A derived metric is composed of an atomic metric, a period, and one or more modifiers. A derived metric reflects the status of a business activity within a specific period and a specific scope. For example, you can use a derived metric to measure the sales amount in the last week for an enterprise in Shanghai. This topic describes how to create a single derived metric and create multiple derived metrics at a time. This topic also describes other operations related to derived metrics, such as viewing the versions of a derived metric, viewing the fields associated with a derived metric, exporting derived metrics, and deleting a derived metric.
Prerequisites
Preparation | Description |
An atomic metric is created. | The atomic metric is used to define a criterion and computing logic for the statistical analysis of a business activity. |
A modifier is created. | The modifier is used to define the scope for the statistical analysis of a business activity. |
A period is created. | The period is used to define the period of time for the statistical analysis of a business activity. |
A dimension table is created. | The dimension table is used to define the statistical dimension of a business activity. |
You must create a data layer based on your business requirements.
| |
|
|
Background information
A derived metric collects statistical data on the status of a business activity for an enterprise. A derived metric is composed of an atomic metric, a period, and one or more modifiers. A derived metric can reference only one atomic metric and collects statistical data on the values of the atomic metric within a specific period based on specific business conditions.
An atomic metric defines the statistical criteria and calculation logic. For example, the total number of orders.
A modifier limits the scope of a business activity. For example, online fresh food outlets and offline fresh food outlets.
NoteA derived metric can contain one or more modifiers.
A period specifies the time range for statistics. For example, a calendar day.
A derived metric consists of an atomic metric, modifiers, and a period. It is used to retrieve the value of a target metric for specific times, dimensions, and business conditions, which reflects the status of a business activity. For example, you can calculate
the total number of orders from online fresh food outlets on a calendar dayorthe total number of orders from online and offline fresh food outlets on a calendar day.
Go to the Derived Metric page
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Data Modeling.
In the top navigation bar of the Data Modeling page, click Data Metric. The Derived Metric page appears.
You can create a derived metric at a common layer or an application layer based on your business requirements. In addition, you can choose to create a single derived metric or create multiple derived metrics at a time.
