The JSON parsing component is available for real-time extract, transform, and load (ETL) tasks in DataWorks Data Integration. You can add a JSON parsing component between a source and a destination to parse JSON data from the source into table data.
Create and configure a JSON parsing component
Step 1: Configure a data integration task
Add the required data sources to DataWorks. For more information, see Data Source Management.
Create a synchronization task in Data Integration. For more information, see the topics in the Data Integration-side synchronization task directory.
NoteIf you create a synchronization task that is used to synchronize data from a single table in real time, you can add data processing components between the source component and the destination component. For more information, see Supported data source types and synchronization operations.
Step 2: Add a JSON parsing component
On the DAG canvas of the real-time ETL task configuration page, click the
 button between the Source and Destination components and select the JSON Parsing component.
button between the Source and Destination components and select the JSON Parsing component.
Configure the JSON parsing component.
ImportantTo obtain the JSON data structure, perform Data Sampling in the source Kafka component.
Add fixed fields for JSON parsing
Obtain JSON-formatted data.
Get JSON data
Description
Illustration
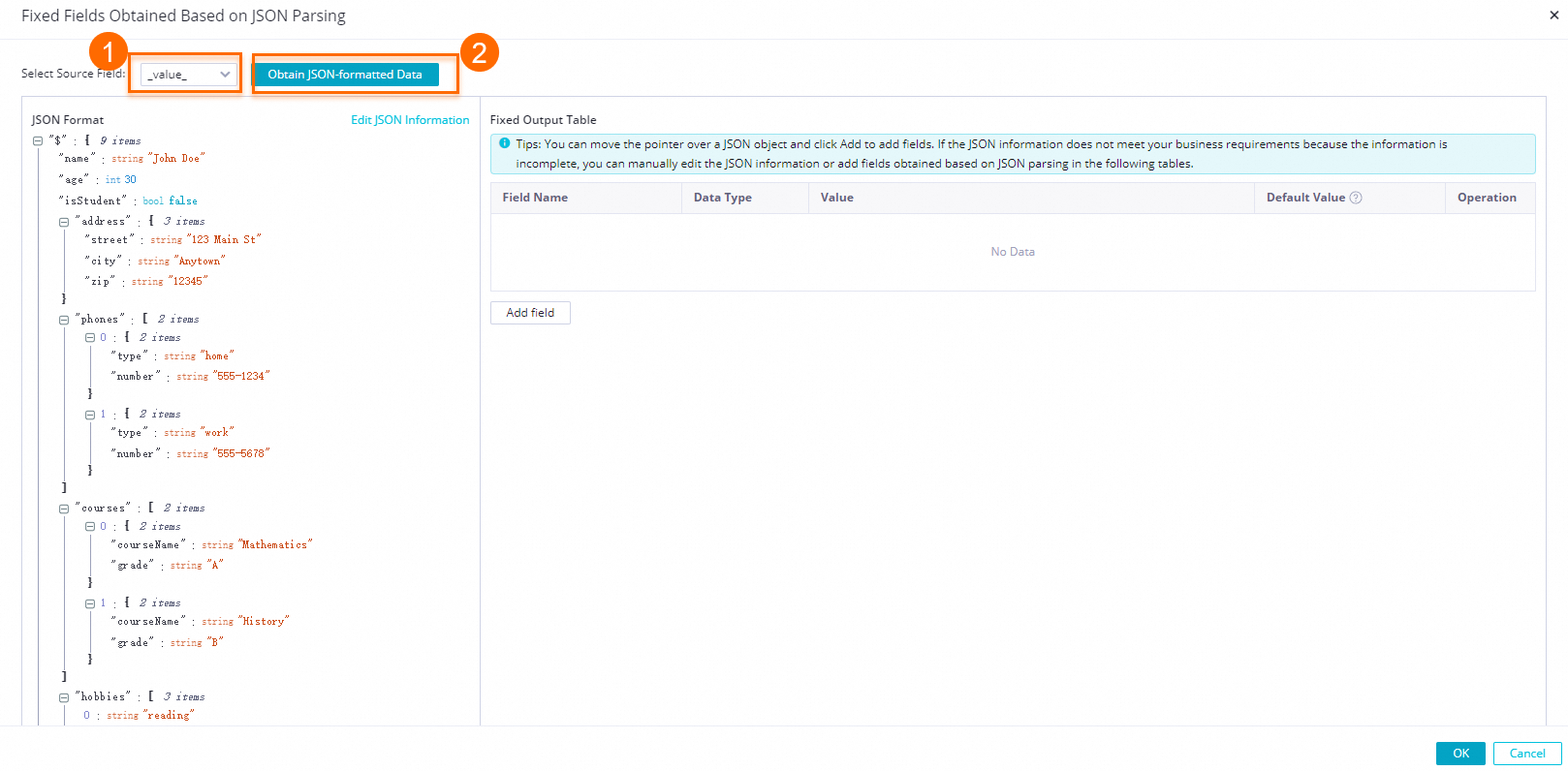
Get JSON data from data sampling
After data sampling, click Add Fixed Field For JSON Parsing. In the Fixed Field For JSON Parsing dialog box, select a source field and click Get JSON Data Structure.
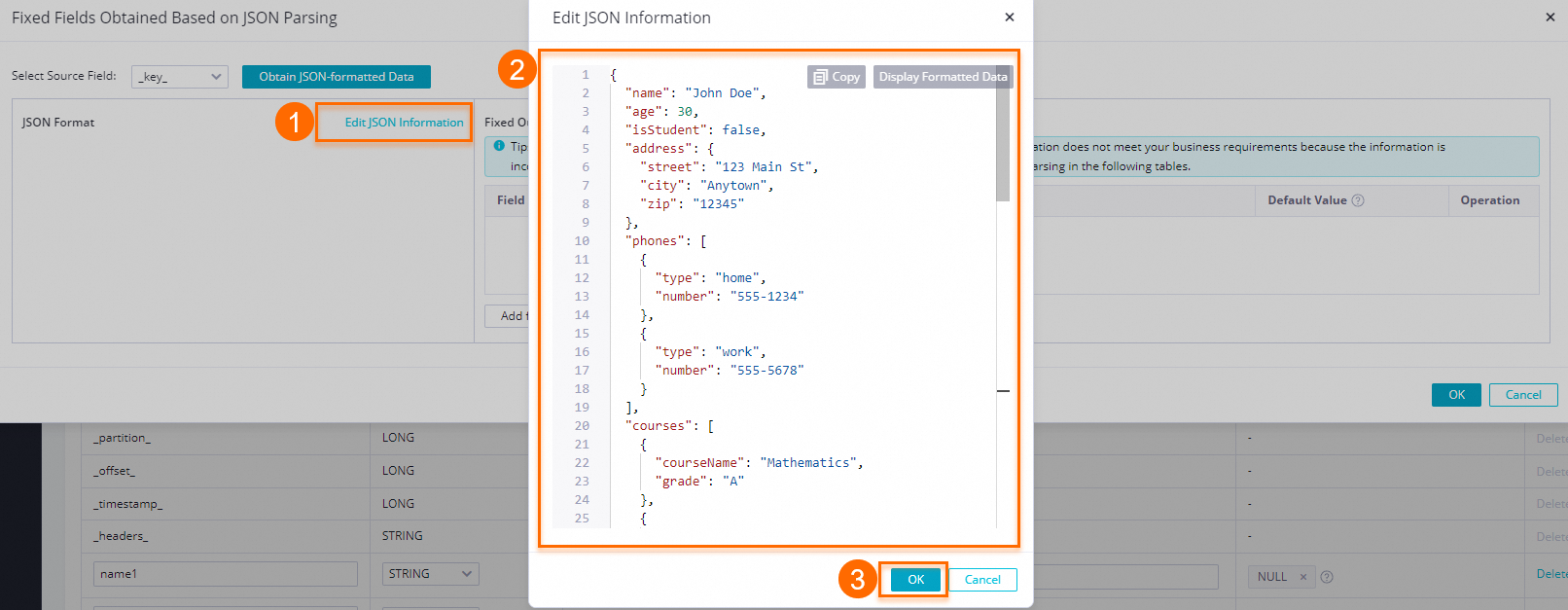
Get manually entered JSON data
If data sampling is not performed or the source data is empty, you can manually edit the fields.
