Configuring the datasource is a crucial step in widget creation and business data visualization. It encompasses data integration, processing, and real-time updates. This guide details the configuration process for widget data.
Feature description
DataV-Board supports the integration of various business data, including static data, databases, and application gateways. Datasource configuration allows for the integration and adaptation of business data to widgets, while optimizing data loading performance, widget parameter interactions, and real-time updates through settings such as Disable Loading State, Controlled Mode, and Automatic Update Requests.
Operation flow
Prerequisites
Log on to the DataV-Board 7.0 console.
Prepare and add relevant data sources.
Enter the dashboard editing page and create a widget.
Configure data
Widgets are equipped with default static data. The following example illustrates configuring a widget's datasource using static data, global variables, and data sources, exemplified by integrating data for a column chart.
Static data adaptation for widgets
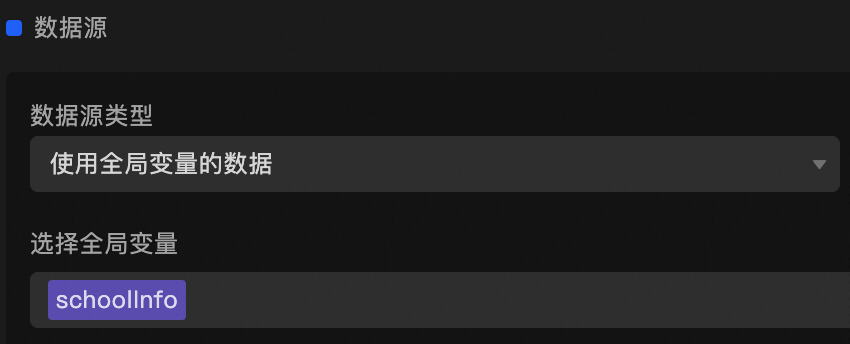
Global variable adaptation for widgets
Configuration item description
Data Item Configuration |
Description |
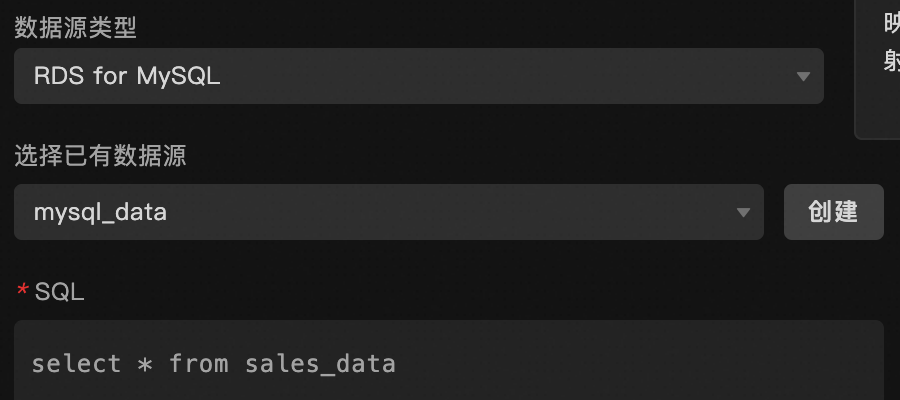
Data Source |
The component's data source displays the data fields contained within the component using code editing or visual editor. You can also modify the data type to flexibly configure the component's data. |
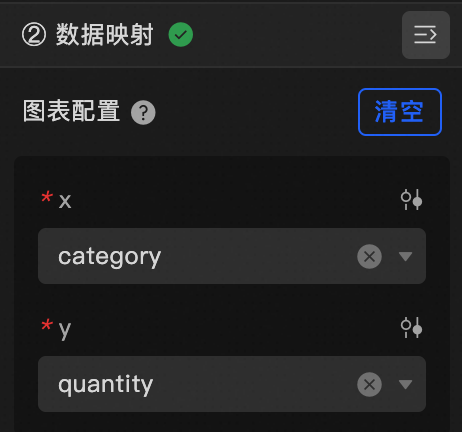
Data Mapping |
When you need to customize chart field configurations, you can set different field mappings in the Data Mapping module to map these fields to the corresponding fields of the component. This allows for real-time data matching without altering the data source fields. Additionally, click the |
Filter |
Open the Filter to select an existing data filter or create a new one, and configure the data filter script to achieve data filtering capabilities. For more information, see manage data filters. |
Data Response Result |
This feature displays the component's data in real-time. When the component's data source changes, the data response result will display the latest data accordingly. In case of a delayed system response, you can click the |
Disable Loading State |
Check the check box to hide the loading content during component updates and data dashboard previews. Unchecking will display the loading content. The default setting is unchecked. |
Controlled Mode |
Check the check box to prevent data requests upon the component's initialization. Data requests will only be initiated through global variables or methods configured in the blueprint editor. Unchecking allows for automatic update requests. The default setting is unchecked. |
Automatic Update Request |
Check the check box to manually set the polling frequency for dynamic polling. Clearing this option disables automatic updates, requiring manual page refreshes or data request triggers through the blueprint editor and global variable events for updates. |
FAQ
For assistance with configuration issues, refer to the datasource configuration FAQ.
