Keys are essential for specific security algorithms, often used in salting, hashing, and encryption/decryption processes. This topic outlines the procedures for registering and managing keys.
Key usage instructions
To prevent unauthorized access and ensure controlled management, it is advisable for each project to register and utilize its own keys, with the exception of public layer data. Sharing keys across multiple projects or with numerous users is discouraged.
Permission instructions
Super administrators and security administrators have the authority to register and manage all keys.
Key owners are authorized to manage the keys they have registered.
You can assign key management permissions during the creation or editing of keys. For more information, see key permission management.
Register key
On the Dataphin home page, select Administration > Data Security from the top menu bar.
In the left navigation bar, choose Sensitive Data Protection > Key Management. On the Key Management page, click the Register Key button.
In the Register Key dialog box, enter the required parameters.
Parameter
Description
Key Name
Specify the key name, which can include Chinese characters, English letters, numbers, or underscores (_), and must not exceed 10 characters.
Key Type
Choose between Hashing Key or Encryption And Decryption Key.
Hashing Key: Suitable for salting and hashing algorithms (e.g., salted MD5), without strict format requirements. Typically, the same key can be used for multiple salting and hashing algorithms.
Encryption And Decryption Key: Applicable for encryption and decryption algorithms (e.g., AES, DES), with specific format requirements. Generally, different algorithms should not share keys.
Encryption And Decryption Algorithm: Select the appropriate encryption and decryption algorithm according to your business needs. Supported algorithms include AES, DES, 3DES, SM2, SM4, PSA, and FF1. For further details on encryption and decryption algorithms, refer to security algorithm instructions.
Key Length: The key's bit length varies with the encryption and decryption algorithm used. Generally, a longer bit length equates to higher security. When using the SM2 algorithm, key length configuration is not applicable. For more information on key lengths for different algorithms, see security algorithm examples.
AES: Supports 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit keys.
DES: Only supports a 64-bit key, which is non-configurable.
3DES: Supports 112-bit and 169-bit keys.
SM4: Only supports a 128-bit key, which is non-configurable.
PSA: Supports 1024-bit, 2048-bit, and 4096-bit keys.
FPE (FF1): Supports 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit keys.
Generated By
Select either System Generated or Custom for key generation.
System Generated: The system automatically generates the key value, requiring no manual input.
Custom: Allows for manual entry of the key value and other parameters.
Key Value: Enter a custom key value. The key's length must correspond with the chosen Key Length. For instance, a 128-bit key requires 16 characters, so the key value must not exceed 16 bytes. For additional information on key lengths and their byte equivalents, refer to encryption and decryption algorithm examples.
NoteIf the key length from the previous data system does not match, it is necessary to understand the original system's key padding method and manually adjust it to the required length.
For encryption and decryption algorithms like SM2 or RSA, configure the following:
Public Key: The public key component.
Private Key: The private key component.
NoteIn key pair scenarios, the public key is used for encryption and the private key for decryption. Dataphin currently supports only public key encryption and private key decryption.
Owner Management Only
By default, this feature is disabled. With the feature turned off, super administrators, security administrators, and key owners are authorized to execute edit, grant, change owner, and delete operations. When enabled (on), only super administrators and key owners retain these privileges, with the caveat that super administrators cannot approve keys.
Key Description
Provide a concise description of the key, limited to 128 characters.
To finalize the key registration, click OK.
View key management list
Once a key is added, you can view, edit, change ownership, and delete it from the key list page.
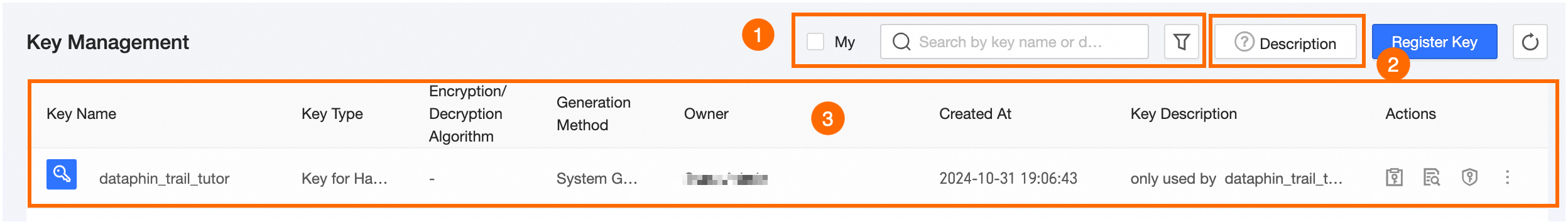
Area | Description |
①Filter and search area | Perform a fuzzy search by key name or description, or use precise filters such as My, Key Type, Encryption And Decryption Algorithm, Generated By, and Owner. |
②Key instructions | Click the Instructions button to access key usage details, including Concept Instructions, Key Type - Hashing Key, Key Type - Encryption And Decryption Key, and Usage Suggestions.
|
③Key list | This interface displays information such as Key Name, Key Type, Encryption and Decryption Algorithm, Generated By, Owner, Created At, and Key Description. Additionally, you can execute various Actions such as View Key Value, Task Reference Record, Permission Management, Edit, Change Owner, and Delete.
|
