DataWorks provides RestAPI Reader for you to read data from RESTful APIs. You can configure an HTTP request URL for RestAPI Reader to enable RestAPI Reader to read data from RestAPI data sources, convert the data to the data types that are supported by Data Integration, and then transfer the converted data to a writer. For example, you can use RestAPI Reader to read data within a specified time range, read paged data, or traverse request parameters in loops to read required data. This topic provides common use examples of a RestAPI data source.
This topic describes how to use RestAPI Reader to read data. For information about parameter settings in the examples of this topic, see Parameters in code for RestAPI Reader.
For information about how to configure scripts for RestAPI Writer, see Code for RestAPI Writer and Parameters in code for RestAPI Writer.
Background information
RestAPI Reader provides the following capabilities in the aspects of data read and result returning.
Dimension | Capability |
Supported response format | RestAPI Reader can read data only from responses in the JSON format. |
Supported data types | RestAPI Reader can read data of the INT, BOOLEAN, DATE, DOUBLE, FLOAT, LONG, and STRING data types. |
Request method | RestAPI Reader can read data from RESTful APIs that are called by using the GET or POST method over HTTP. |
Authentication method | RestAPI Reader allows you to disable authentication or use one of the following authentication methods: basic authentication, token-based authentication, and authentication based on Alibaba Cloud API signature. When you add a RestAPI data source to DataWorks, you can select an authentication method that is supported by the data source and configure the required authentication parameters.
|
Example 1: Read data from a RESTful API that queries data within a specified time range
Sample scenario: Define the RESTful API
In this sample scenario, a batch synchronization task that uses RestAPI Reader is configured to synchronize data from a RESTful API to a MaxCompute partitioned table. The RESTful API is a self-managed API whose request method is GET. The RESTful API returns data within a specified time range based on the time range-related request parameters that are configured for the API. The following descriptions provide the details of the RESTful API.
When you use RestAPI Reader to read data from a RESTful API, you can adjust configurations based on the RESTful API that you use. The RESTful API used in this example is for reference only.
Sample request
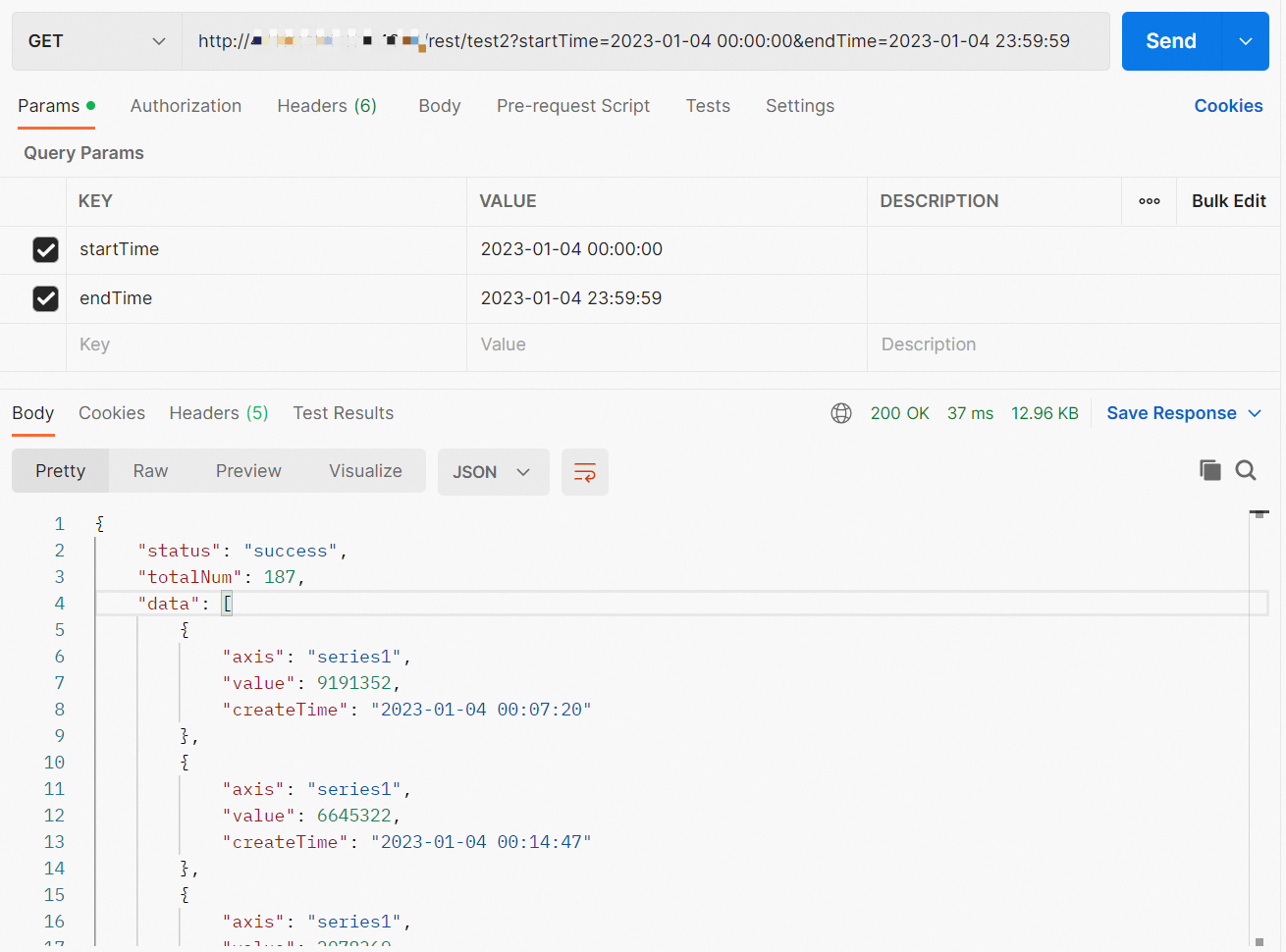
http://TestAPIAddress:Port/rest/test2?startTime=<StartTime>&endTime=<EndTime>startTime and endTime are request parameters of the RESTful API. The parameters specify the time range within which data needs to be queried.
