The GoldenDB output component writes data to a GoldenDB data source. When synchronizing data from other data sources to a GoldenDB data source, you need to configure the target data source for the GoldenDB output component after configuring the source data source information. This topic describes how to configure the GoldenDB output component.
Prerequisites
You have created a GoldenDB data source. For more information, see Create a GoldenDB data source.
The account used to configure the GoldenDB output component properties has the write-through permission for the data source. If you do not have the permission, you need to apply for the data source permission. For more information, see Apply for data source permissions.
Procedure
In the top navigation bar of the Dataphin homepage, choose Develop > Data Integration.
In the top navigation bar of the Integration page, select Project (In Dev-Prod mode, you need to select Environment).
In the navigation pane on the left, click Batch Pipeline. In the Batch Pipeline list, click the offline pipeline that you want to develop to open its configuration page.
Click Component Library in the upper-right corner of the page to open the Component Library panel.
In the navigation pane on the left of the Component Library panel, select Outputs. Find the GoldenDB component in the output component list on the right side, and drag it to the canvas.
Click and drag the
 icon of the target input, transform, or flow component to connect it to the current GoldenDB output component.
icon of the target input, transform, or flow component to connect it to the current GoldenDB output component.On the GoldenDB output component, click the
 icon to open the GoldenDB Output Configuration dialog box.
icon to open the GoldenDB Output Configuration dialog box.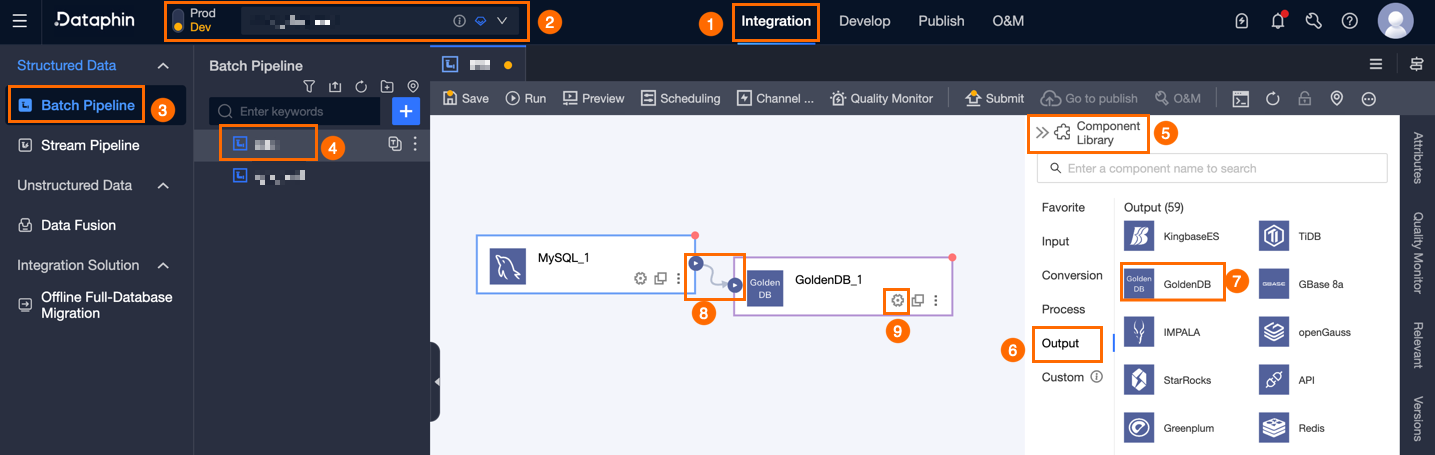
In the GoldenDB Output Configuration dialog box, configure the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Basic Settings
Step Name
The name of the GoldenDB output component. Dataphin automatically generates a step name, which you can modify based on your business scenario. The name must meet the following requirements:
It can contain only Chinese characters, letters, underscores (_), and digits.
It cannot exceed 64 characters.
