Upon integrating node tasks or aggregate table fields into the baseline monitoring protection objects, baseline monitoring is equipped to swiftly identify abnormalities that may hinder the timely completion of baseline tasks, offering preemptive alerts. This capability guarantees the seamless generation of critical data within the anticipated timeframe amidst intricate dependency scenarios, thereby streamlining operations and maintenance, minimizing false alarms, and facilitating the automatic surveillance of all vital tasks.
Prerequisites
You have purchased the Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps) value-added service, and it is currently activated for your tenant.
Scenarios
Manage task precedence: To prioritize critical tasks when facing a growing task volume and limited resources, add these tasks to the baseline and assign a higher precedence, ensuring they receive priority in resource allocation.
Automatically estimate task output time: Task runtime is influenced by available resources and the condition of upstream tasks. By adding tasks to the baseline, Dataphin can provide daily or hourly estimates of task completion times, enabling proactive planning.
Automatic monitoring scope selection: Upon adding tasks or fields requiring protection, the system automatically determines the necessary upstream nodes for the monitoring scope based on dependency relationships, thereby minimizing manual operations and maintenance efforts.
Baseline and event alerts: Assign tasks to the baseline and establish a protection output time. The system will send alerts if it anticipates that tasks will not be completed by this time, or if errors or delays occur in upstream node tasks. These alerts enable timely issue resolution, ensuring task completion within the designated protection output time.
Identify critical paths and instances: Dataphin's Gantt chart feature aids in quickly identifying critical paths and instances that may hinder data output on the baseline, focusing on the path with the longest runtime.
Glossary
Prior to utilizing the Dataphin baseline monitoring feature, familiarize yourself with the fundamental concepts and terminology associated with baseline monitoring.
Baseline: It can be vividly understood as the emergency lane on a highway. When a task is added to the baseline protection object, it has a higher execution precedence compared to regular tasks, and you can pre-set the guaranteed output time. The system will calculate the estimated completion time of the baseline task based on the task's running status. If the system determines that the baseline task may not be completed before the committed time, it will issue an alert.
Protection objects: A baseline may include multiple protection objects, which can be either physical tasks or logical table fields.
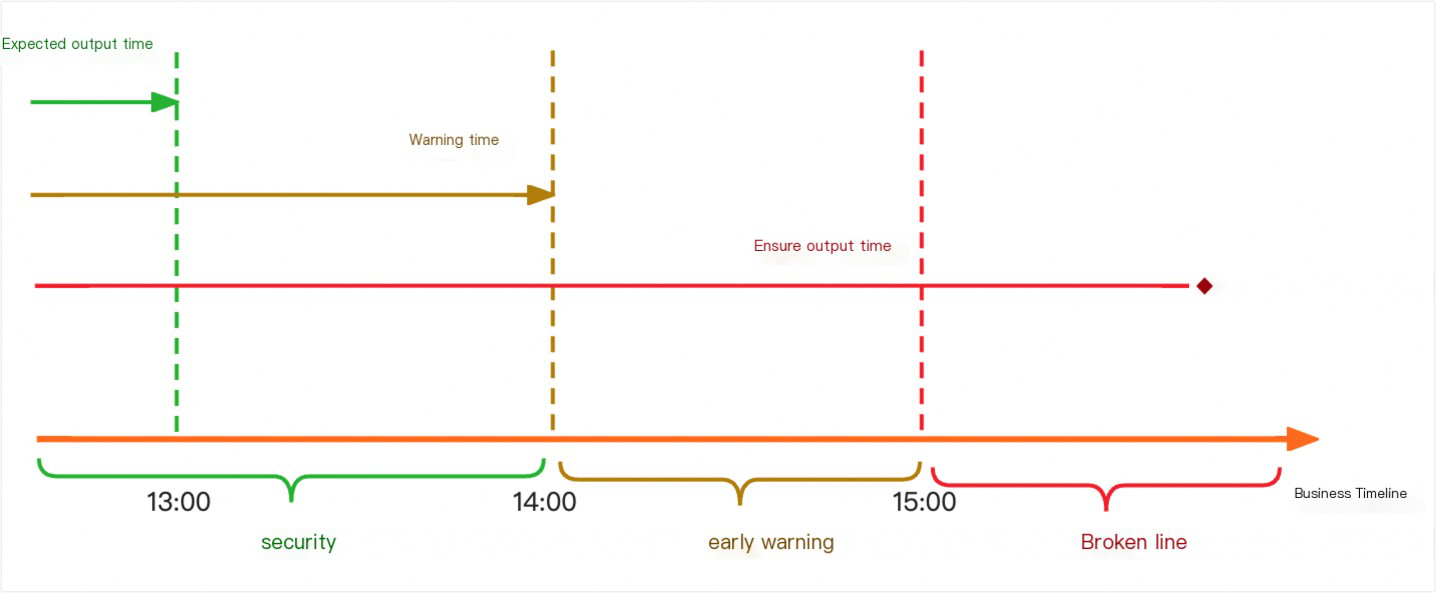
Protection output time:The latest time point for the successful completion of a task, i.e., the task is committed to be completed before this time point. You can also set a warning margin for the baseline, and the system will calculate and use it as the warning time to trigger an alert. If the task is not completed by the warning time, the system will send an alert, allowing time for exception handling before the protection output time.,handle abnormalities in a timely manner.