Sample response
{ "status": "success", "totalNum": 187, "data": [ { "axis": "series1", "value": 9191352, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:07:20" }, { "axis": "series1", "value": 6645322, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:14:47" }, { "axis": "series1", "value": 2078369, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:22:13" }, { "axis": "series1", "value": 7325410, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:29:30" }, { "axis": "series1", "value": 7448456, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:37:04" }, { "axis": "series1", "value": 5808077, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:44:30" }, { "axis": "series1", "value": 5625821, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:52:06" } ] }The data parameter in the response indicates the path in which queried data is stored. The following fields are returned:
axis,value, andcreateTime.Sample call made by using the API test tool
Preparation: Create a MaxCompute partitioned table
In this example, data that is read from a RESTful API needs to be written to a MaxCompute partitioned table. You must create a MaxCompute partitioned table that is used to store the synchronized data in advance.
If you use a MaxCompute partitioned table as the destination table and set the write mode to overwriting for the related batch synchronization task, the existing data in the partitions of the table is overwritten by new data each time the task is run, which makes the batch synchronization task be able to be rerun. During the rerun process, data in the MaxCompute partitioned table is not duplicated, and the MaxCompute partitioned table can facilitate data analysis.
Execute the following statement to create a MaxCompute partitioned table:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ods_xiaobo_rest2
(
`axis` STRING
,`value` BIGINT
,`createTime` STRING
)
PARTITIONED BY
(
ds STRING
)
LIFECYCLE 3650;If you use a workspace in standard mode and deploy the MaxCompute partitioned table to the production environment after it is created, you can view the table in Data Map.
Add a RestAPI data source and configure a batch synchronization task
Add a RestAPI data source.
Add a RestAPI data source to the workspace that you want to use. For more information, see Add a RestAPI data source.
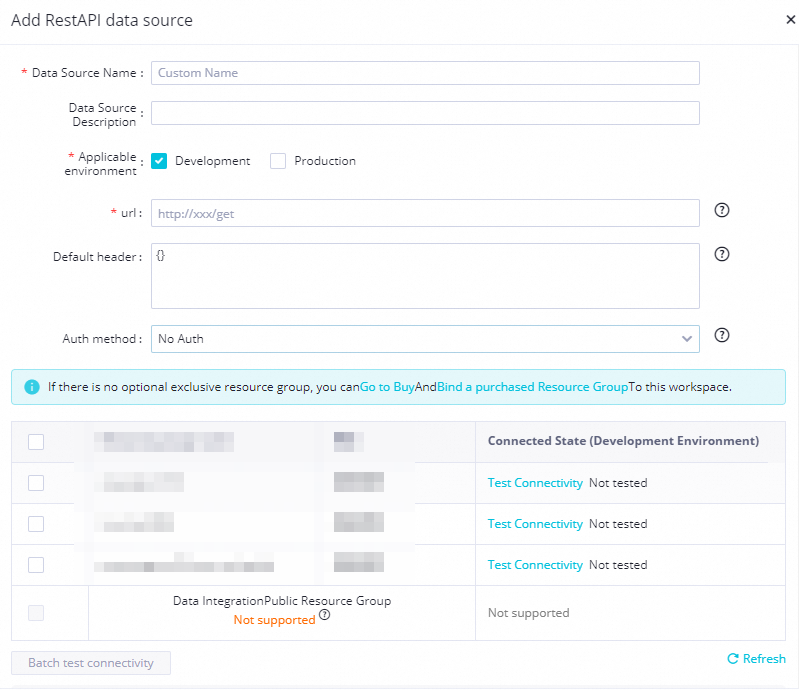 You must take note of the following items:
You must take note of the following items: url: You must specify the URL of the RESTful API.
Auth method: You can select an authentication method that is supported by the RestAPI data source and configure the required authentication parameters.
Network connectivity: RestAPI data sources support only exclusive resource groups for Data Integration. You must select an exclusive resource group for Data Integration that you want to use and test the network connectivity between the resource group and the RestAPI data source.
Create and configure a batch synchronization task.
On the DataStudio page of the DataWorks console, create a batch synchronization task and configure the task by using the codeless user interface (UI). For more information, see Configure a batch synchronization task by using the codeless UI. You must take note of the following items.
Key configuration items for the source:
Data source: You must select the RestAPI data source that is added in the preceding step.
Request Method: In this example, the request method of the RESTful API is GET. You must set the request method to GET.
Data Structure: In this example, the response returned by the RESTful API is a JSON array. You must set the Data Structure parameter to Array Data.
json path to store data: In this example, the fields that are queried by the RESTful API are stored in the data path. You must enter data in the field.
Request parameters: You can use request parameters together with scheduling parameters to enable the batch synchronization task to synchronize data every day.
You can configure the following request parameters:
startTime=${extract_day} ${start_time}&endTime=${extract_day} ${end_time}.When you configure scheduling properties for the batch synchronization task, add the following scheduling parameters:
extract_day=${yyyy-mm-dd},start_time=00:00:00, andend_time=23:59:59.
For example, if the date on which the batch synchronization task is scheduled to run is 2023-01-05, the value of
extract_dayis 2023-01-04. The request parameters are concatenated in the following format:startTime=2023-01-04 00:00:00&endTime=2023-01-04 23:59:59.
Key configuration items for the destination:
Data source and table: You must select the MaxCompute data source that you want to use and the MaxCompute partitioned table that is created in the preparation for this example.
Partition information: You can use a scheduling parameter to specify the partition to which you want to write data in the MaxCompute partitioned table.
You can enter
${bizdate}in the field.When you configure scheduling properties for the data synchronization task, add the scheduling parameter
bizdate=$bizdate.
For example, if the date on which the batch synchronization task is scheduled to run is 2023-01-05, the partition to which data is written is represented by the date 20230104.
Key configuration item for field mappings: When you configure field mappings for the batch synchronization task, you must specify the fields that you want the RESTful API to return based on the data definition in the RESTful API. The field names are case-sensitive. After you specify the fields, you can click Map Fields with Same Name to map source fields to destination fields whose names are the same, or manually drag lines to map source fields to destination fields.