In most cases, the business activities of an enterprise are complex and diverse, and the status of multiple business activities within different periods and scopes needs to be analyzed at the same time. We recommend that you create multiple derived metrics for one type of business activity at a time. For information about how to create multiple derived metrics at a time, see the Create multiple derived metrics at a time section in this topic. For information about how to create a single derived metric, see the Create a single derived metric section in this topic.
Create multiple derived metrics at a time
Select an operation type.
In the Derived Metric pane, move the pointer over the
 icon and click Multiple Derived Metrics.
icon and click Multiple Derived Metrics. Create a metric model that is used to create multiple derived metrics at a time.
Select atomic metrics, modifiers, and periods.
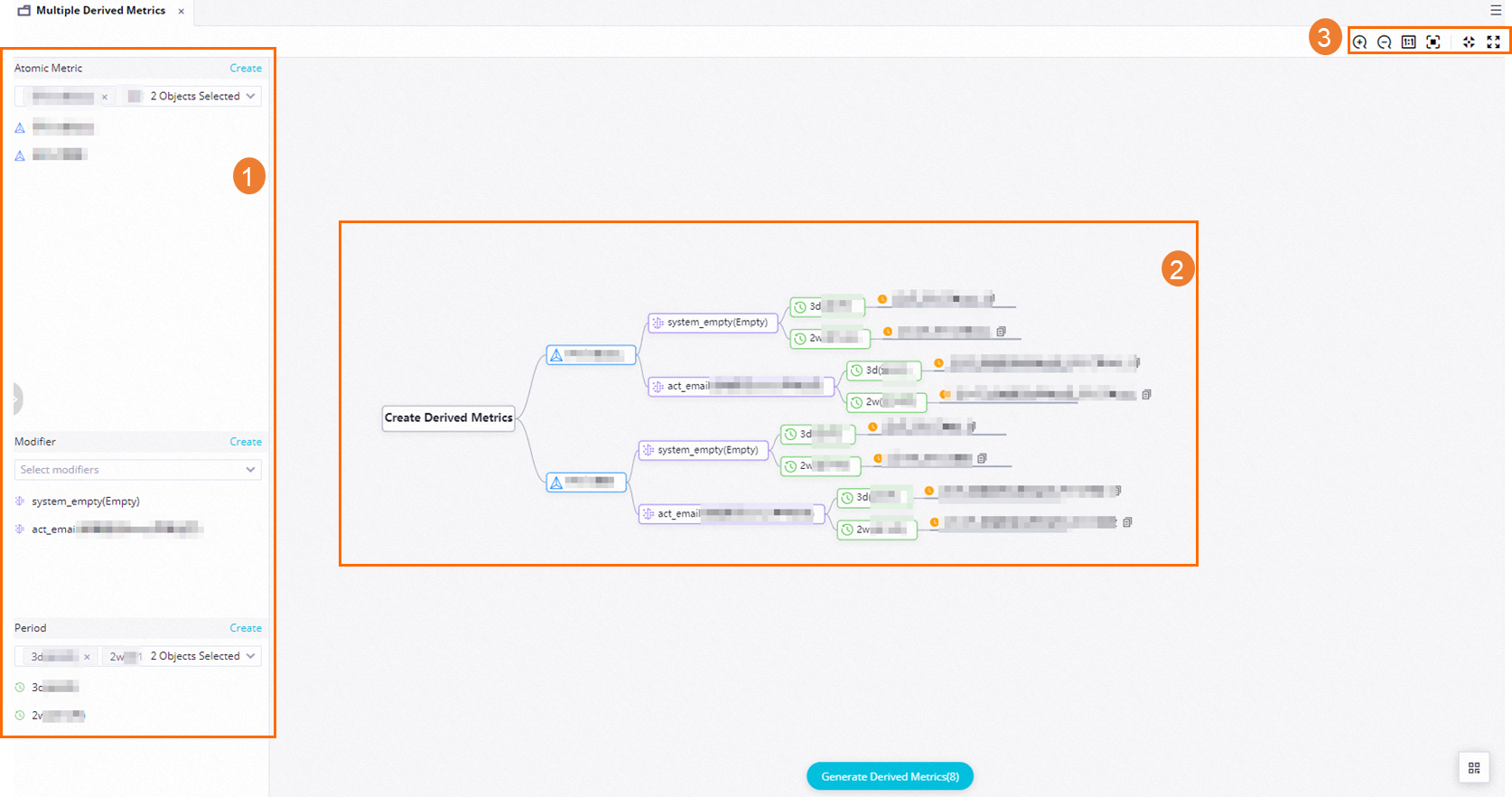
Area
Description
1
In this area, you can select atomic metrics, modifiers, and periods that are used to create multiple derived metrics at a time.
NoteIf the atomic metrics, modifiers, or periods that are displayed do not meet your business requirements, you can click Create to create the desired objects.
A derived metric is composed of an atomic metric, a period, and one or more modifiers.
2
In this area, a render tree is displayed to show all derived metrics that will be created at a time. The following icons can be displayed for a derived metric:
 : indicates that the derived metric does not exist.
: indicates that the derived metric does not exist.  : indicates that the derived metric already exists. When you create derived metrics, the system does not create an existing derived metric again.
: indicates that the derived metric already exists. When you create derived metrics, the system does not create an existing derived metric again.  : allows you to copy the derived metric.
: allows you to copy the derived metric.
3
In this area, you can change the display mode of the render tree. For example, you can zoom in, zoom out, or center the render tree, or present the render tree in full screen.
Click Generate Derived Metrics.
Create multiple derived metrics at a time.
Select a data layer and a checker.
In the Generate Derived Metrics dialog box, select a data layer and a checker based on your business requirements. The checker is used to standardize the naming formats of the derived metrics.
NoteIf no checkers are available, you can create one in Data Warehouse Planning. For more information about how to create a checker, see Configure data warehouse layer checkers.
Click Next.
Select the derived metrics that you want to create.
In the Select Derived Metrics step, select the derived metrics that you want to create based on the created metric model. By default, all derived metrics in the metric model are selected.