Warning time: Calculated as protection output time minus the warning margin.
Historical estimated output time: The system uses data from the past 7 days' successful runs to calculate the estimated output time for each run.
Baseline instance status: This refers to the condition of baseline instances, which can be categorized as safe, warning, or broken.
Safe: Historical estimated completion time is less than the warning time.
Warning: Warning time is less than historical estimated output time, which is less than protection output time.
Issue: Estimated completion time exceeds protection output time.
Critical path (longest path): The longest duration path through a project, determining the shortest time possible to complete the project. It is analogous to the critical path in a PERT (Program Evaluation Review Technique) chart.
Baseline alert: A baseline alert is triggered when the task remains incomplete at the business time's designated warning time.
Event alert: An event alert is triggered when baseline tasks or their upstream counterparts fail, or when critical path tasks experience delays.
Feature overview
After adding important tasks to the baseline, the system ensures their runtime based on the baseline precedence and determines the monitoring scope based on the tasks' upstream and downstream dependencies. Alerts are triggered based on the runtime status of tasks within the monitoring scope.
The basic steps for utilizing baseline monitoring are as follows:
Create a new baseline and add protection objects
You can create and manage baselines on the Baseline Monitoring page: For baseline creation and management operations, see Create Baseline Monitoring.
Select monitoring scope
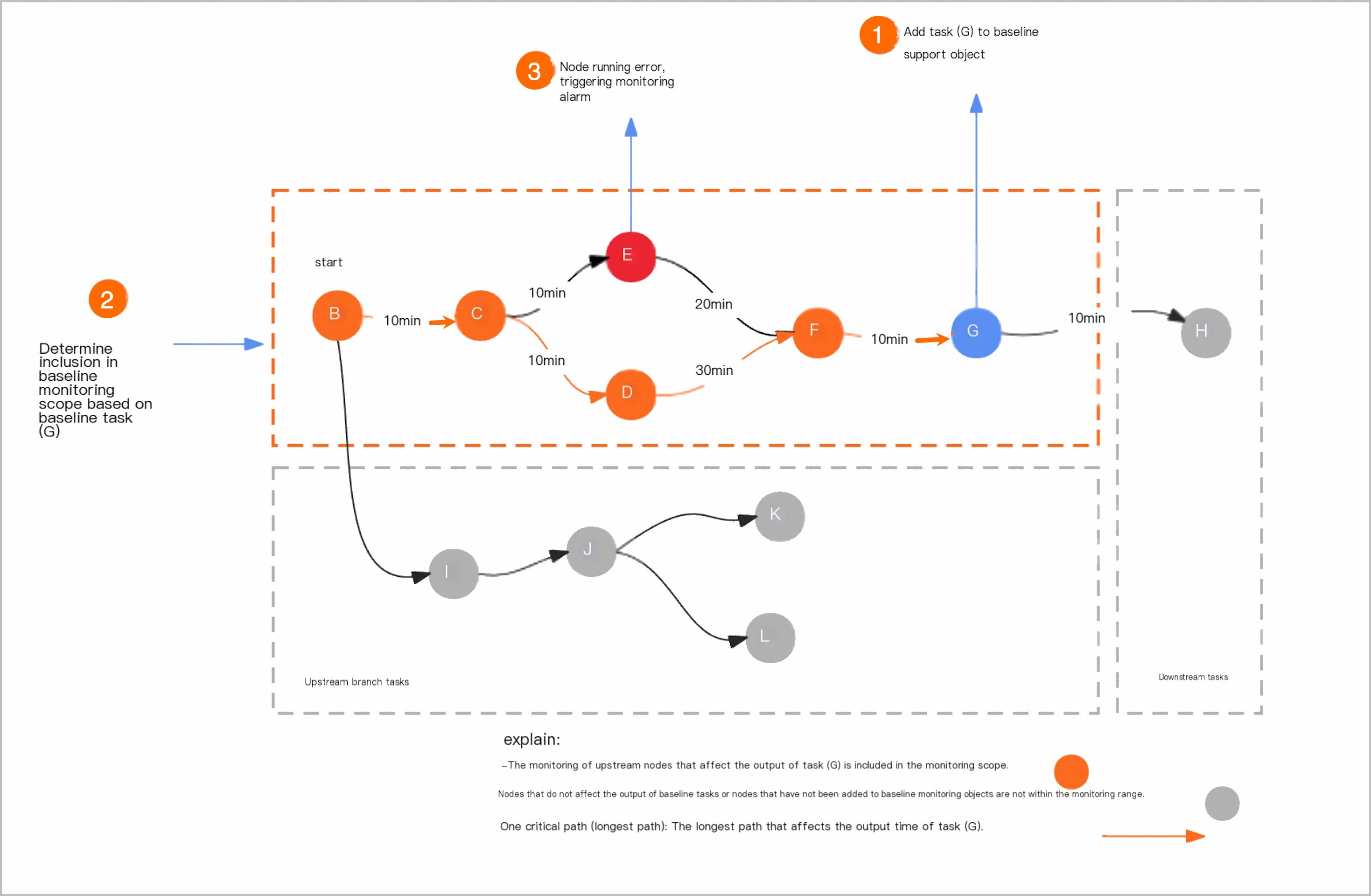
Upon establishing baseline tasks, the system will determine the monitoring scope by analyzing the dependency relationships among the protected objects. It then proceeds to monitor tasks that influence the baseline data output. For details on the selection rules, refer to Monitoring Scope Rules.
Trigger alerts and send alert information
Baseline alert
During task execution, if the business time reaches the baseline's warning time without completion of the baseline tasks, a baseline alert is triggered. For more information on baseline alert rules, see Baseline Alert Rules.
Event alert
Once the monitoring scope is established, event alerts will be triggered if baseline tasks or their upstream tasks fail, or if tasks on the critical path experience delays. For more information on event alert rules, see Event Alert Rules .
Baseline monitoring rules
Before configuring baseline monitoring, it is recommended that you first understand the relevant baseline monitoring rules.The rules include monitoring scope rules, baseline alert rules,event alert rules, historical estimated output time rules, and baseline status rules.
Monitoring scope rules