Test the batch synchronization task
In this example, scheduling parameters are configured for the batch synchronization task. After you complete the configuration of the batch synchronization task, you can click the Run with Parameters icon in the top toolbar of the configuration tab of the task to test the task. After you click the icon, you must specify values for the scheduling parameters in the dialog box that appears.  After you perform the test, you can view the run logs that are generated for the batch synchronization task in the lower part of the configuration tab to check whether the values of the scheduling parameters meet your business requirements.
After you perform the test, you can view the run logs that are generated for the batch synchronization task in the lower part of the configuration tab to check whether the values of the scheduling parameters meet your business requirements.
Check whether data is synchronized to MaxCompute
You can create an ad hoc query node in the Ad Hoc Query pane of the DataStudio page to query the data that is synchronized to MaxCompute. Sample query statement:
select * from ods_xiaobo_rest2 where ds='20230104' order by createtime;ods_xiaobo_rest2 is the MaxCompute partitioned table that is created in the preparation for this example. 20230104 is the partition that is obtained in the preceding test.
After you execute the query statement, you can check whether data is successfully synchronized to MaxCompute on the result tab in the lower part of the configuration tab.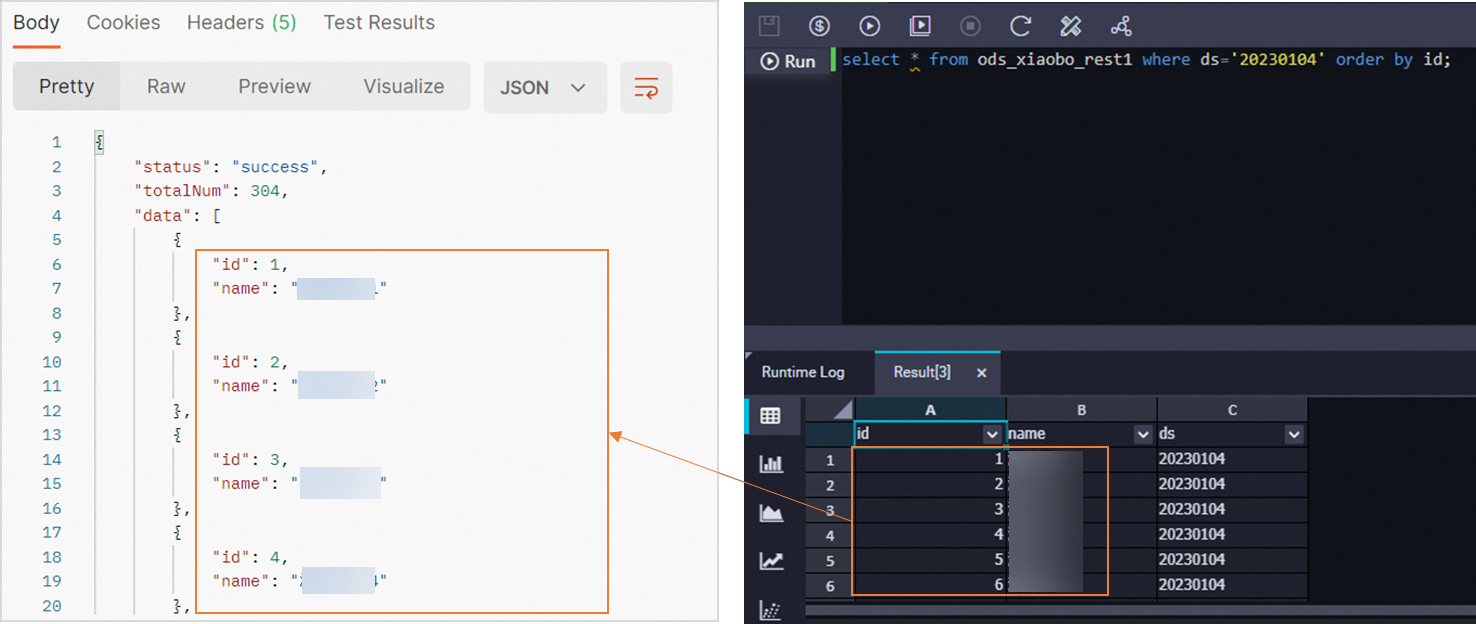
Commit and deploy the batch synchronization task, and backfill data for the batch synchronization task
After the test and data check are complete, you can commit and deploy the batch synchronization task to the production environment. For information about how to deploy a task in a workspace in standard mode, see Deploy a node in a workspace that is in standard mode.  After the batch synchronization task is deployed to the production environment, you can find the task on the Cycle Task page in Operation Center and backfill historical data for the task. For information about the data backfill feature and how to backfill data for a task, see Backfill data for an auto triggered task and view data backfill instances generated for the task.
After the batch synchronization task is deployed to the production environment, you can find the task on the Cycle Task page in Operation Center and backfill historical data for the task. For information about the data backfill feature and how to backfill data for a task, see Backfill data for an auto triggered task and view data backfill instances generated for the task.
Example 2: Read data from the paged result returned by a RESTful API
Sample scenario: Define the RESTful API
In this sample scenario, a batch synchronization task that uses RestAPI Reader is configured to synchronize data from a RESTful API to a MaxCompute partitioned table. The RESTful API is a self-managed API whose request method is GET. The following descriptions provide the details of the RESTful API.
When you use RestAPI Reader to read data from a RESTful API, you can adjust configurations based on the RESTful API that you use. The RESTful API used in this example is for reference only.
