returned, the IPv6 service is enabled. You must configure the IPv6 address.
Configure the IPv6 address.
On the instance details page, retrieve the generated IPv6 address.
Configure the IPv6 address.
For Windows Server 2008/2012/2016, perform the following steps:
Go to .
Click the current network connection. In the status dialog box, click Properties.
Select .
Select Use the Following IPv6 Address, enter the IPv6 address, subnet prefix length, and IPv6 gateway, and then click OK.
(Optional) To attach multiple IPv6 addresses, on the Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IP) Properties page, click Advanced and then click Add to perform a batch operation. When you are finished, click OK.
For Windows Server 2003, perform the following steps:
Go to to find the current network connection name. For example, the name may be Local Area Connection 2.
On the Windows desktop, press the Win+R key combination to open the Run dialog box. Enter cmd and click OK to open the command line interface.
Add the IPv6 address.
To add a single IPv6 address, run the following command:
netsh interface ipv6 add address "Local Area Connection 2" <IPv6 address>
To add multiple IPv6 addresses, run the following commands:
netsh interface ipv6 add address "Local Area Connection 2" <IPv6 address 1>
netsh interface ipv6 add address "Local Area Connection 2" <IPv6 address 2>
Run the following command to add a default route.
netsh interface ipv6 add route ::/0 "Local Area Connection 2" <IPv6 gateway>
(Conditional) If your instance runs Linux, perform this step.
Run the following command to check if the multi-ENI configuration tool is installed.
ls /sbin/eni-ifscan
If the command returns output, the tool is pre-installed, and you must modify the eni-function file.
Note Because this tool lacks default IPv6 support, the system does not automatically recognize the IPv6 network interface, causing the address to be lost after a restart.

How to modify the eni-function file
Run the following command to modify the eni-function file.
vim /etc/eni_utils/eni-function
Press I to enter edit mode. Change IPV6INIT=no to IPV6INIT=yes, and add the DHCPV6C=yes line. Then, save and exit.
Verification: If the command output of ifconfig or ipconfig is the same as the result in Step 1, the configuration is successful.
The ECS instance can now communicate over its private IPv6 address. You can test the private connectivity as follows.
Test private connectivity
Note To test IPv6 network connectivity, you must ensure that both the client and server support and are configured for IPv6. In this example, for two ECS instances to communicate, both ECS01 and ECS02 must have IPv6 configured.
On instance ECS01, run the ping6 <ECS02_private_IPv6_address> command to test private communication with instance ECS02.
If you receive reply packets, communication is successful. The test confirms that IPv6 private communication from ECS01 to ECS02 is working.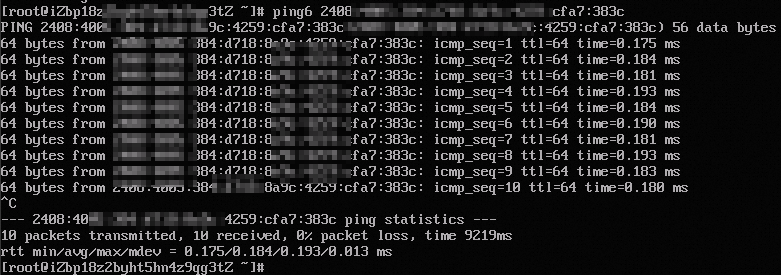
On instance ECS02, run the ping6 <ECS01_private_IPv6_address> command to test private communication with instance ECS01.
If you receive reply packets, communication is successful. The test confirms that IPv6 private communication from ECS02 to ECS01 is working.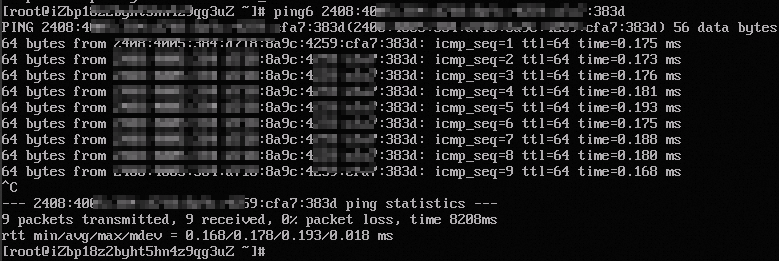
Step 4: Enable IPv6 Internet bandwidth
By default, an ECS instance's IPv6 address only provides private network access. To allow public internet access to and from the IPv6 address, enable IPv6 Internet Bandwidth by following these steps.
Log on to the VPC console.
In the navigation pane, choose .
- In the top navigation bar, select the region where the IPv6 gateway is deployed.
On the IPv6 Gateway page, find the IPv6 gateway for the instance's VPC, and then click the IPv6 gateway ID.
On the details page of the IPv6 gateway, click the IPv6 Internet Bandwidth tab, find the target IPv6 address, and then click Enable Internet Bandwidth in the Actions column.
On the IPv6 Internet Bandwidth (Pay-As-You-Go) page, configure the Internet bandwidth based on the following information, and then click Buy Now and complete the payment.
