This topic describes how to use the Authoritative Zone feature of HTTPDNS to recover your service when public domain name resolution for your app or IoT device is unavailable.
Scenarios
Public DNS resolution fails for your domain names or for third-party domain names on which your business depends.
A domain name is hijacked on the Internet.
A carrier's recursive DNS server is malfunctioning and unavailable.
The public authoritative DNS server that hosts the domain name fails.
How it works
Disaster recovery and restoration within seconds
If DNS resolution for a critical domain name fails for your app or IoT device, the device cannot obtain the correct IP address. This can happen if the authoritative DNS server is down, or if the domain name is hijacked or polluted. You can use the Authoritative Zone feature to quickly restore normal DNS resolution:
Fast switching: In the Authoritative Zone of HTTPDNS, operations and maintenance (O&M) engineers can immediately add a DNS record for the faulty domain name to the Authoritative Zone.
Instant effect: The Authoritative Zone has the highest priority in the internal logic of HTTPDNS. This change takes effect immediately for all devices that use an encrypted protocol and include your Account ID to send resolution requests to HTTPDNS. The resolution path is switched and service traffic is redirected within seconds. This allows your service to recover.

Prioritized internal matching for resolution requests
When an app or IoT device sends a DNS resolution request to HTTPDNS, the system first checks if the domain name is configured in your Authoritative Zone.
Hit in the Authoritative Zone: If the requested domain name matches a record configured in the Authoritative Zone, HTTPDNS directly returns the IP address configured in the Authoritative Zone to the device. This process bypasses traditional recursive queries, potential network latency, and waits for cache refreshes. This provides a response within seconds and is ideal for disaster recovery.
Miss in the Authoritative Zone: For a domain name that is not configured in the Authoritative Zone, HTTPDNS acts as a high-performance recursive server. It performs a standard recursive query (from the root server to the TLD name server and then to the authoritative DNS server) to obtain and return the IP address.
Prerequisites
You must connect your app or IoT device to HTTPDNS using an encrypted protocol. For more information, see the following procedure.
Procedure
Step 1: Connect to HTTPDNS
Activate the service on the Alibaba Cloud DNS - HTTPDNS for Mobile page.
Configure the connection. Go to the HTTPDNS > Access Configuration page, click Create AccessKey Pair, and select Method 1: SDK-based access. For more information, see Access configuration.
Step 2: Configure the Authoritative Zone
Add a domain name. On the HTTPDNS for Mobile - Built-in Authoritative Zone page, click Add Zone to add the domain name that is experiencing a resolution failure.
Add a DNS record. In the Actions column, click the Settings button. On the Settings page, click Add Record.
NoteIf you are unsure of the destination IP address for the failed domain name, you can use the HTTPDNS for Mobile Resolution Logs feature provided by HTTPDNS. Find a previously successful IP address for the domain name from the resolution acknowledgements. Then, configure this IP address as the value for the DNS record in the Authoritative Zone.
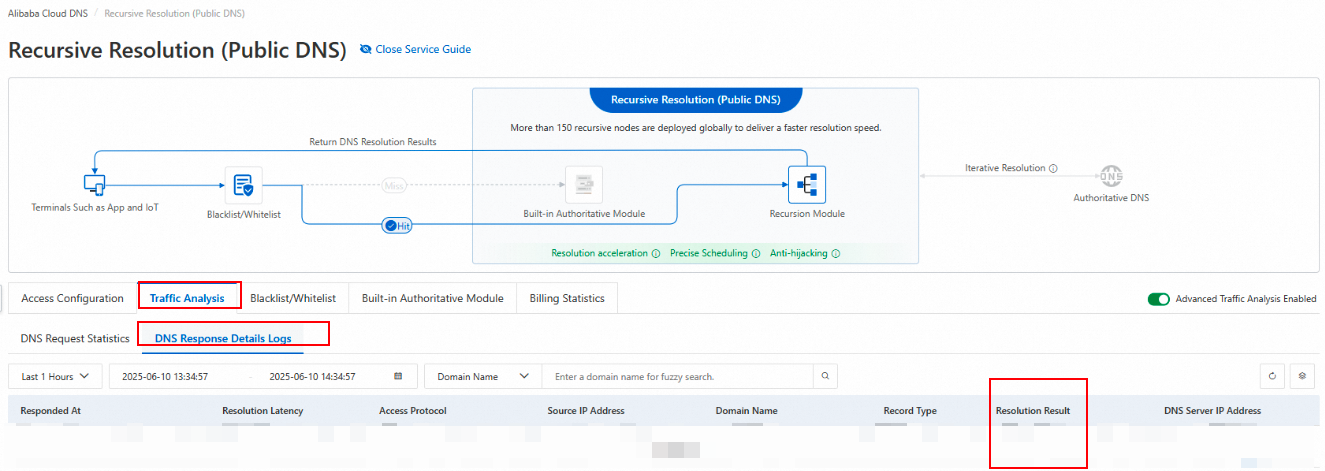
Set the effective scope. Click the Effective Scope button next to the target domain name. On the Zone Settings page, select the effective scope for the domain name. Select your Account ID and submit the form.
Step 3: Verify the resolution recovery
Analyze network traffic
Check whether the Resolution Result for the Domain Name for Resolution that previously failed has returned to normal.
Check your service to verify that the failure is resolved.