Sample request
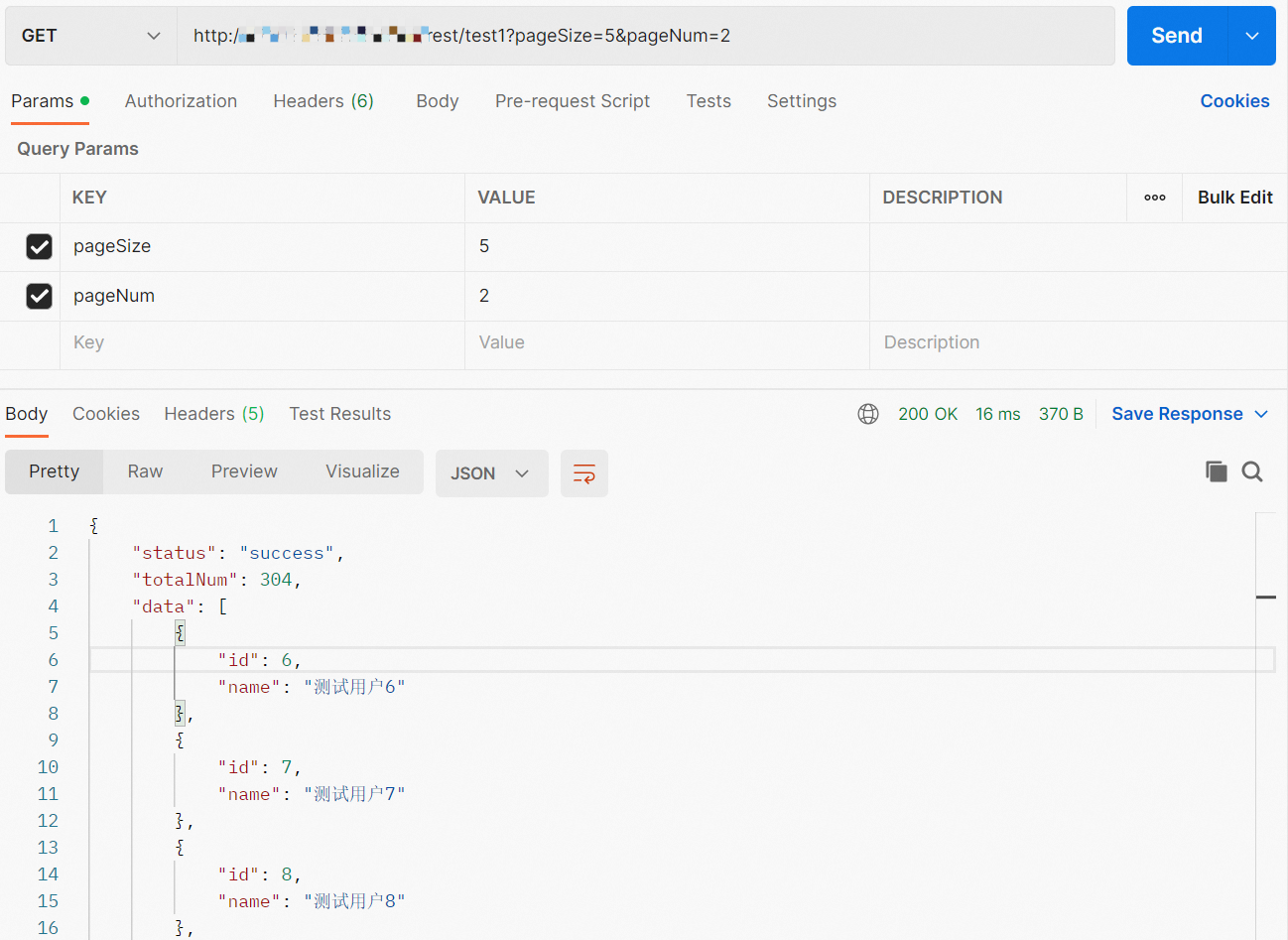
http://TestAPIAddress:Port/rest/test1?pageSize=5&pageNum=1pageSize and pageNum are request parameters of the RESTful API. pageSize specifies the number of entries to return on each page. pageNum specifies the total number of pages to return.
Sample response
{ "status": "success", "totalNum": 304, "data": [ { "id": 6, "name": "User 6" }, { "id": 7, "name": "User 7" }, { "id": 8, "name": "User 8" }, { "id": 9, "name": "User 9" }, { "id": 10, "name": "User 10" } ] }The data parameter in the response indicates the path in which queried data is stored. The following fields are returned:
idandname.Sample call made by using the API test tool
Preparation: Create a MaxCompute partitioned table
In this example, data that is read from a RESTful API needs to be written to a MaxCompute partitioned table. You must create a MaxCompute partitioned table that is used to store the synchronized data in advance.
If you use a MaxCompute partitioned table as the destination table and set the write mode to overwriting for the related batch synchronization task, the existing data in the partitions of the table is overwritten by new data each time the task is run, which makes the batch synchronization task be able to be rerun. During the rerun process, data in the MaxCompute partitioned table is not duplicated, and the MaxCompute partitioned table can facilitate data analysis.
Execute the following statement to create a MaxCompute partitioned table:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ods_xiaobo_rest1
(
`id` BIGINT
,`name` STRING
)
PARTITIONED BY
(
ds STRING
)
LIFECYCLE 3650;If you use a workspace in standard mode and deploy the MaxCompute partitioned table to the production environment after it is created, you can view the table in Data Map.
Add a RestAPI data source and configure a batch synchronization task
Add a RestAPI data source.
Add a RestAPI data source to the workspace that you want to use. For more information, see Add a RestAPI data source.
 You must take note of the following items:
You must take note of the following items: url: You must specify the URL of the RESTful API.
Auth method: You can select an authentication method that is supported by the RestAPI data source and configure the required authentication parameters.
Network connectivity: RestAPI data sources support only exclusive resource groups for Data Integration. You must select an exclusive resource group for Data Integration that you want to use and test the network connectivity between the resource group and the RestAPI data source.
Create and configure a batch synchronization task.
On the DataStudio page of the DataWorks console, create a batch synchronization task and configure the task by using the codeless UI. For more information, see Configure a batch synchronization task by using the codeless UI. You must take note of the following items.
Key configuration items for the source:
Data source: You must select the RestAPI data source that is added in the preceding step.
Request Method: In this example, the request method of the RESTful API is GET. You must set the request method to GET.
Data Structure: In this example, the response returned by the RESTful API is a JSON array. You must set the Data Structure parameter to Array Data.
json path to store data: In this example, the fields that are queried by the RESTful API are stored in the data path. You must enter data in the field.
Request parameters: In this example, you must configure
pageSize=50to limit the number of entries to return on each page to 50. We recommend that you do not specify an excessively large value for the pageSize parameter. Otherwise, loads on the RestAPI server side and the batch synchronization task may be high.Number of requests: In this example, you must select Multiple requests.