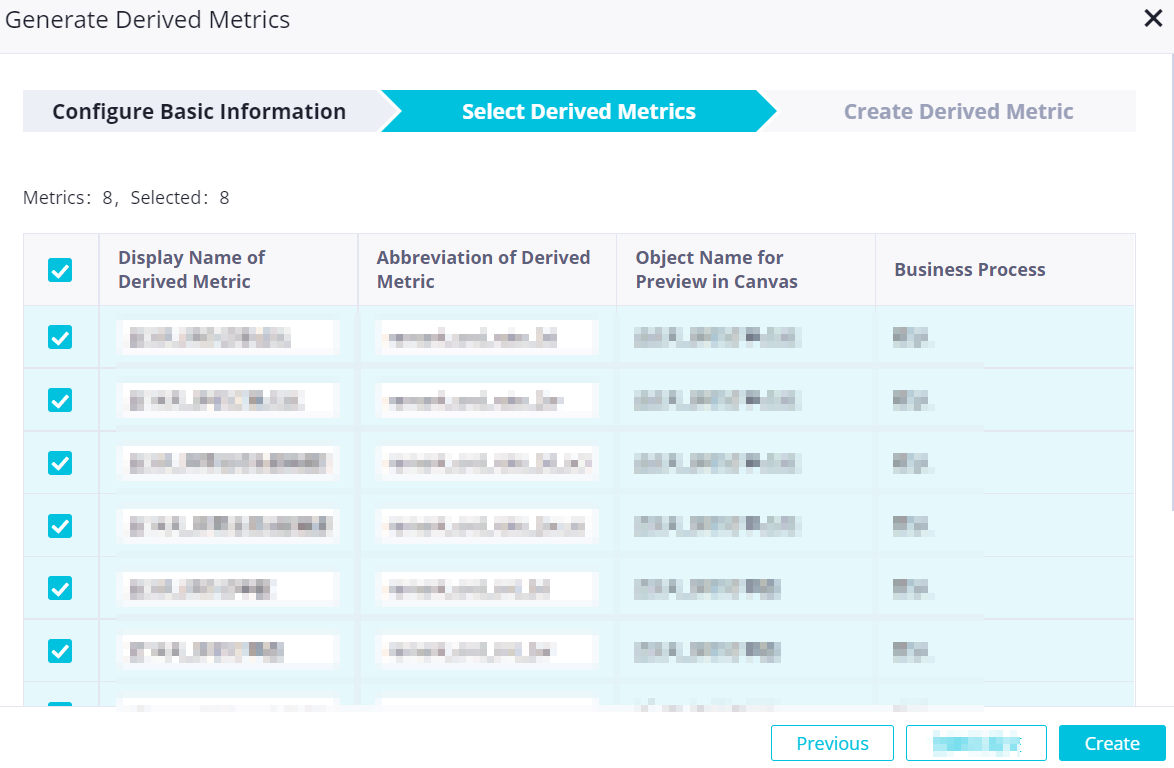
Click Create or Create and Submit. The derived metrics are created at a time.
If you click Create, the selected derived metrics are created. You must go to the configuration tabs of the derived metrics to submit the derived metrics.
If you click Create and Submit, the selected derived metrics are created and submitted. Only submitted derived metrics can be referenced when you create tables.
After a derived metric is created, the state of the metric in the render tree changes from
 to
to  .
.
In the Create Derived Metric step, view the created derived metrics.
You can view information about the created derived metrics in the derived metric list.
Create a single derived metric
Select an operation type.
In the Derived Metric pane, move the pointer over the
 icon and click Derived Metric.
icon and click Derived Metric. Create a derived metric.
Configure business logic.
Configure the parameters listed in the following table based on your business requirements.
Parameter
Description
Period
The period of time for which you want to perform statistical analysis for a business activity. Examples: last day and last week.
Modifier
The scope for the statistical analysis of a business activity. Examples: online and offline.
Atomic Metric
The atomic metric that is used to define a criterion and computing logic for the statistical analysis of a business activity. Example: order amount.
Configure basic information.
You can create a derived metric at the DWS layer or ADS layer based on your business requirements. The following table describes the basic information that you can configure.
Parameter
Description
Data Layer
The data layer at which the derived metric is created.
Business Category
The business category to which the derived metric belongs. A business category can be associated with a data domain or data mart.
This parameter is displayed and required only if you set the Data Layer parameter to Common Layer.
Business Process
The category of the business activity.
This parameter is displayed and required only if you set the Data Layer parameter to Common Layer.
Mart/Subject
The category of the business activity for a specific scenario or product.