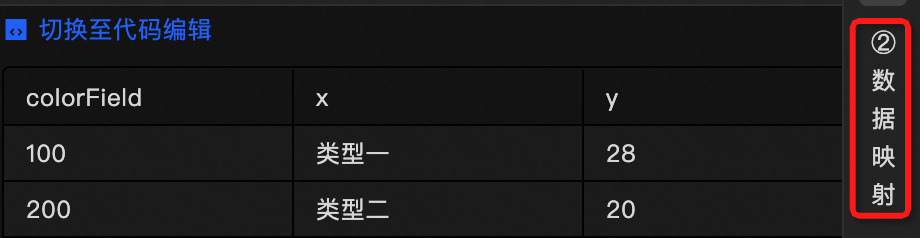
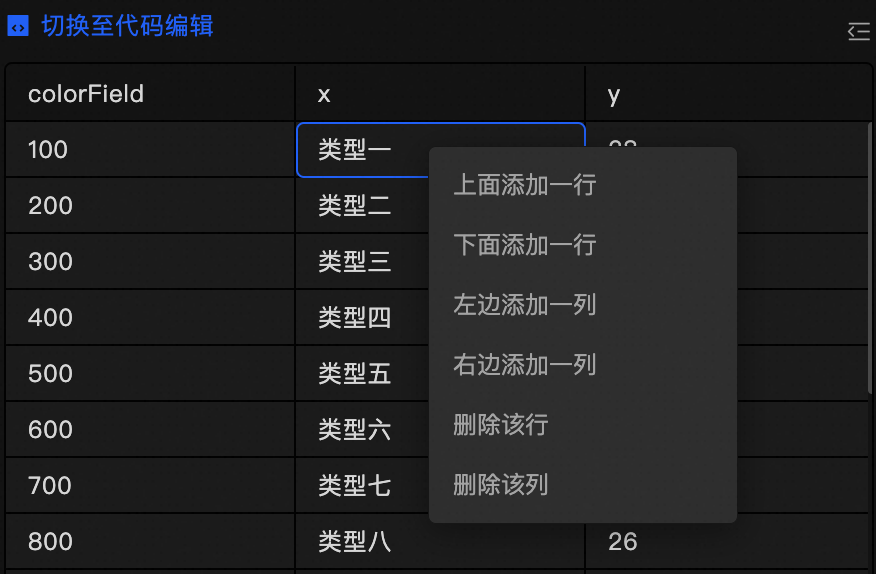
 to switch to the code editor mode. Here, you can edit the datasource by adding, deleting, or modifying the JSON formatted code.
to switch to the code editor mode. Here, you can edit the datasource by adding, deleting, or modifying the JSON formatted code.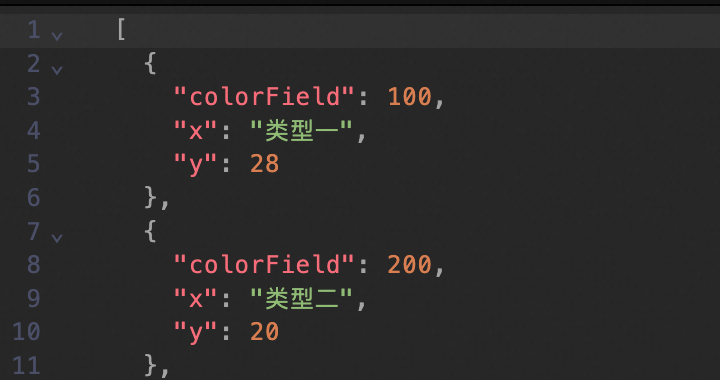



 icon to configure field styles individually.
icon to configure field styles individually. icon on the right to check the current data response result, or click the
icon on the right to check the current data response result, or click the  icon on the right to obtain the most recent data for the component. You can also click to view examples to see sample response results for the current component.
icon on the right to obtain the most recent data for the component. You can also click to view examples to see sample response results for the current component.