Datasource
The data source dropdown list displays all GoldenDB data sources, including those for which you have write-through permissions and those for which you do not. Click the
 icon to copy the current data source name.
icon to copy the current data source name.For data sources for which you do not have write-through permissions, you can click Apply next to the data source to apply for write-through permissions. For more information, see Apply for data source permissions.
If you do not have a GoldenDB data source, click Create Data Source to create one. For more information, see Create a GoldenDB data source.
Table
Select the target table for output data. You can enter a table name keyword to search, or enter the exact table name and click Exact Match. After selecting a table, the system automatically checks the table status. Click the
 icon to copy the name of the currently selected table.
icon to copy the name of the currently selected table.Loading Policy
The policy for writing data to the table in the target data source (GoldenDB data source). Loading policies include overwrite and append. The applicable scenarios are as follows:
Append Data: When a primary key or constraint violation occurs, the system prompts a dirty data error.
Overwrite Data: When a primary key or constraint violation occurs, the system first deletes the original data and then inserts the entire new row of data.
Batch Write Size (optional)
The size of data to be written at once. You can also set Batch Write Count. When writing data, the system writes based on whichever limit is reached first. The default is 32M.
Batch Write Count (optional)
The default is 2048 records. When data is synchronized and written, a batch write strategy is used, with parameters including Batch Write Count and Batch Write Size.
When the accumulated data reaches either of the set limits (i.e., the batch write size or count limit), the system considers a batch of data to be full and immediately writes this batch of data to the target at once.
It is recommended to set the batch write size to 32MB. For the batch insert count limit, you can flexibly adjust it based on the actual size of a single record, usually setting it to a larger value to fully utilize the advantages of batch writing. For example, if the size of a single record is about 1KB, you can set the batch insert byte size to 16MB, and considering this condition, set the batch insert count to greater than the result of 16MB divided by the single record size of 1KB (i.e., greater than 16384 records), assuming here it is set to 20000 records. With this configuration, the system will trigger batch writes based on the batch insert byte size, executing a write operation whenever the accumulated data reaches 16MB.