The paging parameter used in this example for the RESTful API is pageNum. After you select Multiple requests, you must configure the following parameters:
Multiple requests parameter: Enter pageNum.
StartIndex: Enter 1.
Step: Enter 1.
EndIndex: Enter 100.
Key configuration items for the destination:
Data source and table: You must select the MaxCompute data source that you want to use and the MaxCompute partitioned table that is created in the preparation for this example.
Partition information: You can use a scheduling parameter to specify the partition to which you want to write data in the MaxCompute partitioned table.
You can enter
${bizdate}in the field.When you configure scheduling properties for the data synchronization task, add the scheduling parameter
bizdate=$bizdate.
For example, if the date on which the batch synchronization task is scheduled to run is 2023-01-05, the partition to which data is written is represented by the date 20230104.
Key configuration item for field mappings: When you configure field mappings for the batch synchronization task, you must specify the fields that you want the RESTful API to return based on the data definition in the RESTful API. The field names are case-sensitive. After you specify the fields, you can click Map Fields with Same Name to map source fields to destination fields whose names are the same, or manually drag lines to map source fields to destination fields.
Test the batch synchronization task
In this example, scheduling parameters are configured for the batch synchronization task. After you complete the configuration of the batch synchronization task, you can click the Run with Parameters icon in the top toolbar of the configuration tab of the task to test the task. After you click the icon, you must specify values for the scheduling parameters in the dialog box that appears.  After you perform the test, you can view the run logs that are generated for the batch synchronization task in the lower part of the configuration tab to check whether the values of the scheduling parameters meet your business requirements.
After you perform the test, you can view the run logs that are generated for the batch synchronization task in the lower part of the configuration tab to check whether the values of the scheduling parameters meet your business requirements.
Check whether data is synchronized to MaxCompute
You can create an ad hoc query node in the Ad Hoc Query pane of the DataStudio page to query the data that is synchronized to MaxCompute. Sample query statement:
select * from ods_xiaobo_rest1 where ds='20230104' order by id;ods_xiaobo_rest1 is the MaxCompute partitioned table that is created in the preparation for this example. 20230104 is the partition that is obtained in the preceding test.
After you execute the query statement, you can check whether data is successfully synchronized to MaxCompute on the result tab in the lower part of the configuration tab.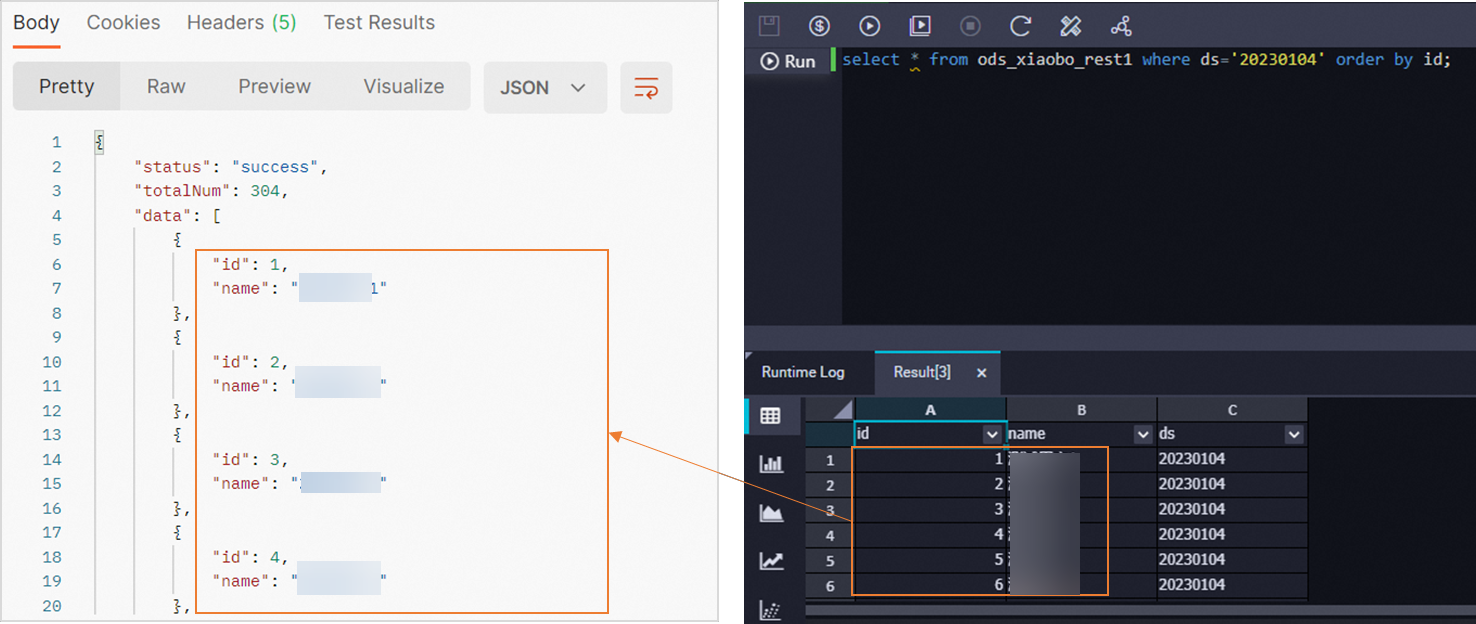
Example 3: Read data from a RESTful API whose request method is POST
Sample scenario: Define the RESTful API
In this sample scenario, a batch synchronization task that uses RestAPI Reader is configured to synchronize data from a RESTful API to a MaxCompute partitioned table. The RESTful API is a self-managed API whose request method is POST. Details of the RESTful API:
When you use RestAPI Reader to read data from a RESTful API, you can adjust configurations based on the RESTful API that you use. The RESTful API used in this example is for reference only.
