DataWorks provides two workspace modes, basic mode and standard mode, to meet various data production, security, and governance needs. This topic compares the architecture and development workflows of basic mode and standard mode.
Background
This topic covers the following sections:
Section | Description |
Describes the architecture of each workspace mode. | |
Impact of different modes on production node development and O&M | Explains the development and O&M mechanisms in DataWorks, which are based on the architectural properties of each mode. |
Compares the pros and cons of each workspace mode. | |
Illustrates the role-based workflow and governance in a standard mode workspace. | |
Explains how DataWorks modules connect to data sources in the different environments available in each mode. | |
Provides guidance for users of basic mode workspaces who want to implement separation between development and production. |
Notes
Each workspace mode has specific requirements for creating data sources. To achieve environment isolation in a standard mode workspace, create physically separate data sources for the development and production environments. For more information about creating data sources in a workspace, see Data source management.
The ability to access resources or data across different projects or databases depends on the features of the data source itself. If you configure different data sources for the development and production environments, the data source's capabilities determine whether you can access production tables, resources, or functions from the development environment.
By default, nodes in a standard mode development environment are not scheduled for periodic execution. Only nodes that are deployed to the production environment can be periodically scheduled.
Introduction to basic and standard modes
You can create a workspace in either mode to explore DataWorks. However, for actual development work, we strongly recommend using a standard mode workspace. This allows you to implement code isolation between development and production environments, use separate computing resources, enforce permission controls, and establish a governed node deployment process.
If you use a basic mode workspace and want to preserve its code, you can upgrade it to standard mode. For more information, see Upgrade workspace mode.
The following table compares basic mode and standard mode workspaces.
Aspect | Basic mode | Standard mode (recommended) |
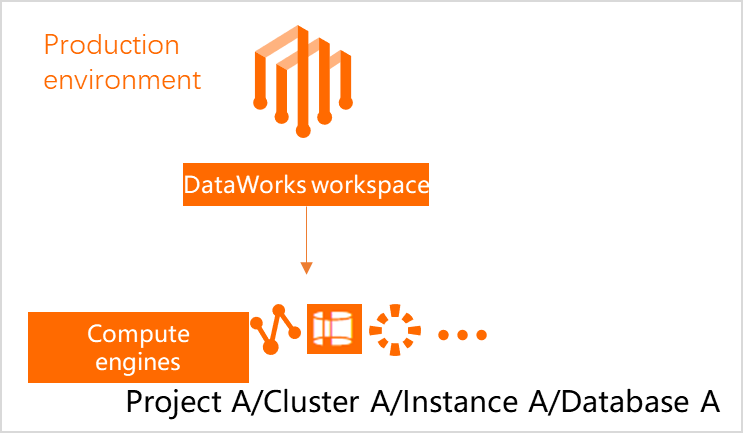
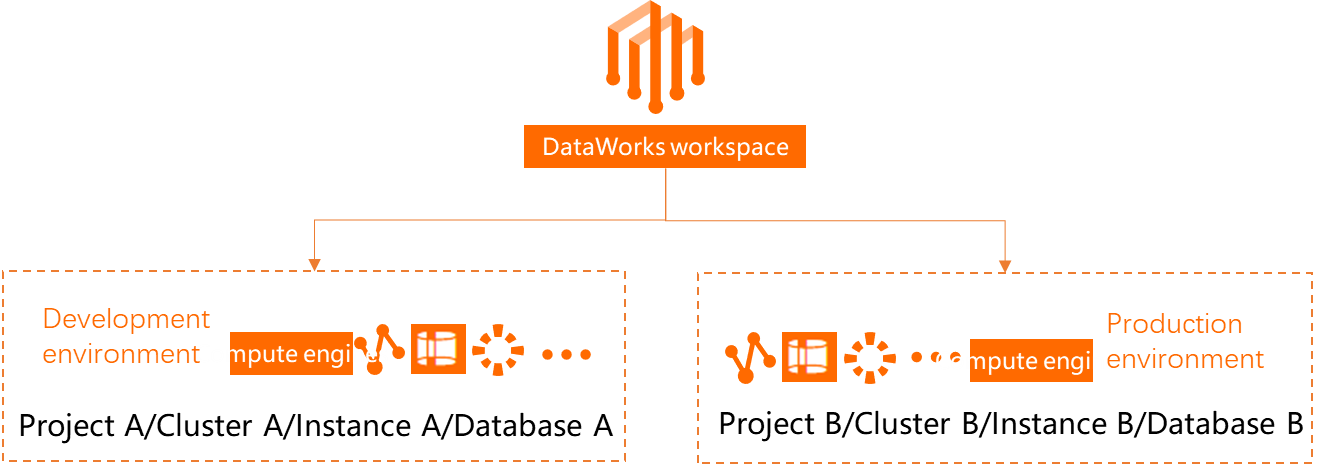
Number of data sources | A basic mode workspace connects to a single data source. | One DataWorks workspace is associated with two data sources, allowing you to isolate the data sources for the development and production environments. Note To achieve environment isolation, create physically separate data sources for the development and production environments.