This parameter is displayed and required only if you set the Data Layer parameter to Application Layer.
Display Name
The display name of the derived metric. You can click Intelligent Recommendation on the right side to generate a display name in the
Period name_Modifier names_Atomic metric nameformat. The generated display name can help you identify the meaning of statistical data collected by the derived metric in an efficient manner.NoteIntelligent Recommendation is displayed only after you specify an atomic metric and a period when you configure business logic for the derived metric.
You can click the
 icon and select a checker to check whether the display name of the derived metric complies with the specified naming convention. If the checkers that are displayed do not meet your business requirements, you can create one at the related data layer. For more information about how to create a checker, see Configure data warehouse layer checkers.
icon and select a checker to check whether the display name of the derived metric complies with the specified naming convention. If the checkers that are displayed do not meet your business requirements, you can create one at the related data layer. For more information about how to create a checker, see Configure data warehouse layer checkers.
Abbreviation
The abbreviation for the name of the derived metric. You can click Intelligent Recommendation on the right side to generate an abbreviation in the
Period name_Modifier names_Atomic metric nameformat. The generated abbreviation can help you identify the meaning of statistical data collected by the derived metric in an efficient manner.NoteIntelligent Recommendation is displayed only after you specify an atomic metric and a period when you configure business logic for the derived metric.
You can click the
 icon and select a checker to check whether the display name of the derived metric complies with the specified naming convention. If the checkers that are displayed do not meet your business requirements, you can create one at the related data layer. For more information about how to create a checker, see Configure data warehouse layer checkers.
icon and select a checker to check whether the display name of the derived metric complies with the specified naming convention. If the checkers that are displayed do not meet your business requirements, you can create one at the related data layer. For more information about how to create a checker, see Configure data warehouse layer checkers.
Name
The name of the derived metric.
Owner