Once baseline tasks are created, the baseline establishes the monitoring scope according to the dependency relationships among the protected objects. The rules governing the monitoring scope are as follows:
Upstream tasks: Tasks that influence the data output of baseline tasks are incorporated into the baseline monitoring scope.
Upstream branch tasks: Tasks in upstream branches that do not impact the data output of baseline tasks are excluded from the baseline monitoring scope.
Downstream tasks are excluded from the baseline monitoring scope.
Baseline alert rules
After adding important tasks to the baseline and setting the baseline protection output time and warning margin, the system will use protection output time - warning margin as warning time. During the actual runtime of tasks,when the business time reaches the warning time of the baseline and the baseline tasks are not completed, a baseline alert will be generated.
Event alert rules
When tasks within the monitoring scope encounter exceptions, an event alert is triggered. Task exceptions include failure and slowdown, with the latter based on historical average runtime data.
Failure: Task runtime failed.
Slowdown: A slowdown alert is triggered if the current runtime exceeds the historical average runtime by 30%.
Navigate to the Alert Center to review alert events information. For more details, see documentation.
Historical estimated output time rules
The historical estimated output time of the baseline is calculated based on the tasks added to the baseline, using the records of successful runs in the last 7 days to estimate the output time for each run. When the baseline has multiple guaranteed objects, the historical estimated output time of the baseline is calculated based on the average completion time of each baseline task.
Hourly tasks are not included in the calculation. When data is insufficient, there may be errors, and the information is for reference only.
Baseline status rules
After setting the baseline protection objects, protection output time, and warning margin, the baseline will determine the time nodes for the baseline status based on the set parameters. The baseline status varies at different time nodes. For example, if the estimated output time of the baseline is 13:00, the set protection output time is 15:00,and the warning margin is 60 minutes, i.e., 1 hour.Then, when the business time is before protection output time -warning margin = 14:00, the baseline status is safe. After 12:00, a baseline alert will be triggered, and the status will be warning. When the business time reaches the protection output time of 15:00, if the baseline tasks are still not completed, the status will be broken.After 12:00, a baseline alert will be triggered, and the status will be a warning. When the business time reaches the guaranteed output time of 15:00, if the baseline node is still not completed, the status will be a breach.
