Database Gateway allows you to connect on-premises databases or databases that are hosted on third-party clouds to Alibaba Cloud services. You do not need to use public IP addresses of databases to establish connections. This prevents possible security risks. In Data Management (DMS), you can use Database Gateway to register on-premises databases or databases that are hosted on third-party clouds and then manage these databases.
Background information
You can connect an on-premises database or a database that is hosted on a third-party cloud to Alibaba Cloud by using one of the following methods. However, each of these methods has limits.
Use a leased line, a VPN gateway, or a Smart Access Gateway (SAG) instance: This method is not suitable for individual users due to high costs.
Expose the service port of the desired database to the Internet: This method causes potential security risks.
Use a user-created proxy to forward service requests: This method does not ensure high stability and requires users to master advanced technical skills, which increases costs.
To resolve the preceding issues, DMS allows you to use Database Gateway to register on-premises databases or databases that are hosted on third-party clouds. You do not need to use the public IP addresses of the databases to establish connections. Database Gateway also encrypts data transmission. For more information about Database Gateway, see What is Database Gateway?
Procedure
- Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, click Solution. In the left-side navigation pane, click Database gateway.
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose All functions > Solution > Database gateway.
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose All functions > Solution > Database gateway. In the upper-left corner, select the region where the database is deployed. China (Hangzhou) is selected by default. Then, click Create Gateway.
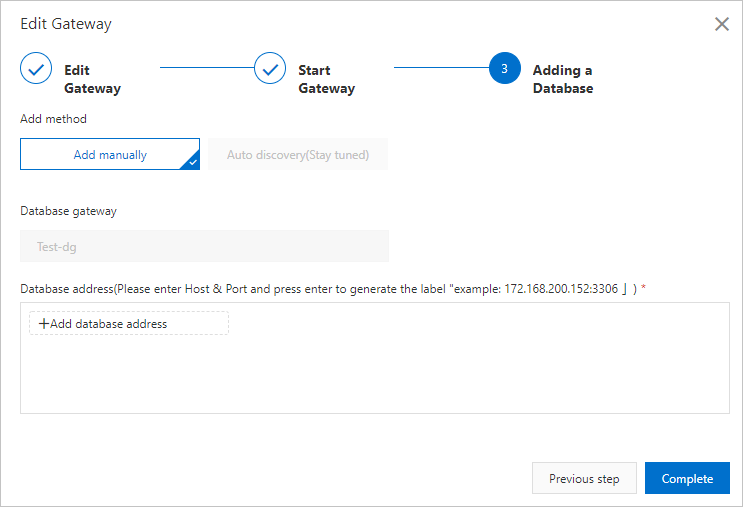
In the Create Gateway step of the wizard that appears, specify Gateway Name and Note. Then, click Next step.
Install a Database Gateway agent. Select an installation method based on the type of your operating system. If you use a Windows operating system, click Download gateway. If you use other operating systems, copy and paste the command to the machine where the Database Gateway agent is to be installed. Then, press Enter to run the command. If the Database Gateway agent is started successfully, you are redirected to the Adding a Database wizard page. You can also click Next step to navigate to this page.
NoteDatabase Gateway is available for free. You must make sure that the machine where your Database Gateway agent is deployed meets the following requirements:
The machine can connect to the database that is to be accessed. If the machine and the database are deployed in the same internal network, the network latency is reduced.
The machine can access the Internet. No public IP address is required. The service port does not need to be exposed to the Internet. The machine does not need to be accessed by users over the Internet.
Add a database. You can click Add database address to add a database to the database gateway. Alternatively, you can add a database later. For more information about how to add a database, see the procedure in Create a database gateway.
Log on to the DMS console. In the upper-left corner of the page, click
 to add a database instance.
to add a database instance. In the Add Instance dialog box, click Third-party Cloud/Self-managed. Then, select a database type.
In the Add Instance dialog box, specify the instance information based on the descriptions in the following table.
Tab
Parameter
Description
Basic Information
Database Type
The type of the database.
Instance Region
The region in which the database gateway is deployed.
Gateway ID
The ID of the database gateway. If you have not created database gateways, click Click here to add a database gateway to create a database gateway.
Database address
The internal endpoint of the database.
Database Account
The username that you use to log on to the database.
Database Password
The password of the username for the database.
Control Mode
The control mode that is used to manage the database. For more information, see Control modes.
Sensitive Data Protection
Specifies whether to enable the sensitive data protection feature. DMS provides the sensitive data protection feature. You can use this feature to scan a database for sensitive data. Then, you can de-identify and manage the sensitive data.
Advanced Information
Environment type
The type of the environment where the database is deployed.
Instance Name
The custom name of the database instance.
Lock-free Schema Change
Specifies whether to enable the lock-free schema change feature. For more information, see Perform lock-free DDL operations.
Enable SSL
Specifies whether to allow DMS to connect to the database by using SSL connections. After this feature is enabled, DMS can connect to the database by using SSL connections. Note that your database must support SSL connections so that this feature can take effect.
DBA
The database administrator (DBA) who handles subsequent processes, such as the process of applying for permissions.
Query Timeout(s)
The timeout period for the execution of an SQL query statement. If the execution of an SQL query statement lasts longer than the specified timeout period, the execution of the statement is terminated to protect the database.
Export Timeout(s)
The timeout period for the execution of an SQL export statement. If the execution of an SQL export statement lasts longer than the specified timeout period, the execution of the statement is terminated to protect the database.
In the lower-left corner of the dialog box, click Test Connectivity and wait until the connection passes the test.
NoteIf the connection fails the test, check the instance information that you specify.
Click Submit. Now your on-premises database or database hosted on a third-party cloud has been registered in DMS. In the instance list in the left-side navigation pane of the DMS console, you can view and manage your database.