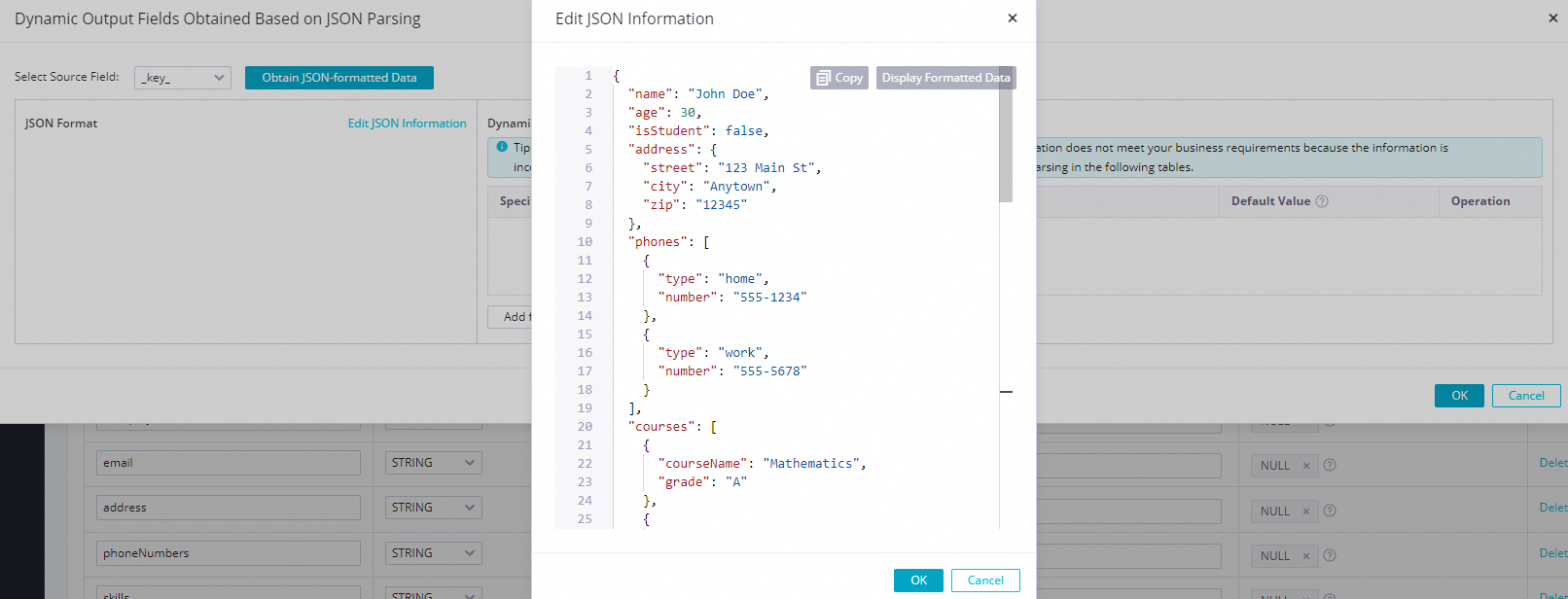
Click Add Fixed Field for JSON Parsing. In the Fixed Field for JSON Parsing dialog box, click Edit JSON Text. In the Edit JSON Text dialog box, manually enter the JSON content and click OK to format the uploaded JSON content.
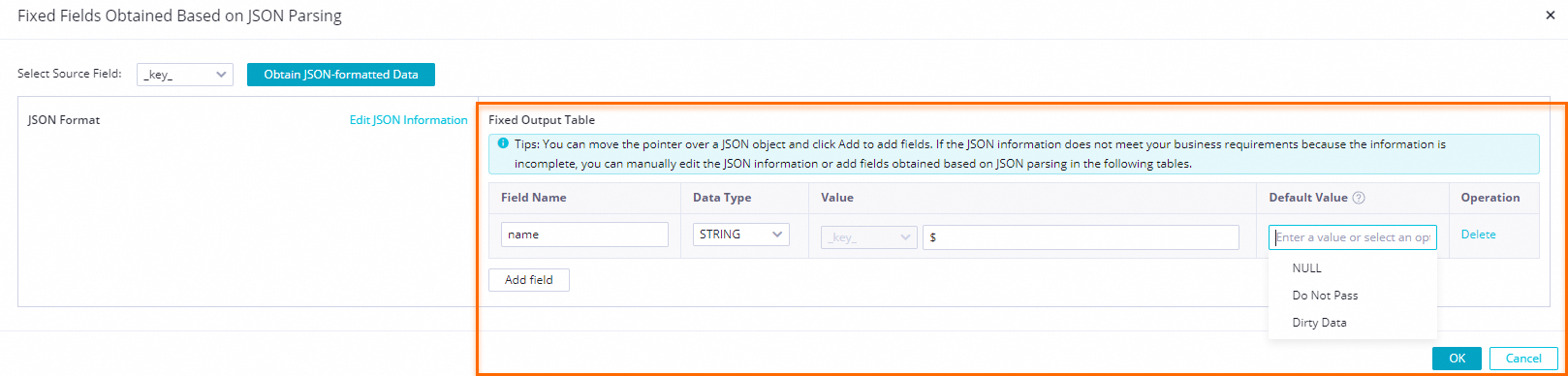
Manually add a field by clicking Add A Field. If you cannot obtain the upstream field value and have not uploaded JSON content by clicking the Edit JSON Text button, you can manually define a fixed field parsing rule. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Field Name
The name of the new parsed field to be referenced in downstream nodes.