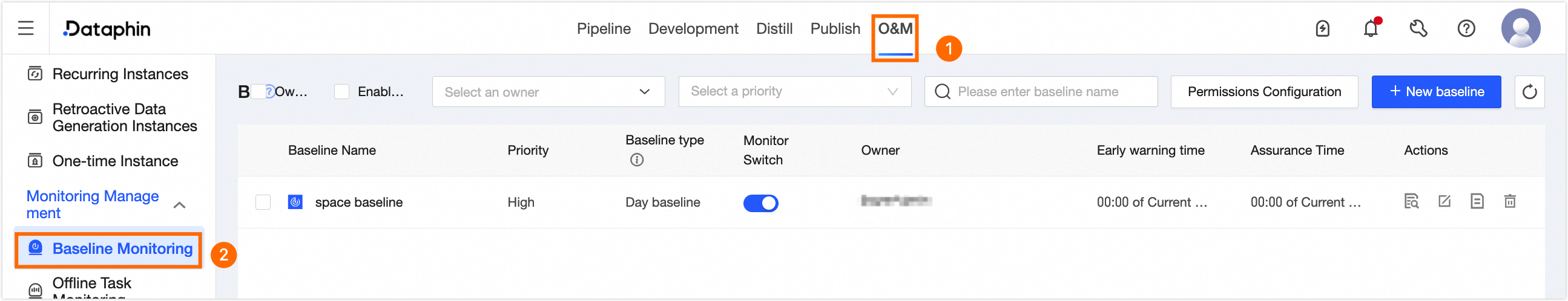
Baseline monitoring entry
On the Dataphin home page, click the top menu bar Development.
On the O&M Center page, select Baseline Monitoring from the side navigation bar to access the Baseline Monitoring page.
Baseline monitoring page introduction
Baseline Monitoring page mainly consists of the search and filter area, baseline task list, and batch operation area. You can view, edit, change records, delete, and perform other operation and maintenance tasks on the created baseline monitoring on the baseline monitoring page.
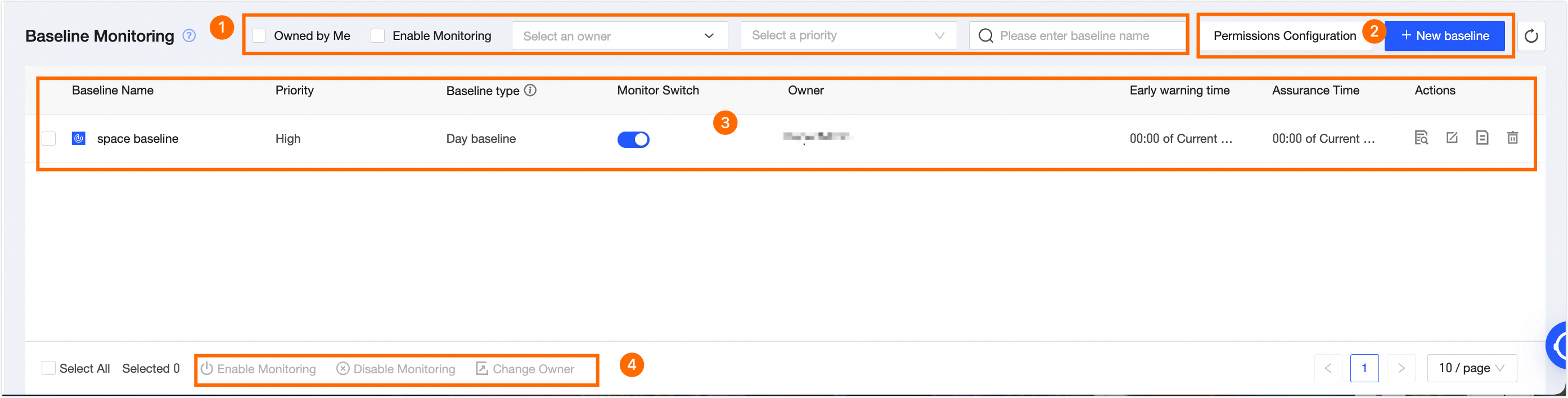
Area | Description |
①Search and Filter Area | The search and filter area allows users to filter baseline monitoring by entering a baseline name or quickly filter through options such as baselines for which I am responsible, monitoring status, baseline owner, and monitoring precedence.
|
②Operation Area |
|
③Baseline Monitoring List | The baseline monitoring page presents a list of configured monitors, detailing baseline name, precedence, type, monitoring switch status, owner, warning time, and protection time. To toggle baseline monitoring on or off, simply click the Monitoring Switch located beneath the Note Baseline types include Daily Baseline and Empty Baseline.
Perform operation and maintenance management on baseline monitoring, with supported operations including viewing details, editing, viewing change records, and deleting.
|
④Batch Operation Area | The batch operation area facilitates enabling or disabling monitoring and changing the owner in batches to enhance operational efficiency. |