Prepare Statement (optional)
The SQL script to be executed on the database before data import.
For example, to ensure continuous service availability, before the current step writes data, it first creates a target table Target_A, executes writing to Target_A, and after the current step completes writing data, renames the continuously serving table Service_B to Temp_C, then renames table Target_A to Service_B, and finally deletes Temp_C.
Post Statement (optional)
The SQL script to be executed on the database after data import.
Field Mapping
Input Fields
Displays the input fields based on the output of the upstream component.
Output Fields
Displays the output fields. You can perform the following operations:
Field Management: Click Field Management to select output fields.
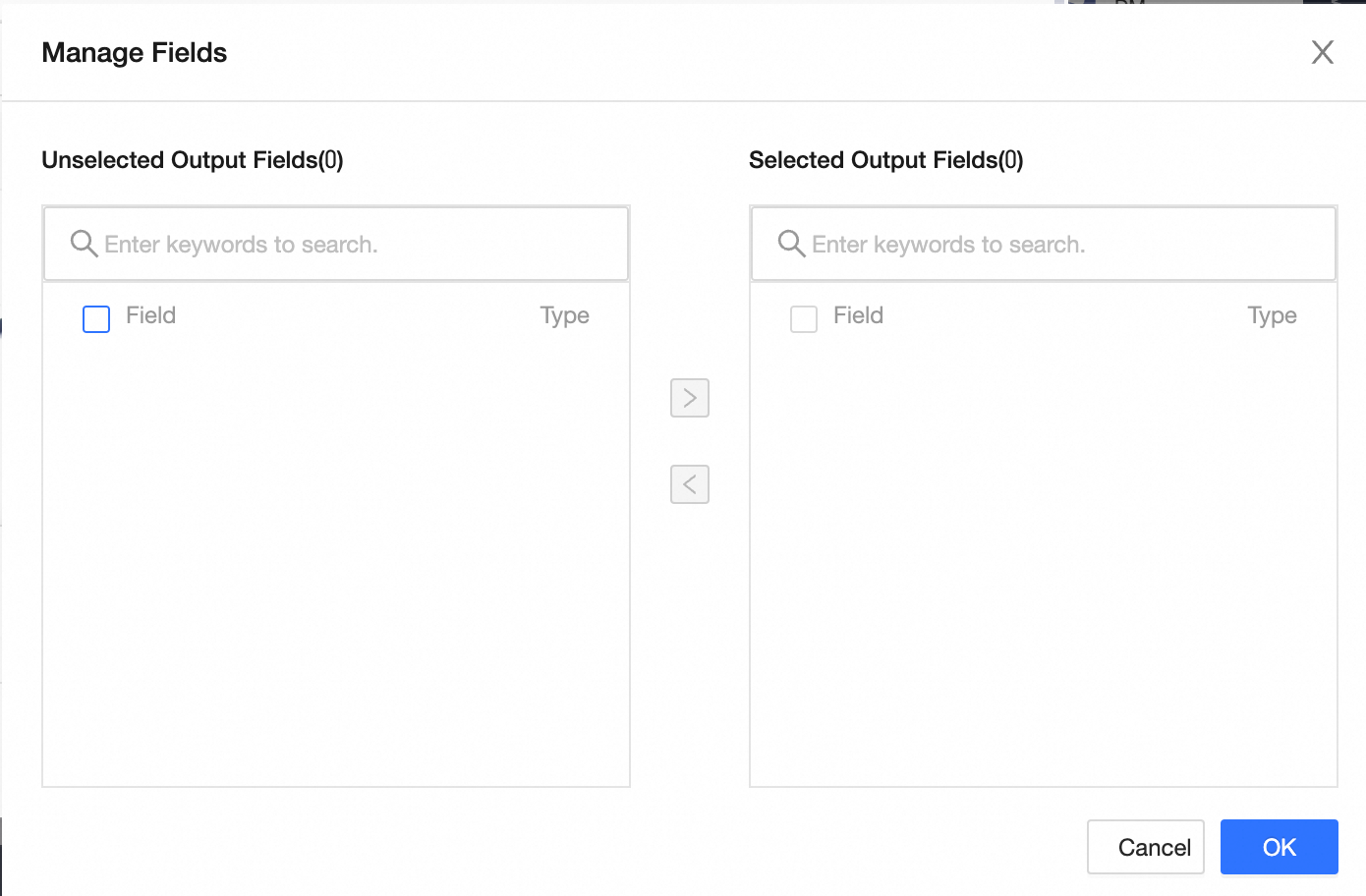
Click the
 icon to move Selected Input Fields to Unselected Input Fields.
icon to move Selected Input Fields to Unselected Input Fields.Click the
 icon to move Unselected Input Fields to Selected Input Fields.
icon to move Unselected Input Fields to Selected Input Fields.
Batch Add: Click Batch Add to configure in JSON, TEXT, or DDL format.
Batch configuration in JSON format, for example:
// Example: [{ "name": "user_id", "type": "String" }, { "name": "user_name", "type": "String" }]Note`name` is the name of the imported field. `type` is the data type of the field after import. For example,
"name":"user_id","type":"String"imports the field named `user_id` and sets its data type to `String`.Batch configuration in TEXT format, for example:
// Example: user_id,String user_name,StringRow delimiters are used to separate information for each field. The default is a line feed (\n), and it supports line feed (\n), semicolon (;), and period (.).
Column delimiters are used to separate field names from field types. The default is a comma (,).
Batch configuration in DDL format, for example:
CREATE TABLE tablename ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(50), age INT );
Create New Output Field: Click +Create New Output Field, fill in the Column and select the Type as prompted. After completing the configuration for the current row, click the
 icon to save.
icon to save.
Mapping
Based on the upstream input and the target table fields, you can manually select field mappings. Mapping includes Same Row Mapping and Same Name Mapping.
Same Name Mapping: Maps fields with the same name.
Same Row Mapping: Maps fields in the same row when the field names in the source and target tables are different but the data in the corresponding rows needs to be mapped.
Click Confirm to complete the property configuration of the GoldenDB output component.