Value
Specifies the JSON parsing path. The parsing syntax is as follows:
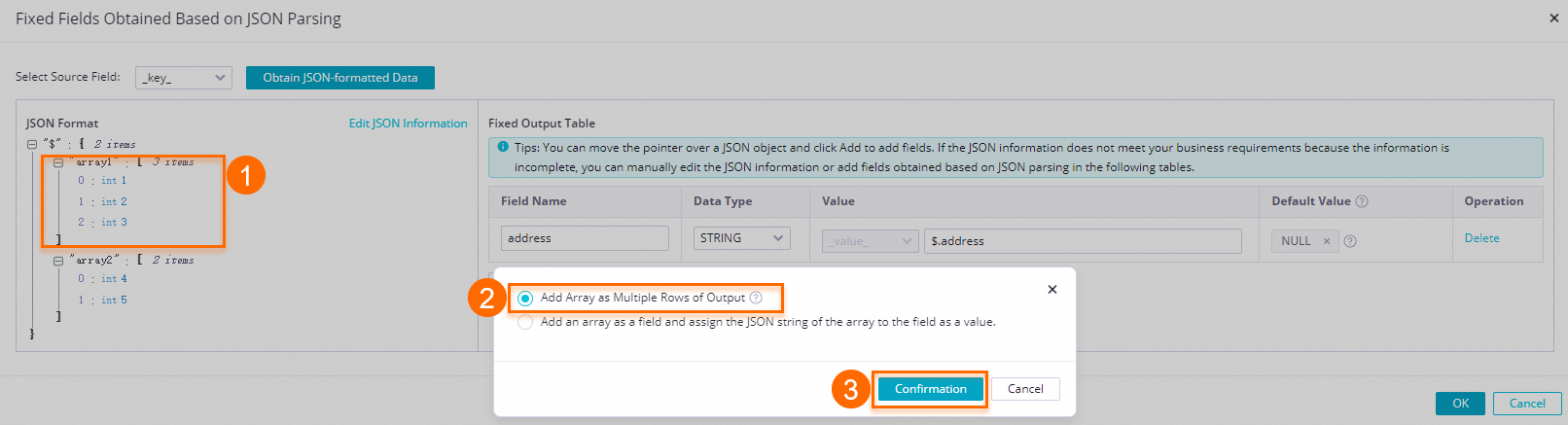
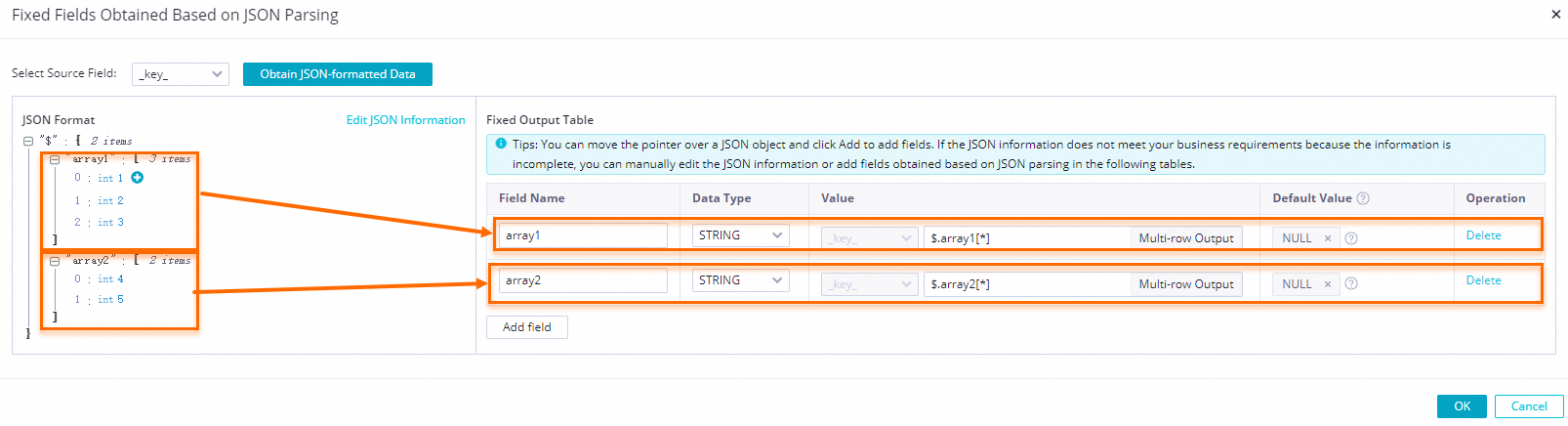
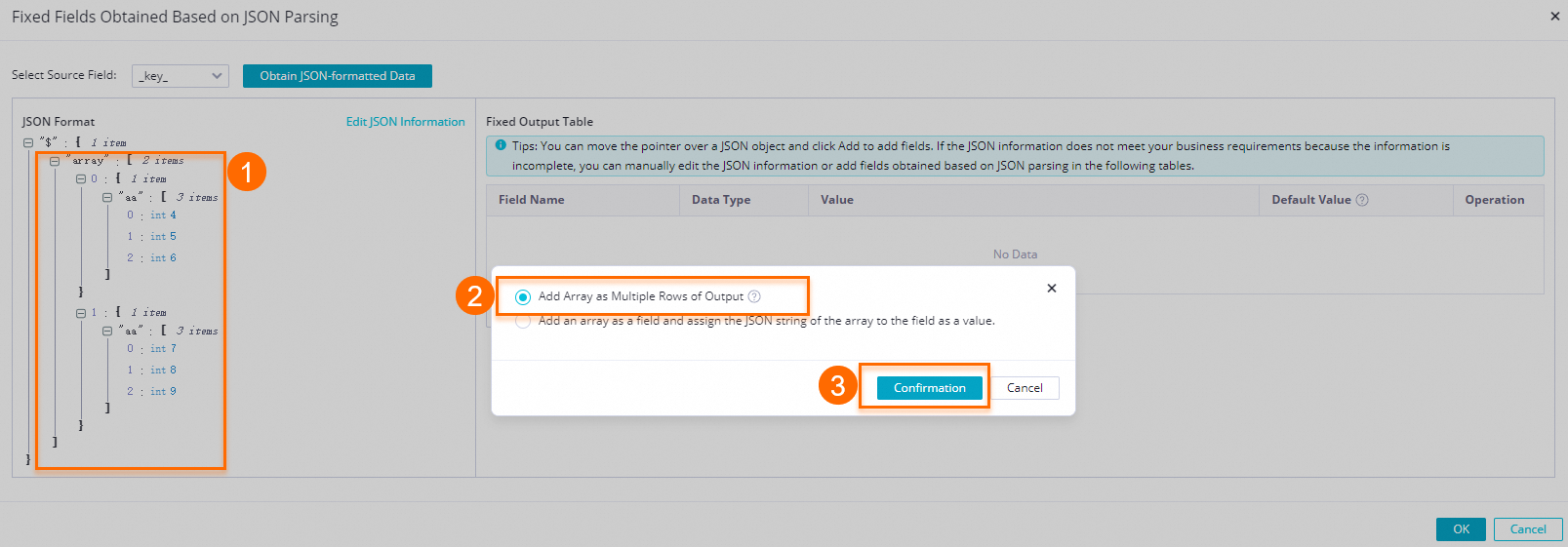
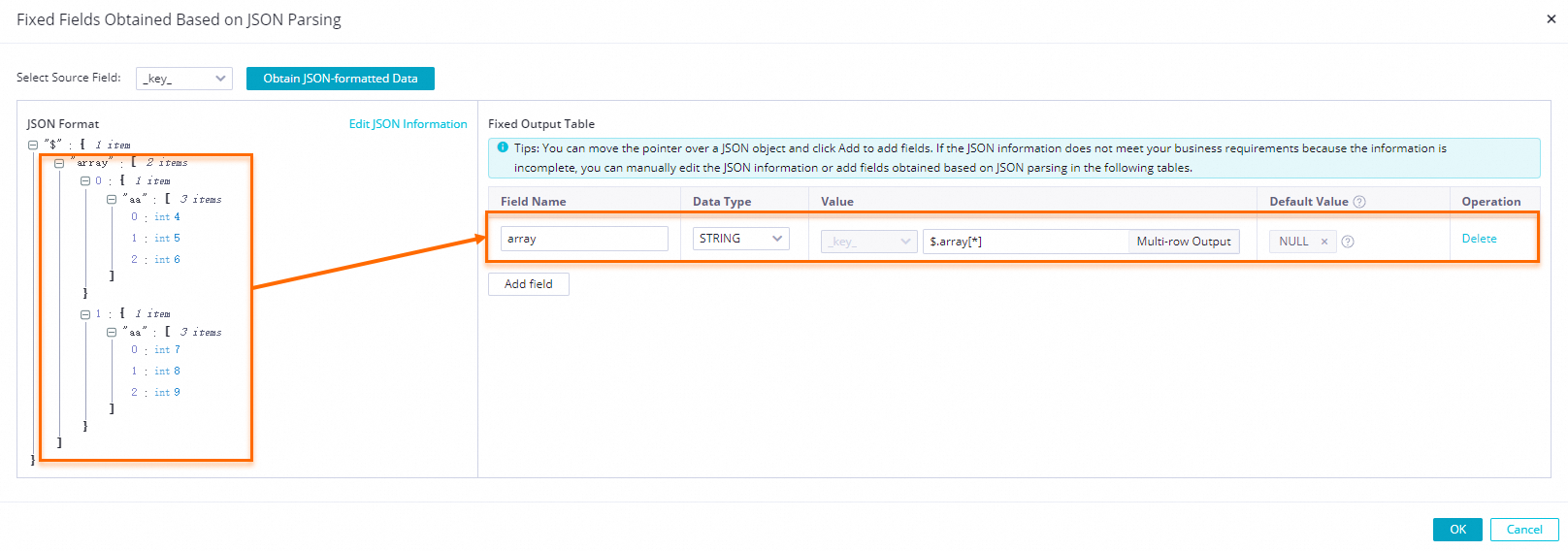
$: The root node..: A child node.[]:[number]indicates an array index. The index starts from 0.[*]: Expands an array into a multi-row output. Each element is combined with other fields in the record to form a separate row that is output to downstream nodes.
NoteA JSON field name in a JSON parsing path can contain only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
Default Value
The default value to use when the JSON path for obtaining a value does not exist because the fields in an upstream table change.
NULL: The field is assigned the NULL value.