Parameter | Description |
Traffic | Select a billing method for the Internet bandwidth. The following billing methods are supported: pay-by-bandwidth and pay-by-traffic. For more information, see IPv6 gateway billing. |
Bandwidth | Adjust the peak bandwidth as needed. |
Billing Cycle | The billing cycle of the Internet bandwidth. The billing cycle can be Day or Hour. If you select pay-by-bandwidth, the billing cycle is Day. If you select pay-by-traffic, the billing cycle is Hour.
|
After you enable IPv6 Internet Bandwidth, you can test public IPv6 connectivity.
Note To test IPv6 network connectivity, you must ensure that both the client and server support and are configured for IPv6.
ping -6 aliyun.com
If the system returns output similar to the following figure, the network connection is successful.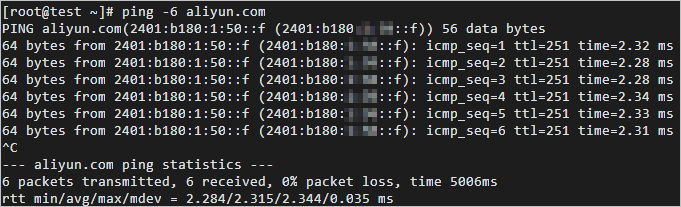
Note In this example, the website aliyun.com supports IPv6. After your ECS instance is configured, you can access aliyun.com over IPv6.
Other operations
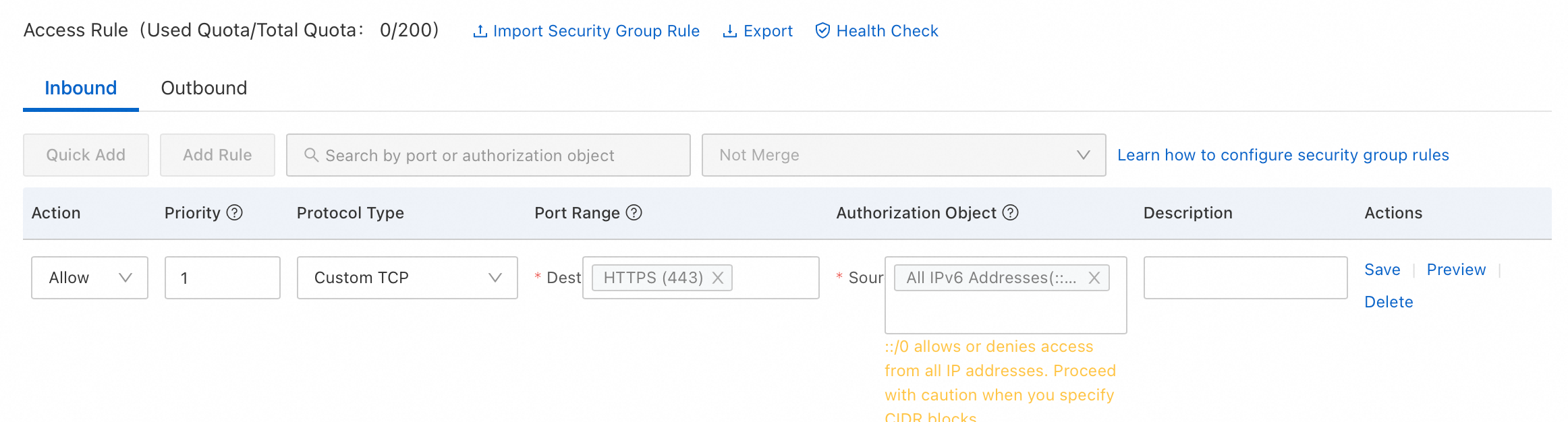
Add IPv6 security group rules
IPv4 and IPv6 communication are independent. If the current security group rules are insufficient for your needs, configure new IPv6 rules for your ECS instance to enhance network security.
How to add IPv6 security group rules
-
Go to ECS console - Security Groups.
-
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage. 
Find the target security group and click Manage Rules in the Operation column.
On the security group details page, in the Rules section, select Inbound or Outbound.
Add a security group rule. For more information, see Add a security group rule.
Note You can set Source to an IPv6 address range, such as 2001:db8:1234:1a00::***. For more information, see Security group rules.
Delete an assigned IPv6 address
If an IPv6 address is no longer needed on your ECS instance, you can delete it. You can still use the IPv4 address after deleting the IPv6 address. This section describes how to delete an IPv6 address from the ECS console.
Important Make sure that the instance is in the Running or Stopped state.
Procedure
-
Go to ECS console - Elastic Network Interfaces.
-
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage. 
On the ENIs page, find the ENI that is attached to the target instance and has an assigned IPv6 address. In the Operation column, click Manage ENI IP Addresses.
In the Manage ENI IP Addresses dialog box, click the  icon to the right of the target IPv6 address.
icon to the right of the target IPv6 address.
Click Confirm.
References
If an IPv6 address no longer requires internet access, you can release its Internet bandwidth. For more information, see Delete IPv6 Internet bandwidth.
You can manage IPv6 traffic within your VPC by adding and managing IPv6 routes in a route table. For more information, see Create and manage IPv6 routes.










 icon to the right of the target IPv6 address.
icon to the right of the target IPv6 address.