|
Corresponding DataWorks environment | The single data source serves as the production environment for DataWorks. | One data source serves as the DataWorks development environment, and the other serves as the production environment. Note You can configure different types of data sources for each environment. For example:
|
Impact of different modes on production node development and O&M
Comparison | Basic mode | Standard mode (recommended) |
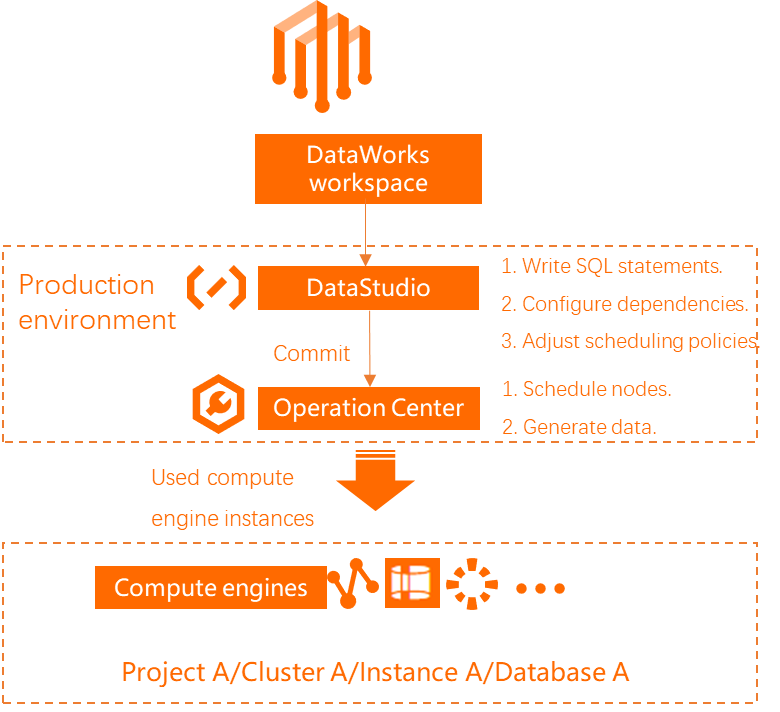
Control over the production node development workflow | After a node is committed, the scheduling system can immediately run it periodically to generate output data. No deployment step is required. (Commit -> Production)
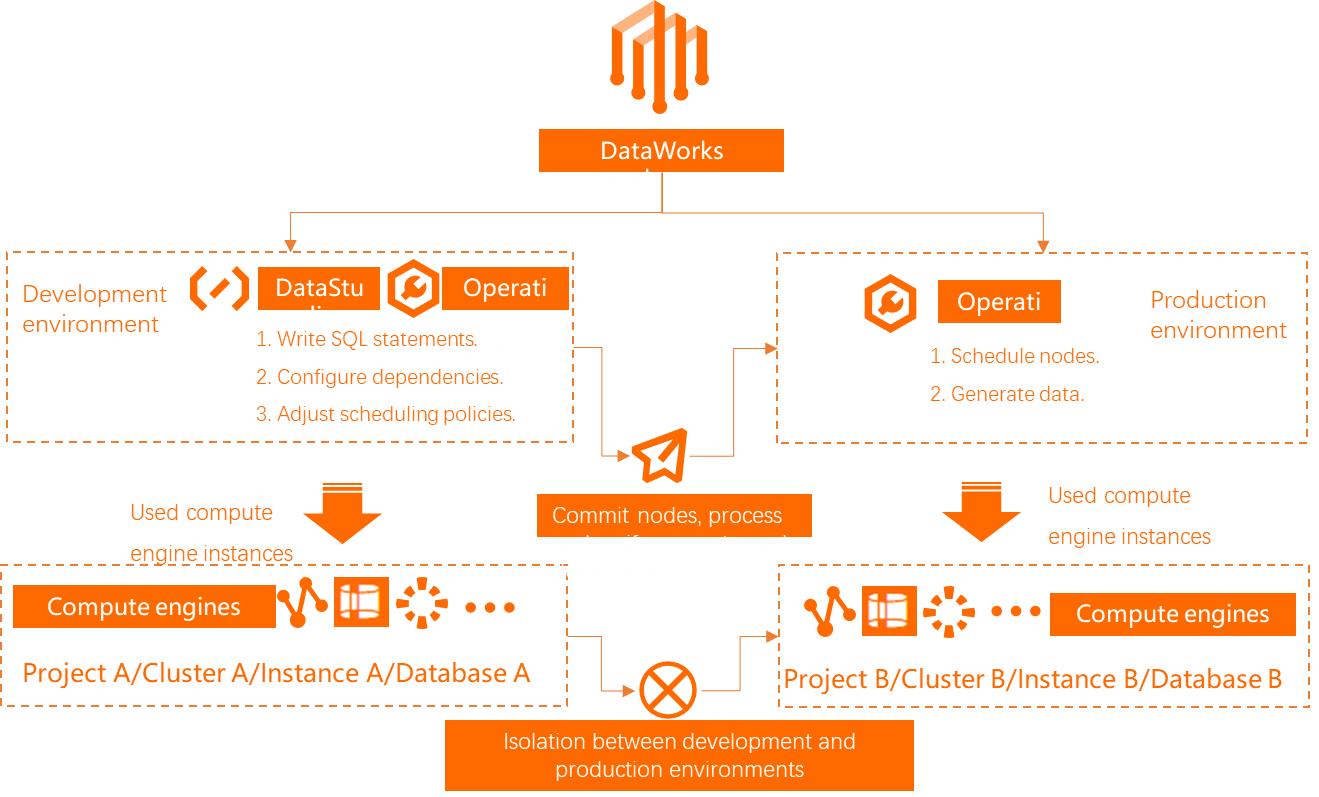
| A node must first be committed to the development environment. Then, it must be deployed to the production environment before it can be automatically scheduled and run. (Commit -> Deploy -> Production) Note In standard mode, only nodes in the production environment are automatically scheduled.
|
Control over O&M permissions for production nodes | Developers can directly edit the code of production nodes. | Developers can only edit and commit code in Data Studio. They cannot directly deploy code to the production environment. Deploying to the production environment requires O&M permissions, which are held by roles such as Workspace Owner, Administrator, and O&M.
|
Control over production data permissions | Developers can directly use production data for testing, which poses a risk to data security. | In the development environment, developers can use test data for testing. They can also be granted or apply for permissions to use production table data for verification. Note
|
Differences in data access identity | A single identity is used to directly operate on the production environment. For MaxCompute, Hologres, EMR, and CDH, the access identity can be an Alibaba Cloud account, a RAM user, a RAM role (MaxCompute only), or the node owner. Note For other compute engines, such as AnalyticDB for MySQL and AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, the access identity depends on the account you bind when creating the data source. The permissions are consistent with those of the account in the database. |
Note For MaxCompute, Hologres, EMR, and CDH:
For other compute engines, such as AnalyticDB for MySQL and AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, the access identity depends on the account you bind to each environment when creating the data source. The permissions are consistent with those of the account in the database. |
Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of each mode
Aspect | Basic mode | Standard mode |
Advantages | Simple and easy to use. You only need to grant developers the developer role to perform all data warehousing development tasks. | Secure and well-governed.
|
Disadvantages | Carries risks of instability and insecurity.
| The workflow is more complex. Typically, a single person cannot manage the entire development-to-production lifecycle. |
Use case: Impact of standard mode on the workflow
As shown in the following diagram, the environment isolation in standard mode impacts workflows such as data model design, data processing logic, and code deployment.

Data source mapping for DataWorks modules in each mode
You can view the bound computing resources in Data Studio by navigating to the Computing Resource page. After binding, the DataWorks modules operate on the following data sources in each Workspace Mode:
DataWorks module | Standard mode | Basic mode |
Data Studio | Operates on the development environment data source (instance, project, or database). | Operates on the production environment data source (instance, project, or database). |
Operation Center |
|
Achieve environment isolation in basic mode
Goal: To isolate the development and production environments while using Basic Mode workspaces.
Implementation: You can use two separate basic mode workspaces, one as a development environment and the other as a production environment. You can then use the cross-workspace deployment feature to deploy nodes from the development workspace to the production workspace. This approach isolates the environments.
Disadvantage: With this approach, you can still directly edit production code in the Data Studio module of the production workspace. This means the production environment lacks a single, controlled entry point for code updates, which bypasses the controls of a governed workflow.
Recommendation: We strongly recommend upgrading your basic mode workspace to a standard mode workspace to establish a more robust and governed development workflow. For more information, see Upgrade workspace mode.