Data Disaster Recovery provides features such as full backup, incremental backup, and data restoration. This topic describes how to create and configure a backup schedule, back up databases, and restore databases. This helps you understand and get started with database backup and management.
For information about whether Data Disaster Recovery supports the backup and restoration of your database and the granularity of database backup and restoration, see Supported database types and features.
For information about the specifications of backup schedule types and suggestions on selecting a backup schedule type, see Differences between logical backup and physical backup.
For information about the definitions of and differences between logical backup and physical backup, see Logical backup, physical backup, and snapshot.
Create a backup schedule
Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose . On the Backup Schedules page, click Create Schedule in the upper-right corner to go to the Create Schedule.
Configure the following parameters and click Buy and Start in the lower-right corner of the page.
Parameter
Description
Product Type
The backup schedule that you want to use.
NoteYou cannot create a pay-as-you-go backup schedule in the Dada Management (DMS) console.
Region
The region in which you want to store the backup data.
NoteBackup in the same region: Select the region in which the database to be backed up resides.
Geo-redundancy: Select a region different from that of the database to be backed up. This method provides a better disaster recovery capability but may charge you additional fees. For example, if you want to back up a database from the China (Beijing) region to the China (Shanghai) region, select the China (Shanghai) region.
Data Source Type
The data source type of the database to be backed up.
NoteIf the data source is an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, a self-managed MySQL database, or a PolarDB for MySQL cluster, select MySQL. For more information about how to select a data source type, see Supported database types and features.
Specification
The backup schedule specifications that you want to use. Higher specifications offer higher backup and restoration performance. Data Disaster Recovery supports the following backup schedule specifications: micro, small, medium, large, and xlarge. The xlarge specification type provides extra large specifications without an upper limit on the amount of backup data.
To ensure fast backup and restoration of specific database instances, such as database instances in the production environment, we recommend that you select the xlarge or large specification type.
If you do not require high backup and restoration performance, you can select the most cost-effective backup schedule specifications based on your business requirements. For more information, see Select the backup method and backup schedule type.
If the databases and tables that you want to back up involve issues such as unreasonable table schemas, large tables, or large fields, and you select a low-specification backup schedule type, the resources of the backup schedule may be insufficient to back up the databases or tables. In this case, backup exceptions occur. To prevent backup exceptions, we recommend that you select a high-specification backup schedule type.
Backup Method
The backup method that you want to use. Valid values:
Physical Backup: You can perform a physical backup only on self-managed databases, but not ApsaraDB RDS instances.
You can use this method to back up database files in the operating system. In most cases, physical backup and restoration are faster than logical backup and restoration. You can also use a sandbox instance for emergency disaster recovery.
Logical Backup: You can perform a logical backup on ApsaraDB RDS instances, self-managed databases in data centers, and self-managed databases hosted on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances.
You can use this method to back up database objects, including tables, indexes, and stored procedures. Data Disaster Recovery allows you to back up specified databases and tables in a fine-grained way.
NoteFor information about the definitions of and differences between logical backup and physical backup, see Logical backup, physical backup, and snapshot and Select a backup method.
Storage Size
The storage capacity of the backup schedule that you want to purchase. You do not need to specify the storage capacity when you purchase a backup schedule. You are charged for the amount of your data that is stored in Data Disaster Recovery.
NoteIf you back up a large amount of data, we recommend that you purchase a backup instance storage plan provided by DBS to offset the storage fees of built-in DBS storage for the backup schedule. For more information about how to purchase a storage plan, see the FAQ section of this topic.
For information about fees that may be incurred for a backup schedule, see Billing FAQ.
Resource Group
The resource group that is used by the backup schedule. You can select the default resource group or a custom resource group to facilitate backup schedule management.
Quantity
The number of backup schedules that you want to purchase.
NoteA backup schedule can be used to back up only one database instance. To back up multiple database instances, you must purchase multiple backup schedules. For example, if you want to back up ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL Instance A and ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL Instance B, you must purchase two backup schedules.
A backup schedule can be used to back up only one type of database. To back up multiple types of databases, you must purchase multiple backup schedules. For example, if you want to back up a self-managed SQL Server database and a self-managed MySQL database, you must purchase two backup schedules.
Subscription Duration
The subscription duration for the backup schedule that you want to purchase.
On the Confirm Order page, confirm the order information, read and select the terms of services, and then click Pay.
After you pay for the order, go to the Backup Schedules page to view the new backup schedule.
Configure a backup schedule
Prerequisites
An account is created for the database that you want to back up, and the required permissions are granted to the database account. For more information, see Account permissions.
A backup gateway is installed on the server of the database on which you want to perform a physical backup. For more information, see Install a backup gateway.
NoteTo check whether a backup gateway is installed, go to the Backup Gateways page in the console.
Procedure
In this example, a logical backup schedule is configured for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. The backup schedule varies for different database engines.