Do Not Fill: The field is not filled with any value. The difference from selecting NULL is that when writing to the corresponding field in the destination table, if the destination field is configured with a default value, that default value is used instead of NULL.
Dirty Data: The record is counted as dirty data for the sync task. The system then decides whether to stop the task with an error based on the dirty data tolerance configuration.
Manually enter a constant: Use a manually entered constant as the field value.
Add dynamic fields for JSON parsing
Obtain JSON-formatted data.
Get JSON data
Description
Illustration
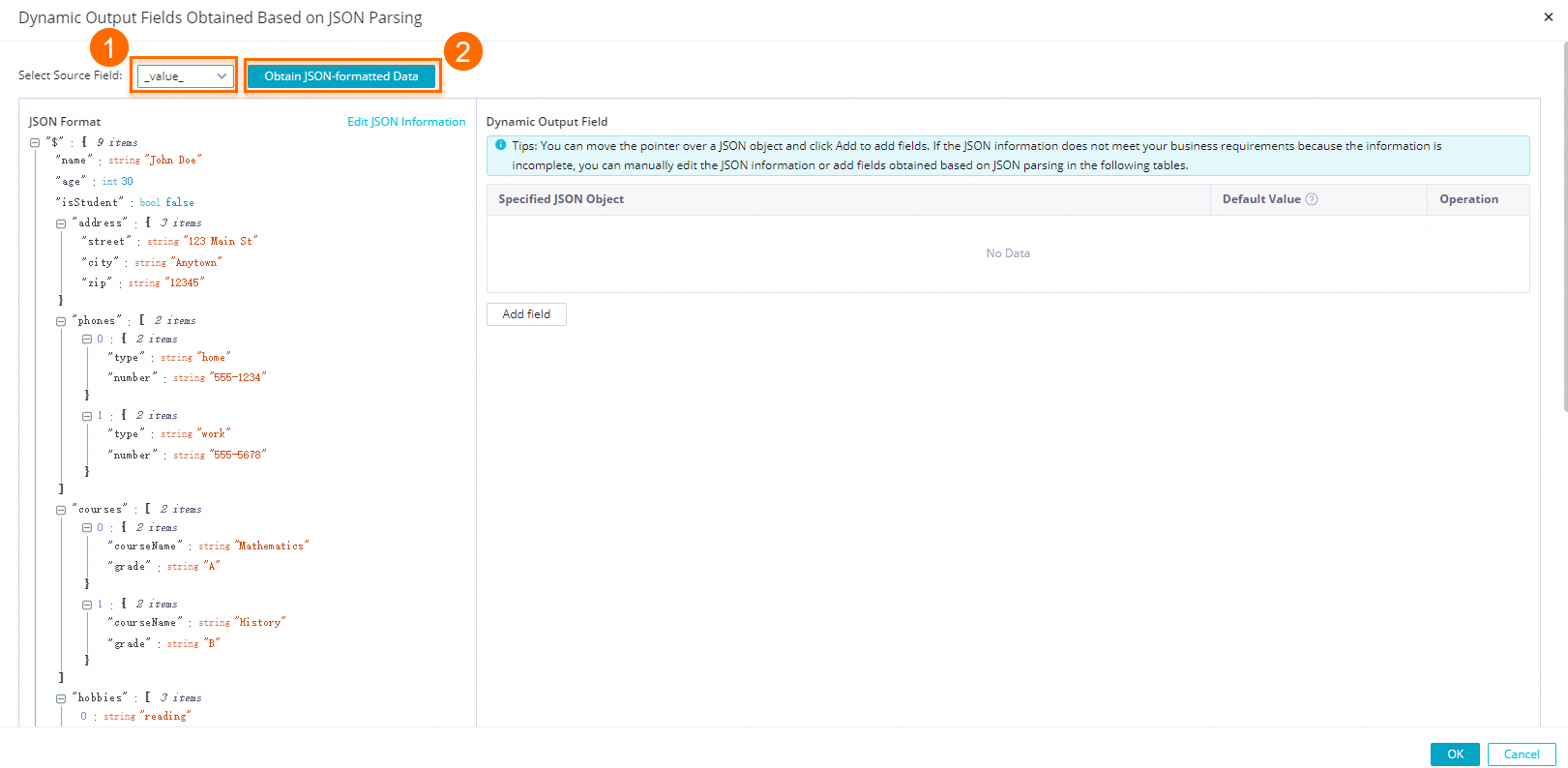
Get JSON data from data sampling
After data sampling, click Add Dynamic Field For JSON Parsing. In the Dynamic Output Field For JSON Parsing dialog box, select a source field and click Get JSON Data Structure.