The owner of the derived metric. The default owner is the creator of the derived metric.
Description
The description of the derived metric.
Click Save in the upper part of the configuration tab. The derived metric is created.
Click Submit in the upper part of the configuration tab. The derived metric is submitted. Only derived metrics that are submitted can be referenced when you create tables.
NoteOnly derived metrics that are saved can be submitted.
Each time you submit the same derived metric, a new version is generated for the derived metric. You can submit a derived metric of a specific version only once.
Manage the versions of a derived metric and view the fields associated with a derived metric
In the right-side navigation pane of the configuration tab of a metric, you can click Version Management to manage the versions of the metric, and can click Associate Tables to view the fields that are associated with the metric.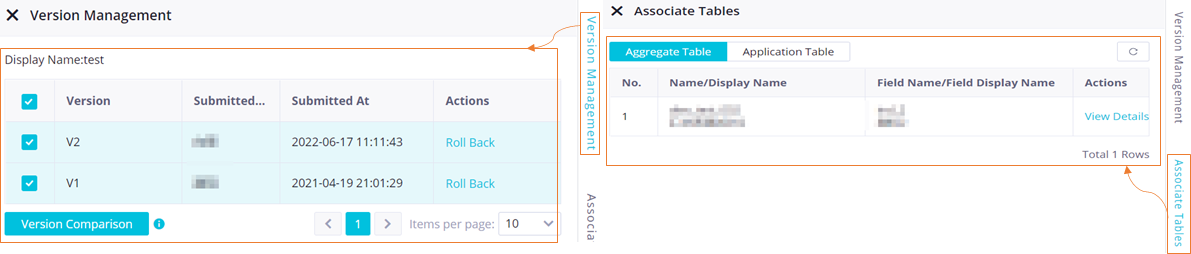
Operation | Description |
Manage the versions of the metric | You can click Version Management to view the version information of the metric. You can also perform the following operations:
|
View the fields associated with the metric | You can view the fields that are associated with the metric. You can click View Details in the Actions column of a field that is associated with the metric to go to the details page of the table to which the field belongs. Then, you can view more information about the table on the details page. |
Export derived metrics
If you want to export multiple derived metrics at a time, you can use the export feature.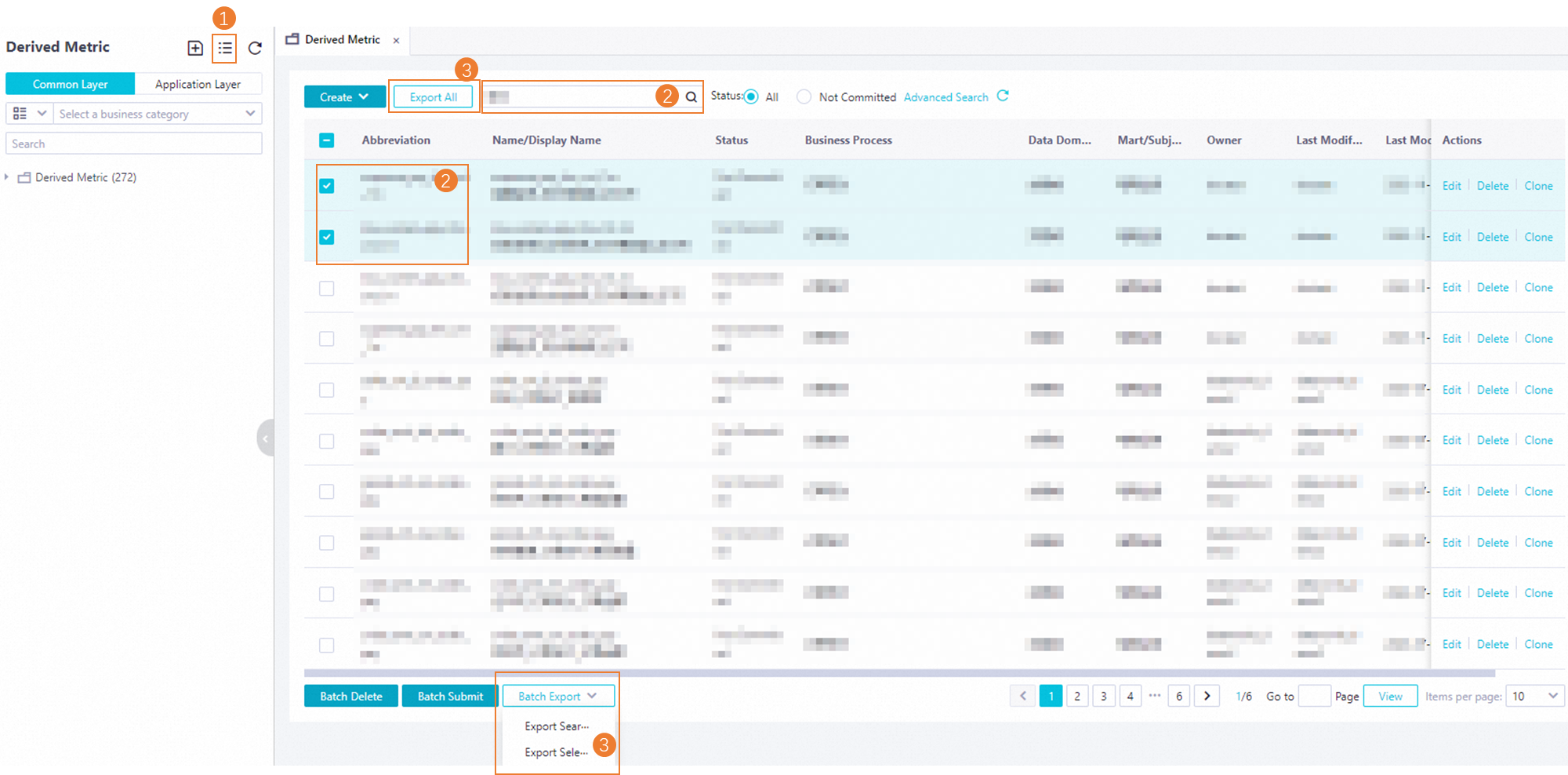
Go to the tab that displays the derived metric list.
In the Derived Metric pane, click the
 icon to go to the tab that displays the derived metric list. On this tab, you can view information about all derived metrics that are created.
icon to go to the tab that displays the derived metric list. On this tab, you can view information about all derived metrics that are created. Select the derived metrics that you want to export.
NoteIf you want to export all existing derived metrics, you can skip this step.
You can use one of the following methods to select the derived metrics that you want to export:
Search for the desired derived metrics by keyword: You can enter a keyword in the search box to search for the desired derived metrics and select the derived metrics.
NoteFuzzy match is supported. After you enter a keyword in the search box, all derived metrics whose names contain the keyword are displayed.