On the Backup Schedules page, find the ID of the backup schedule that you want to configure and click Configure Backup Schedule in the Actions column.

In the Configure Backup Source and Destination step of the Configure Backup Schedule wizard, configure the backup source and destination, and click Next in the lower-right corner of the page.
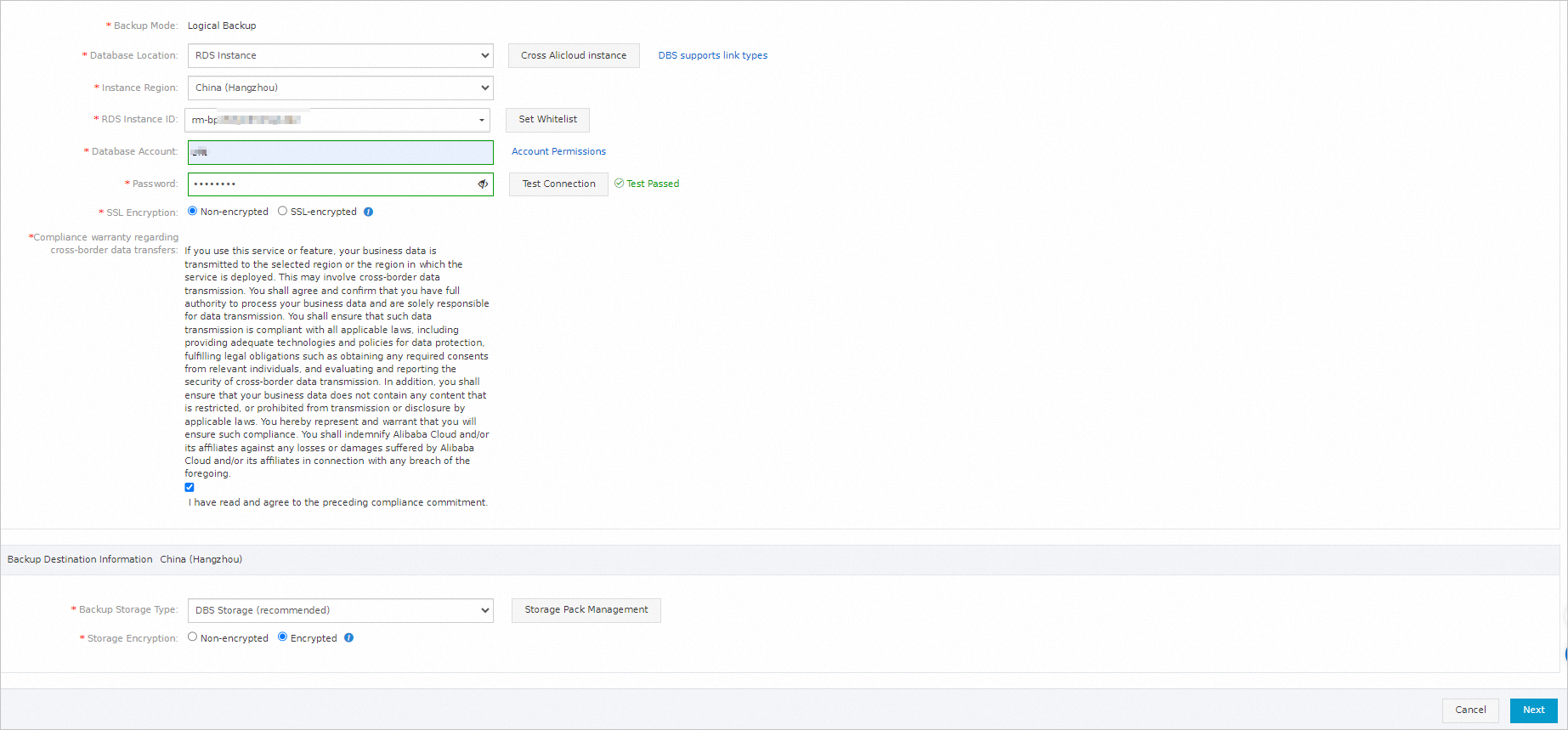
In the Edit Backup Objects step, find the database or table that you want to back up and add it to the Selected section. Then, click Next.
NoteIf you selected Logical Backup when you purchased a backup schedule, Data Disaster Recovery allows you to specify the databases and tables to be backed up during full backups. You can back up a single table, a single database, multiple databases, or an entire database instance for some types of databases during full backups. Data Disaster Recovery supports incremental backups only for some types of databases. By default, all the incremental data is backed up during incremental backups.
If you selected Physical Backup when you purchased a backup schedule, you must back up an entire database instance.
In the Configure Backup Time step, configure the parameters that are described in the following table and click Next.
In the Edit Lifecycle step, configure the lifecycle for full backup data.