Sample request
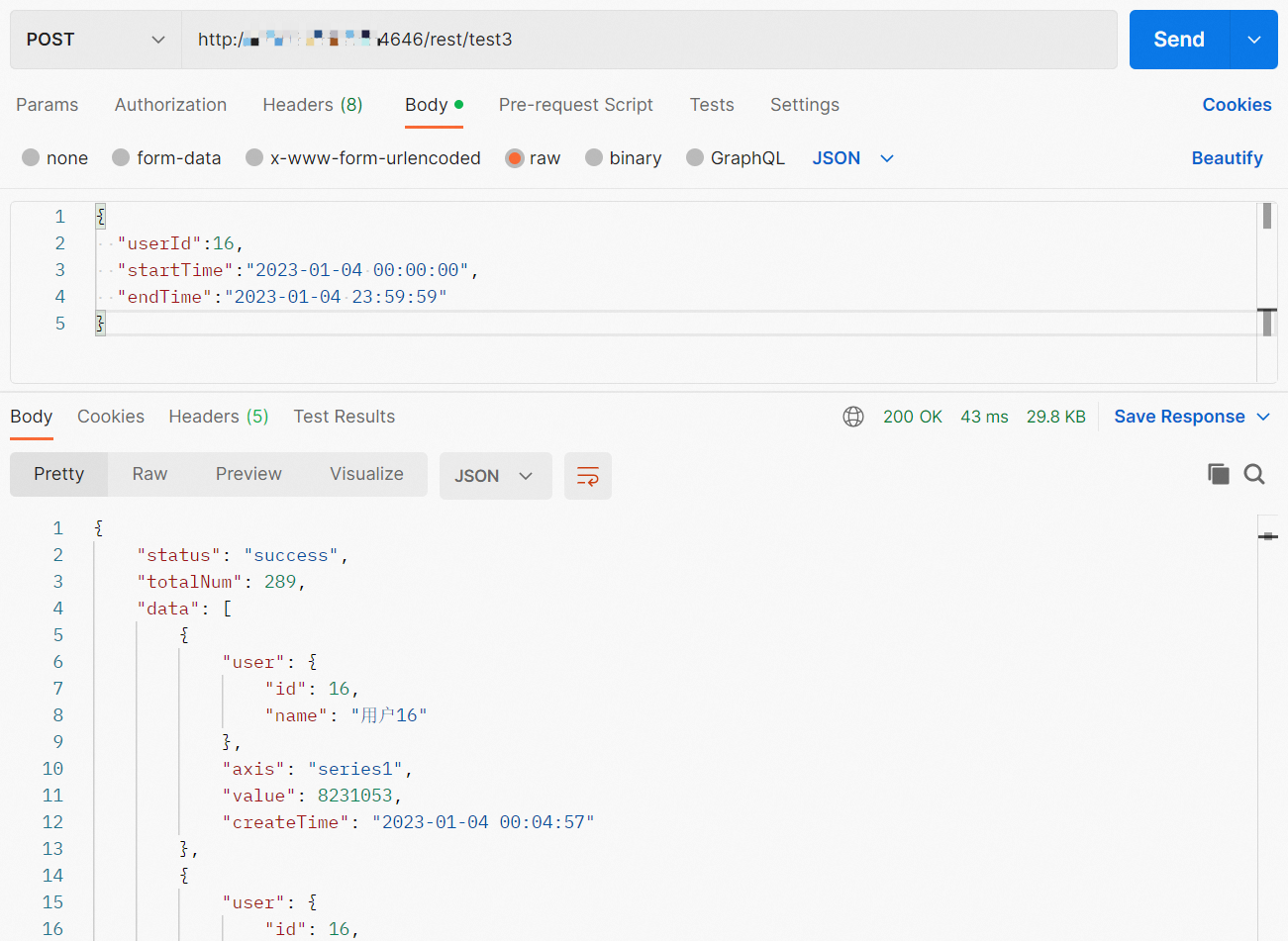
http://TestAPIAddress:Port/rest/test3The request body is in the JSON format.
{ "userId":16, "startTime":"2023-01-04 00:00:00", "endTime":"2023-01-04 23:59:59" }Sample response
{ "status": "success", "totalNum": 289, "data": [ { "user": { "id": 16, "name": "User 16" }, "axis": "series1", "value": 8231053, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:04:57" }, { "user": { "id": 16, "name": "User 16" }, "axis": "series1", "value": 6519928, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:09:51" }, { "user": { "id": 16, "name": "User 16" }, "axis": "series1", "value": 2915920, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:14:36" }, { "user": { "id": 16, "name": "User 16" }, "axis": "series1", "value": 7971851, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:19:51" }, { "user": { "id": 16, "name": "User 16" }, "axis": "series1", "value": 6598996, "createTime": "2023-01-04 00:24:30" } ] }The data parameter in the response indicates the path in which queried data is stored. The following fields are returned:
user.id,user.name,axis,value, andcreateTime.Sample call made by using the API test tool
Preparation: Create a MaxCompute partitioned table
In this example, data that is read from a RESTful API needs to be written to a MaxCompute partitioned table. You must create a MaxCompute partitioned table that is used to store the synchronized data in advance.
If you use a MaxCompute partitioned table as the destination table and set the write mode to overwriting for the related batch synchronization task, the existing data in the partitions of the table is overwritten by new data each time the task is run, which makes the batch synchronization task be able to be rerun. During the rerun process, data in the MaxCompute partitioned table is not duplicated, and the MaxCompute partitioned table can facilitate data analysis.
Execute the following statement to create a MaxCompute partitioned table:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ods_xiaobo_rest3
(
`user_id` BIGINT
,`name` STRING
,`axis` STRING
,`value` BIGINT
,`create_time` STRING
)
PARTITIONED BY
(
ds STRING
)
LIFECYCLE 3650;If you use a workspace in standard mode and deploy the MaxCompute partitioned table to the production environment after it is created, you can view the table in Data Map.
Add a RestAPI data source and configure a batch synchronization task
Add a RestAPI data source.
Add a RestAPI data source to the workspace that you want to use. For more information, see Add a RestAPI data source.
 You must take note of the following items:
You must take note of the following items: url: You must specify the URL of the RESTful API.
Auth method: You can select an authentication method that is supported by the RestAPI data source and configure the required authentication parameters.
Network connectivity: RestAPI data sources support only exclusive resource groups for Data Integration. You must select an exclusive resource group for Data Integration that you want to use and test the network connectivity between the resource group and the RestAPI data source.