Get manually entered JSON data
Click Add Dynamic Field For JSON Parsing. In the Dynamic Output Field For JSON Parsing dialog box, if you cannot get the upstream field value or the value does not conform to JSON specifications, click Edit JSON Text. In the Edit JSON Text dialog box, manually enter the JSON content and click OK to format the uploaded JSON content.
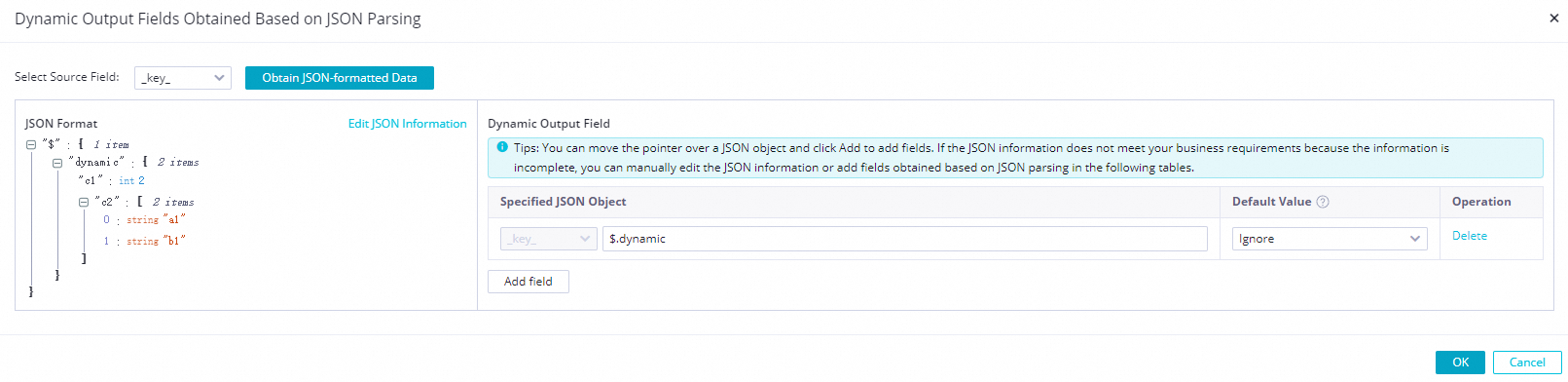
Dynamically parse JSON objects.
In the JSON content, select the JSON object field that you want to dynamically parse. The system automatically adds the parsing configuration for each field in the JSON object to the fixed output fields.
Configure dynamic parsing for a JSON object. When the sync task is running, each field of the JSON object at the specified path is added to the record as a STRING type with the original JSON field name and value, and then sent to downstream nodes. This allows the system to automatically detect and output structural changes, such as new fields, during synchronization.
The following figures show an example.
Before the object is parsed:
After the object is parsed:
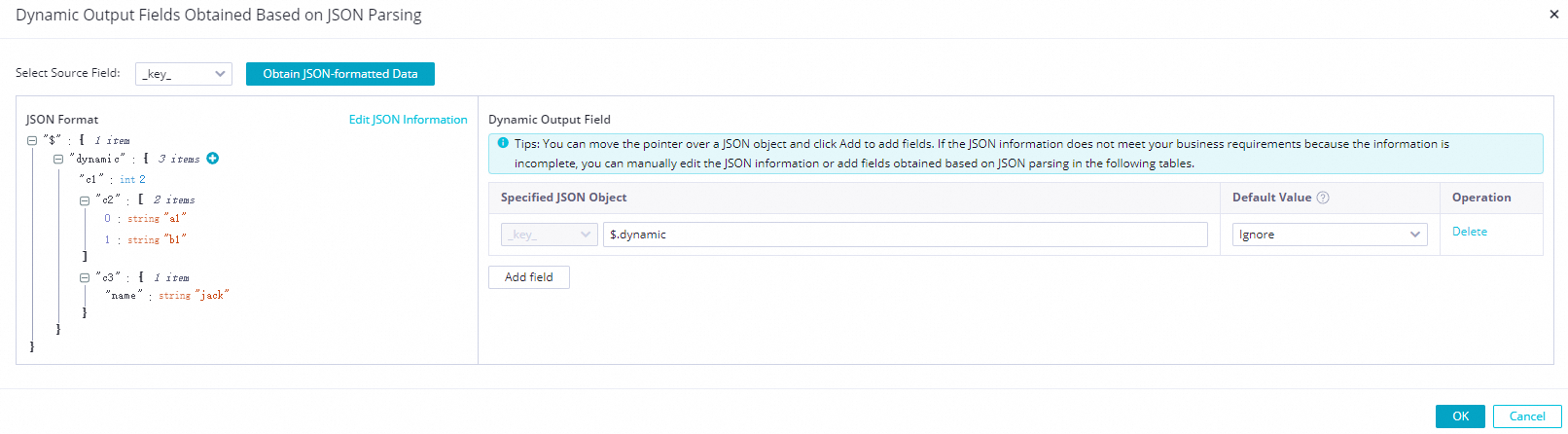
The following table shows the parsing results.
_value_(STRING)
c1(STRING)
c2(STRING)
c3(STRING)
{ "dynamic": { "c1": 2, "c2": ["a1","b1"] } }2["a1","b1"]Not filled
{ "dynamic": { "c1": 2, "c2": ["a1","b1"], "c3": {"name": "jack"} } }2["a1","b1"]{"name": "jack"}
Manually add a field.
You can also manually add a field. If you cannot obtain the value of an upstream child field and have not uploaded JSON content by clicking the Edit JSON Text button, you can manually define a dynamic field parsing rule by editing its value.
Parameter
Description
Specify JSON Object
Specifies the JSON object parsing path. The parsing syntax is as follows:
$: The root node..: A child node.[]: [number] indicates an array index. The index starts from 0.
Note: A JSON field name in a JSON parsing path can contain only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
Default Value
Specifies the default behavior when the specified JSON parsing path fails to be parsed or the corresponding field does not exist.