Select the desired derived metrics from the derived metric list: You can directly select the desired derived metrics from the derived metric list.
Export the derived metrics at a time.
You can use one of the following methods to export the derived metrics at a time:
Export All: You can click Export All in the upper part of the tab to export all derived metrics that are created in the current workspace.
Export Searched Objects: You can enter a keyword in the search box to search for the derived metrics that you want to export, click the Batch Export drop-down list in the lower part of the tab, and then select Export Searched Objects. Then, all atomic metrics that are displayed in the search result are exported.
Export Selected Objects: You can select the derived metrics that you want to export, click the Batch Export drop-down list in the lower part of the tab, and then select Export Selected Objects. Then, all derived metrics that you selected are exported.
View and download the export result.
After you initiate an export task, you are navigated to the Details of Export Status of Derived Metrics page. On this page, you can view the status of the export task. After the derived metrics are exported, you can click Download File to download the derived metrics that are exported.
Delete or submit multiple derived metrics at a time
If you want to delete multiple derived metrics that are no longer required or submit multiple derived metrics that are saved, you can select the derived metrics and click the related button to delete or submit the derived metrics at a time.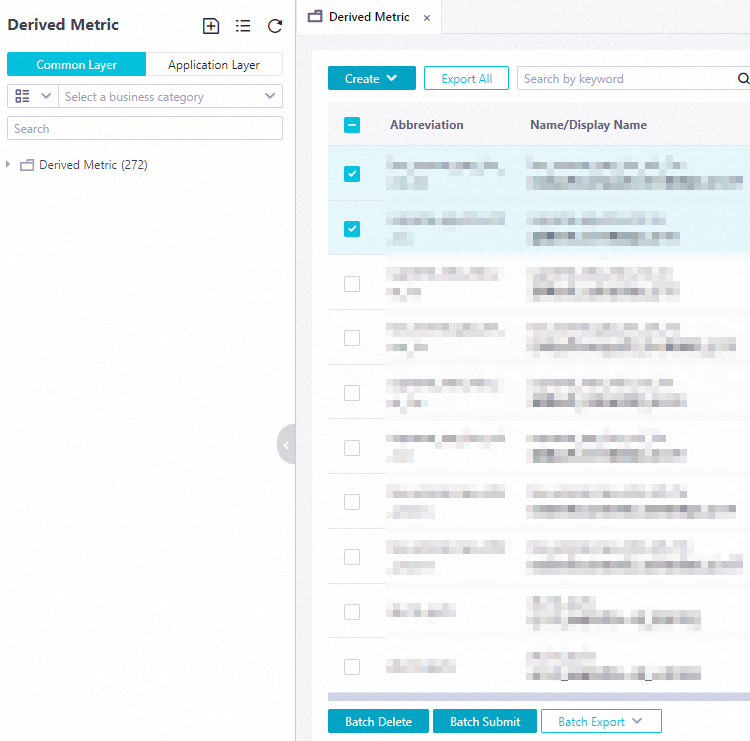
Go to the tab that displays the derived metric list.
In the Derived Metric pane, click the
 icon to go to the tab that displays the derived metric list. On this tab, you can view information about all derived metrics that are created.
icon to go to the tab that displays the derived metric list. On this tab, you can view information about all derived metrics that are created. Select the derived metrics that you want to delete or submit.
NoteOnly derived metrics that are saved but not submitted can be submitted at a time.
Click Batch Delete or Batch Submit based on your business requirements.
Batch Delete: After you click this button, the selected derived metrics are deleted at a time. The deleted derived metrics cannot be referenced when you create tables.
NoteIf a derived metric is referenced by a table, you must remove the reference relationship before you delete the derived metric.
Batch Submit: After you click this button, the selected derived metrics are submitted at a time. Then, they can be referenced when you create tables, and the latest versions are generated for the derived metrics. For more information about the versions of a derived metric, see the Manage the versions of a derived metric and view the fields associated with a derived metric section in this topic.
What to do next
After the derived metric is created, you can reference the derived metric when you create an aggregate table or application table. The aggregate table or application table lays a foundation for subsequent operations such as business queries, OLAP analysis, and data distribution. For more information about how to reference a derived metric when you create a table, see Materialize a table to a compute engine.