Create and configure a batch synchronization task.
On the DataStudio page of the DataWorks console, create a batch synchronization task and configure the task by using the codeless UI. For more information, see Configure a batch synchronization task by using the codeless UI. You must take note of the following items.
Key configuration items for the source:
Data source: You must select the RestAPI data source that is added in the preceding step.
Request Method: In this example, the request method of the RESTful API is POST. You must set the request method to POST.
Data Structure: In this example, the response returned by the RESTful API is a JSON array. You must set the Data Structure parameter to Array Data.
json path to store data: In this example, the fields that are queried by the RESTful API are stored in the data path. You must enter data in the field.
Header: The request body of the RESTful API used in this example is in the JSON format. In this example, you must enter
{"Content-Type":"application/json"}in the field.Request parameters: You can use request parameters together with scheduling parameters to enable the batch synchronization task to synchronize data every day.
The following code provides an example for the configuration of request parameters:
{ "userId":16, "startTime":"${extract_day} 00:00:00", "endTime":"${extract_day} 23:59:59" }When you configure scheduling properties for the batch synchronization task, add the scheduling parameter
extract_day=${yyyy-mm-dd}.
Key configuration items for the destination:
Data source and table: You must select the MaxCompute data source that you want to use and the MaxCompute partitioned table that is created in the preparation for this example.
Partition information: You can use a scheduling parameter to specify the partition to which you want to write data in the MaxCompute partitioned table.
You can enter
${bizdate}in the field.When you configure scheduling properties for the data synchronization task, add the scheduling parameter
bizdate=$bizdate.
For example, if the date on which the batch synchronization task is scheduled to run is 2023-01-05, the partition to which data is written is represented by the date 20230104.
Key configuration items for field mappings: When you configure field mappings for the batch synchronization task, you must specify the fields that you want the RESTful API to return based on the data definition in the RESTful API. If a field that you want to specify is a nested field, you can use a period (.) in the field name when you specify the field. The field names are case-sensitive. After you specify the fields, you can click Map Fields with Same Name to map source fields to destination fields whose names are the same, or manually drag lines to map source fields to destination fields.
Test the batch synchronization task
In this example, scheduling parameters are configured for the batch synchronization task. After you complete the configuration of the batch synchronization task, you can click the Run with Parameters icon in the top toolbar of the configuration tab of the task to test the task. After you click the icon, you must specify values for the scheduling parameters in the dialog box that appears.  After you perform the test, you can view the run logs that are generated for the batch synchronization task in the lower part of the configuration tab to check whether the values of the scheduling parameters meet your business requirements.
After you perform the test, you can view the run logs that are generated for the batch synchronization task in the lower part of the configuration tab to check whether the values of the scheduling parameters meet your business requirements.
Check whether data is synchronized to MaxCompute
You can create an ad hoc query node in the Ad Hoc Query pane of the DataStudio page to query the data that is synchronized to MaxCompute. Sample query statement:
select * from ods_xiaobo_rest3 where ds='20230105' order by create_time;ods_xiaobo_rest3 is the MaxCompute partitioned table that is created in the preparation for this example. 20230105 is the partition that is obtained in the preceding test.
After you execute the query statement, you can check whether data is successfully synchronized to MaxCompute on the result tab in the lower part of the configuration tab.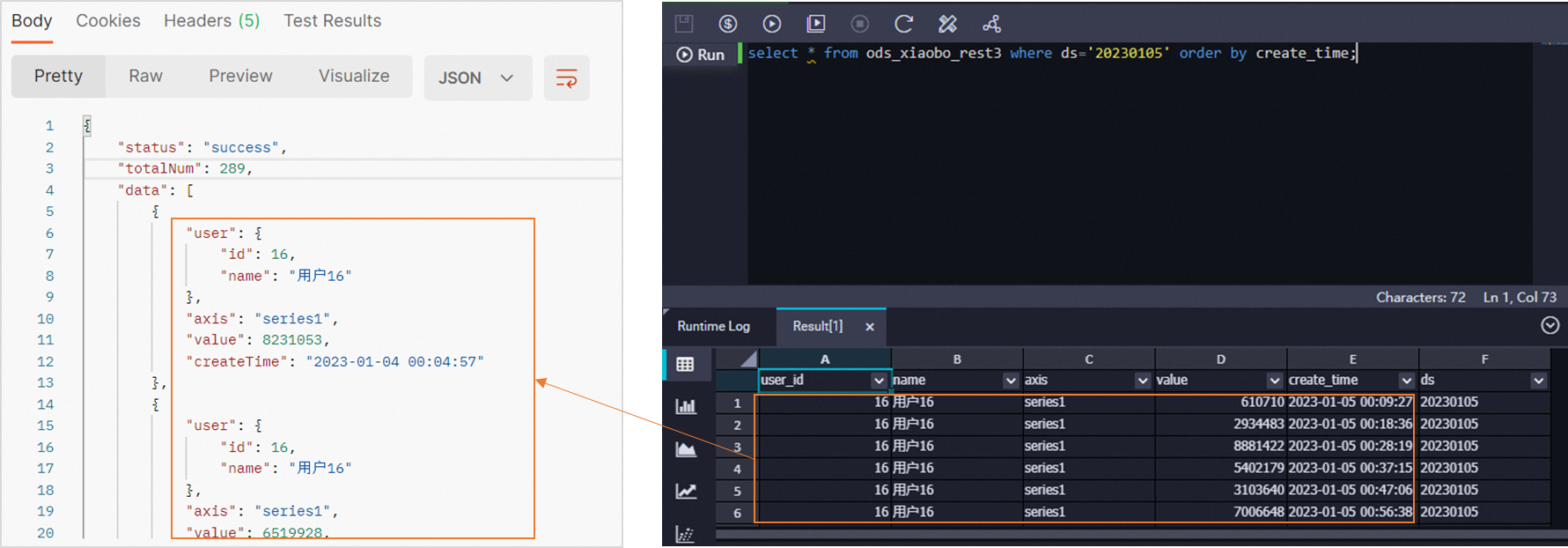
Example 4: Traverse request parameters of a RESTful API in loops to read data
Sample scenario: Define the RESTful API
In this sample scenario, a batch synchronization task that uses RestAPI Reader is configured to repeatedly read data from a RESTful API to a MaxCompute partitioned table. The RESTful API is a self-managed API whose request method is GET and returns data related to temperature based on the following request parameters: date, province, and city.