Ignore: Dynamic parsing is not performed.Dirty data: The record is counted as dirty data for the sync task. The system then decides whether to stop the task with an error based on the dirty data tolerance configuration.
Policy for handling existing fields with the same name.
When dynamic JSON fields are expanded by key-value pairs, only the first layer is expanded. If an expanded field has the same name as an existing field, you must select a conflict resolution policy. The available policies are described as follows:
Overwrite: Replaces the value of the existing field with the value of the new field.
Discard: Keeps the value of the existing field and discards the value of the new field.
Error: The task reports an error and stops running.
More operations
After you configure the Source, JSON Parsing, and Destination settings, click Run Simulation in the upper-right corner to simulate the data integration task. This lets you verify that the output data meets your requirements.
 to select a leaf field. A corresponding parsing configuration is automatically added to the Fixed Output Fields section.
to select a leaf field. A corresponding parsing configuration is automatically added to the Fixed Output Fields section.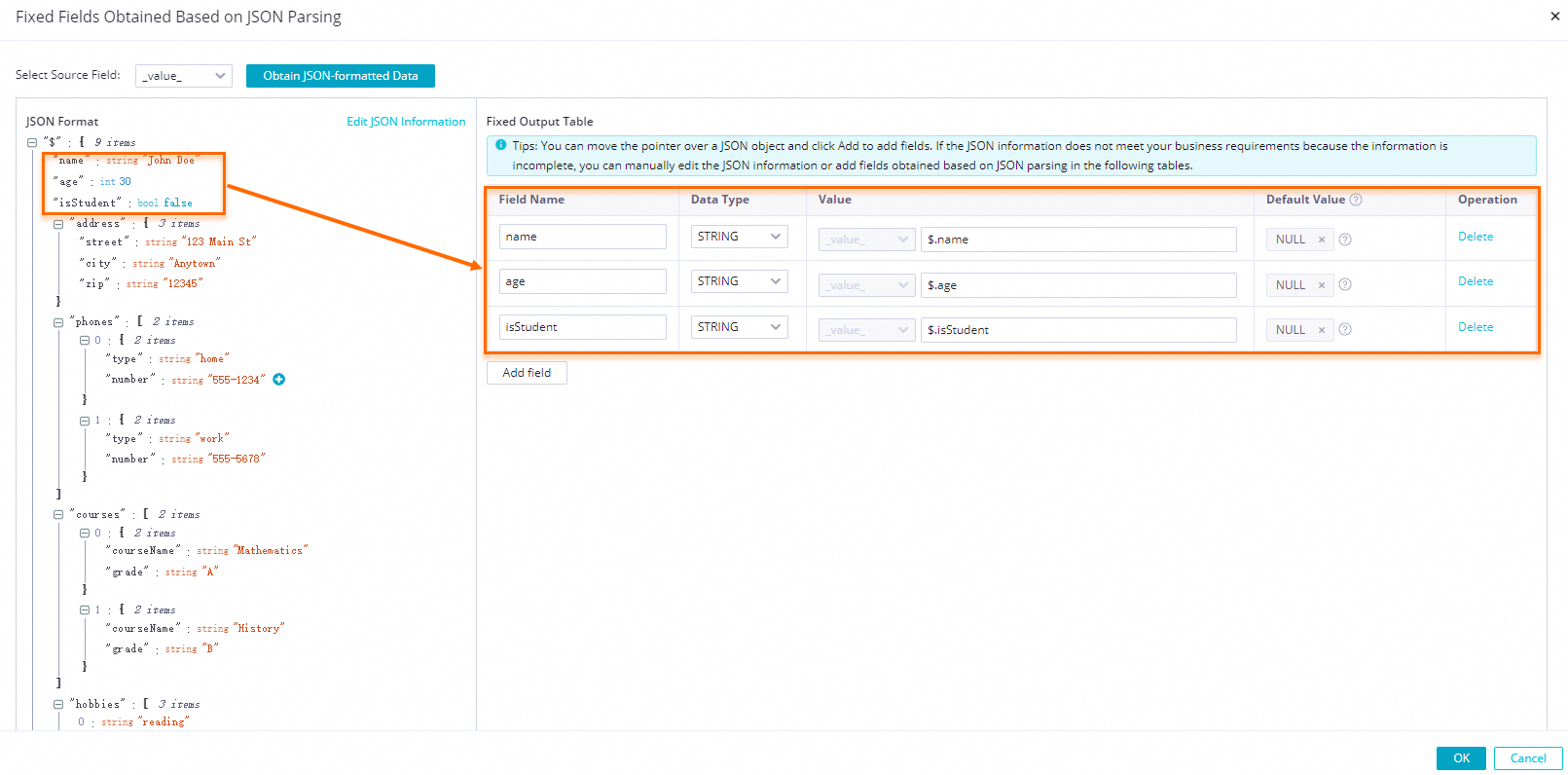

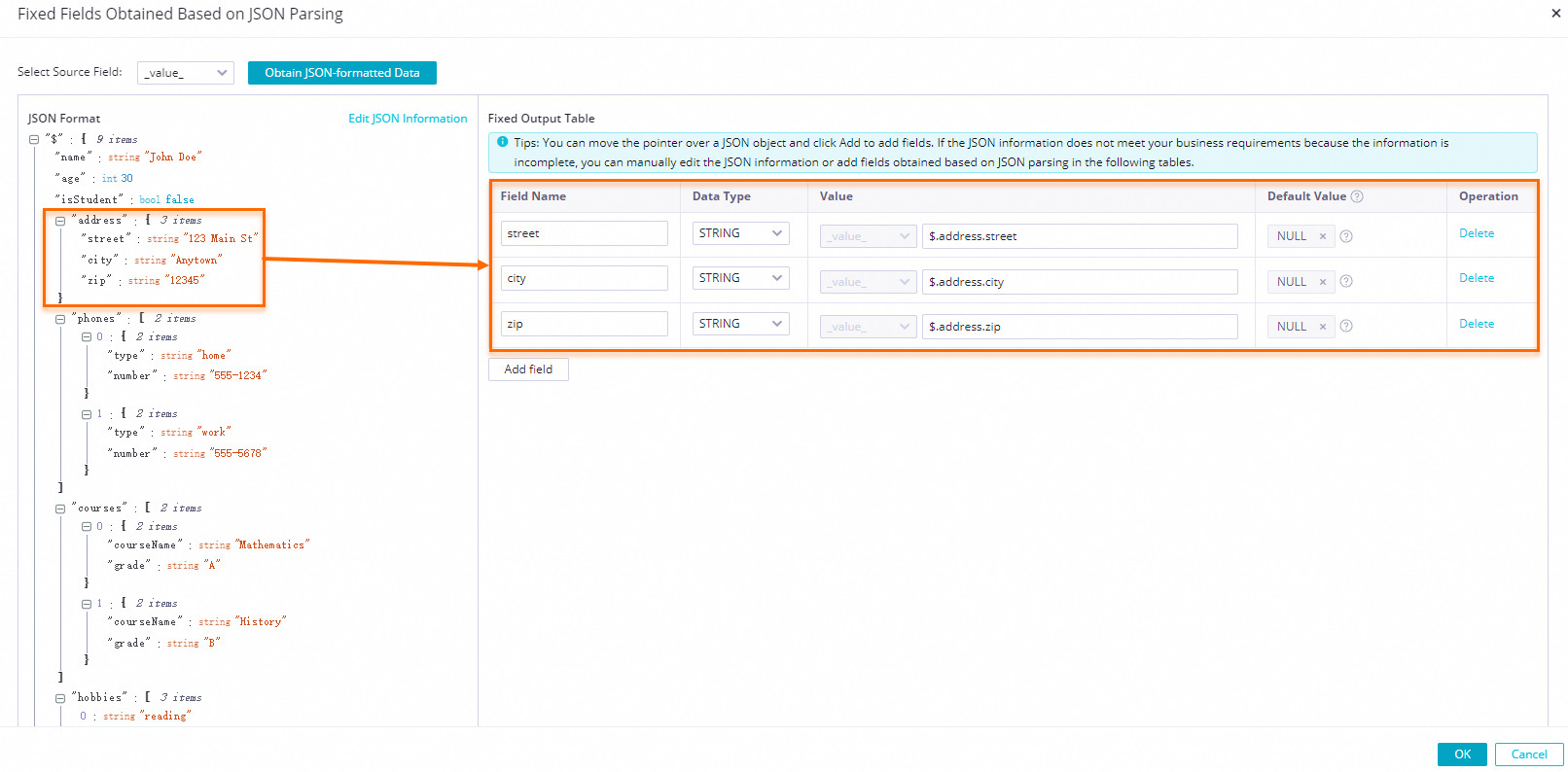
 icon next to the address field and select Add each key-value pair in the JSON object as a separate field. The key is used as the field name and is assigned its corresponding value. in the dialog box.