NoteIf you set the Incremental Backup parameter to Enable in the previous step, you must configure the lifecycle for incremental backup data.
After the configurations are complete, click Precheck in the lower-right corner of the page.
If the Precheck Passed message appears, click Start Task.
NoteIf the state of the backup schedule changes to Running, the backup schedule takes effect.
If an exception or error occurs in the backup schedule, join the DingTalk group (ID: 35585947) for technical support.
Restore a database
Usage notes
If you use Data Disaster Recovery to restore a database to an ApsaraDB RDS instance in another region, make sure that the destination ApsaraDB RDS instance is accessible over a public endpoint.
For example, if a backup schedule is created in the China (Hangzhou) region and you want to use the backup schedule to restore data to an ApsaraDB RDS instance in the China (Beijing) region, make sure that the ApsaraDB RDS instance in the China (Beijing) region is accessible over a public endpoint.
The restoration duration depends on the specifications of the backup schedule and the size of the database to be restored. The restoration duration is shorter for a backup schedule with higher specifications. The restoration duration is longer if the database to be restored is larger.
Procedure
This example describes only a general procedure for restoring databases. The specific restoration procedure varies based on database engines.
Data Disaster Recovery also provides the sandbox feature based on the copy data management (CDM) technology. This feature allows you to restore databases with a recovery time objective (RTO) of several seconds. You can analyze, test, and verify data in a sandbox instance. For more information, see Use the emergency recovery feature for a self-managed MySQL database.
On the Backup Schedules page, find the backup schedule that you want to use and click Manage in the Actions column.
On the Configure Task page, click Restore Database in the upper-right corner.
In the Set Time Restored To step of the Create Restore Task wizard, configure the parameters in the Set Time Restored To and Configure Destination Database sections. Then, click Next in the lower-right corner of the page.
NoteThe restoration configurations vary for different database engines.
Data Disaster Recovery allows you to restore a database such as MySQL or SQL Server to a new ApsaraDB RDS instance without the need to create the instance in advance.
In the Configure Objects to Restore step, configure the parameters that are described in the following table and click Precheck.
Parameter
Description
Conflict Handling
By default, Rename Object with the Same Name is selected for the Conflict Handling parameter. For example, if the
job_infotable to be restored shares the same name with a table in the destination database, the system renames the restored table in the following format:job_info_dbs_<Restore task ID>_<Timestamp>.Objects to Restore
Select the database or table that you want to restore in the Available section and click the rightwards arrow to add it to the Selected section.
NoteData Disaster Recovery allows you to restore some databases by database or table. This reduces the amount of data to be restored and shortens the recovery time objective (RTO). For more information about the supported restoration granularity, see Supported database types and features.
After the Precheck Passed message appears in the Precheck dialog box, click Start Task.
To view the database restoration progress, click Restore Tasks in the left-side navigation pane.
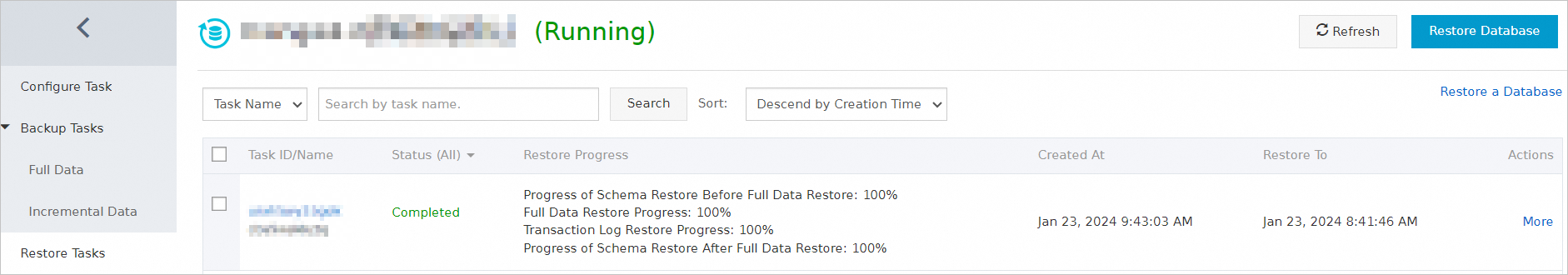 Note
NoteThe restoration duration depends on the specifications of the backup schedule and the size of the database to be restored. The restoration duration is shorter for a backup schedule with higher specifications.
If you restore a database to a new ApsaraDB RDS instance, the system needs about 5 to 10 minutes to create the instance. After the database is restored, you can view the new ApsaraDB RDS instance in the ApsaraDB RDS console. Alternatively, perform the following operations to view the new ApsaraDB RDS instance: On the Restore Tasks page, click the ID of the restore task. On the page that appears, click the ID of the ApsaraDB RDS instance in the Basic Information section. You are navigated to the ApsaraDB RDS console.