When you use RestAPI Reader to read data from a RESTful API, you can adjust configurations based on the RESTful API that you use. The RESTful API used in this example is for reference only.
Sample request
http://TestAPIAddress:Port/rest/test5?date=2023-01-04&province=zhejiang&city=hangzhouSample response
{ "province": "P1", "city": "hz", "date": "2023-01-04", "minTemperature": "-14", "maxTemperature": "-7", "unit": "℃", "weather": "cool" }Sample call made by using the API test tool

Preparation: Create a parameter table and a MaxCompute partitioned table
In this example, data that is read from a RESTful API needs to be written to a MaxCompute partitioned table. You must create a parameter table and a MaxCompute partitioned table in advance. The parameter table is used to store values of the province and city parameters, which need to be traversed in loops. The MaxCompute partitioned table is used to store the synchronized data.
If you use a MaxCompute partitioned table as the destination table and set the write mode to overwriting for the related batch synchronization task, the existing data in the partitions of the table is overwritten by new data each time the task is run, which makes the batch synchronization task be able to be rerun. During the rerun process, data in the MaxCompute partitioned table is not duplicated, and the MaxCompute partitioned table can facilitate data analysis.
Execute the following statements to create tables:
Create a parameter table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `citys`
(
`province` STRING ,
`city` STRING
);
insert into citys
select 'shanghai','shanghai'
union all select 'zhejiang','hangzhou'
union all select 'sichuan','chengdu';Create a MaxCompute partitioned table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ods_xiaobo_rest5
(
`minTemperature` STRING ,
`maxTemperature` STRING ,
`unit` STRING ,
`weather` STRING
)
PARTITIONED BY
(
`province` STRING ,
`city` STRING ,
`ds` STRING
)
LIFECYCLE 3650;If you use a workspace in standard mode and you commit and deploy the two tables to the production environment after they are created, you can view the tables in Data Map.
Add a RestAPI data source and configure a batch synchronization task
Add a RestAPI data source.
Add a RestAPI data source to the workspace that you want to use. For more information, see Add a RestAPI data source.
 You must take note of the following items:
You must take note of the following items:url: You must specify the URL of the RESTful API.
Auth method: You can select an authentication method that is supported by the RestAPI data source and configure the required authentication parameters.
Network connectivity: You must select a resource group that you want to use and test the network connectivity between the resource group and the RestAPI data source.
Create and configure an assignment node named setval_citys on the DataStudio page. For more information, see Configure an assignment node.
You must take note of the following items.
No.
Description
1
Programming language: ODPS SQL
Code for value assignment:
SELECT province ,city FROM citys;
2
Rerun property: Set the rerun property to Allow Regardless of Running Status.
After the configuration of the assignment node is complete, commit and deploy the node.
Create and configure a for-each node on the DataStudio page. For more information, see topics in the Configure a for-each node directory. You must take note of the following items.
Parameter
Description
Rerun property
Set the rerun property to Allow Regardless of Running Status.
Ancestor node
Select the setval_citys assignment node.
Input parameter
Select the sources of the input parameters.
Batch synchronization task
Refer to the following step to create and configure a batch synchronization task within the for-each node.
Create and configure a batch synchronization task by using the codeless UI. For more information, see Configure a batch synchronization task by using the codeless UI.
You must take note of the following items.
Parameter
Description
scheduling parameters
Configure the following scheduling parameters:
bizdate=$[yyyymmdd-1] bizdate_year=$[yyyy-1] bizdate_month=$[mm-1] bizdate_day=$[dd-1]request parameters
Configure request parameters for the RESTful API. The province and city parameters are the output parameters of the for-each node.
date=${bizdate_year}-${bizdate_month}-${bizdate_day}&province=${dag.foreach.current[0]}&city=${dag.foreach.current[1]}province parameter
Configure the province parameter to specify the destination MaxCompute partition. The province parameter is the output parameter of the for-each node.
province=${dag.foreach.current[0]}city parameter
Configure the city parameter to specify the destination MaxCompute partition. The city parameter is the output parameter of the for-each node.
city=${dag.foreach.current[1]}ds parameter
Configure the ds parameter to specify the destination MaxCompute partition. The ds parameter is a scheduling parameter.
ds=${bizdate}field mappings
Specify the fields that you want the RESTful API to return based on the data definition in the RESTful API. The field names are case-sensitive. After you specify the fields, you can click Map Fields with Same Name to map source fields to destination fields whose names are the same, or manually drag lines to map source fields to destination fields.
After the configuration is complete, commit and deploy the for-each node.
Test the assignment node and for-each node.
After you commit and deploy the assignment node and for-each node, find the assignment node on the Cycle Task page in Operation Center and backfill data for the assignment node. For more information, see Backfill data and view data backfill instances (new version).
Select a data timestamp and the nodes for which you want to backfill data. The data timestamp includes a start point in time and an end point in time.
After data backfill instances are generated for the nodes, check whether the scheduling parameters are correctly rendered in the run logs of the assignment node.
In the preceding figure, the scheduling parameters are correctly rendered. Data will be written to the
province=shanghai,city=shanghai,ds=20231215partition of the MaxCompute table.
Check whether data is synchronized to MaxCompute
You can create an ad hoc query node in the Ad Hoc Query pane of the DataStudio page to query the data that is synchronized to MaxCompute.
ods_xiaobo_rest5 in the following sample statement is the MaxCompute partitioned table that is created in the Preparation: Create a MaxCompute partitioned table subsection.
SELECT weather
,mintemperature
,maxtemperature
,unit
,province
,city
,ds
FROM ods_xiaobo_rest5
WHERE ds != 1
ORDER BY ds,province,city;After you execute the query statement, you can check whether data is successfully synchronized to MaxCompute on the result tab in the lower part of the configuration tab.