icon next to the address field and select Add each key-value pair in the JSON object as a separate field. The key is used as the field name and is assigned its corresponding value. in the dialog box.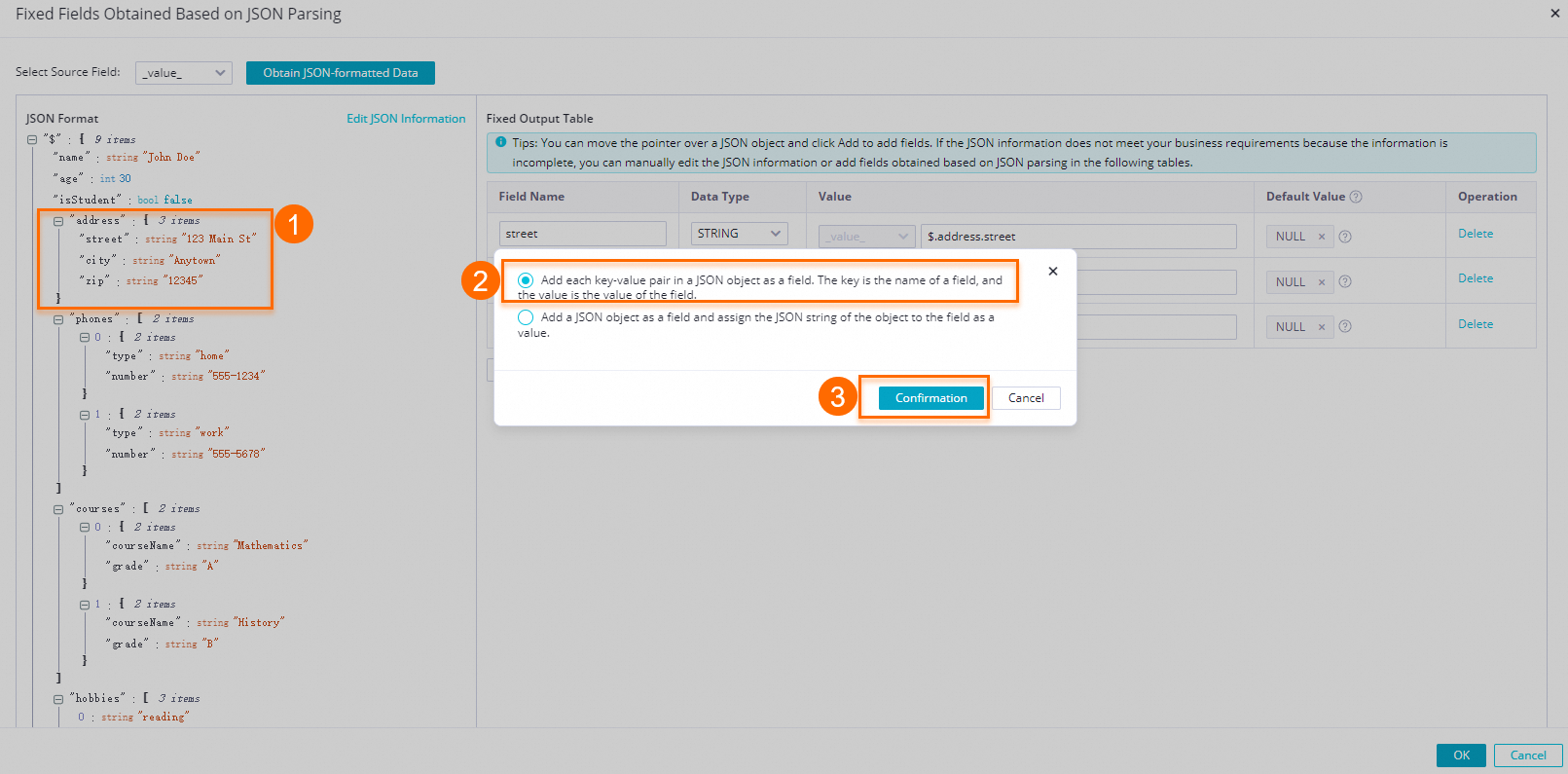

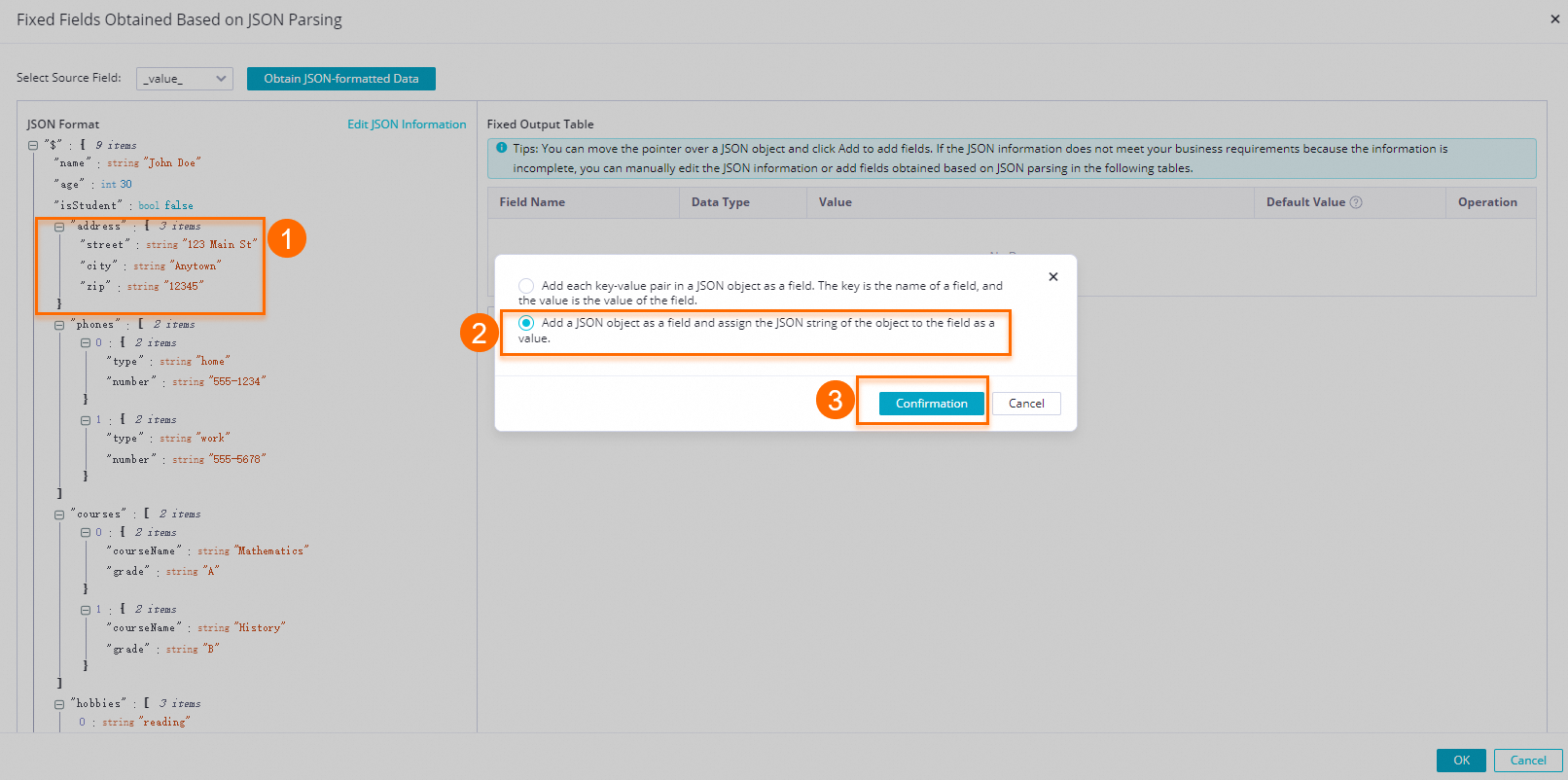
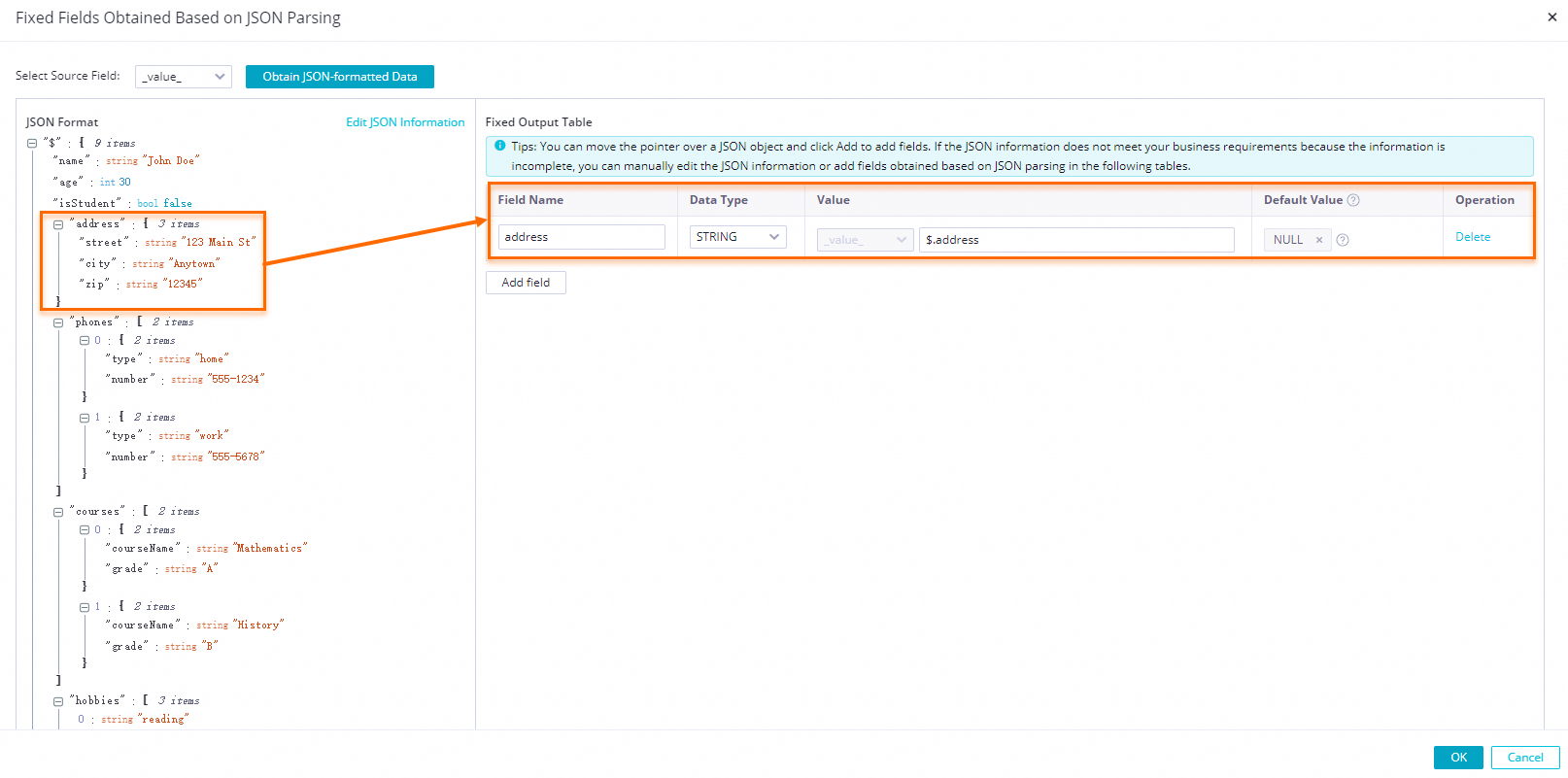

 icon next to the array1 and array2 fields and select Add the array as a multi-row output. in the dialog box.
icon next to the array1 and array2 fields and select Add the array as a multi-row output. in the dialog box.