This topic describes the release notes for training-nv-pytorch 25.07.
Main Features and Bug Fix Lists
Main Features
Upgraded vllm to v0.9.2.
Support for transformerEngine v2.3.0+5de3e14, peft v0.16.0, and diffusers v0.34.0.
Bugs Fix
(None at this time)
Contents
Scenarios | Training/Inference |
Frame | pytorch |
Requirements | NVIDIA Driver release >= 575 |
Core components |
|
Assets
25.07
egslingjun-registry.cn-wulanchabu.cr.aliyuncs.com/egslingjun/training-nv-pytorch:25.07-serverless
VPC image
acs-registry-vpc.{region-id}.cr.aliyuncs.com/egslingjun/{image:tag}
{region-id}indicates the region where your ACS is activated, such as cn-beijing and cn-wulanchabu.{image:tag}indicates the name and tag of the image.
Currently, you can pull only images in the China (Beijing) region over a VPC.
egslingjun-registry.cn-wulanchabu.cr.aliyuncs.com/egslingjun/training-nv-pytorch:25.07-serverless image is applicable to ACS product form and Lingjun multi-tenant product form. This image is not applicable to Lingjun single-tenant product form. Do not use it in Lingjun single-tenant scenarios.
Driver Requirements
25.07 Release is based on CUDA 12.8.0 and requires NVIDIA driver version 575 or higher. However, if you are running on data center GPUs (such as T4 or any other data center GPU), you can use NVIDIA driver version 470.57 (or higher R470), 525.85 (or higher R525), 535.86 (or higher R535), or 545.23 (or higher R545).
The CUDA driver compatibility package only supports specific drivers. Therefore, users should upgrade from all R418, R440, R450, R460, R510, R520, R530, R545, R555, and R560 drivers, which are not forward compatible with CUDA 12.8. For a complete list of supported drivers, see CUDA application compatibility. For more information, see CUDA compatibility and upgradation.
Key Features and Enhancements
PyTorch compiling optimization
The compiling optimization feature introduced in PyTorch 2.0 is suitable or small-scale training on one GPU. However, LLM training requires GPU memory optimization and a distributed framework, such as FSDP or DeepSpeed. Consequently, torch.compile() cannot benefit your training or provide negative benefits.
Controlling the communication granularity in the DeepSpeed framework helps the compiler obtain a complete compute graph for a wider scope of compiling optimization.
Optimized PyTorch:
The frontend of the PyTorch compiler is optimized to ensure compiling when any graph break occurs in a compute graph.
The mode matching and dynamic shape capabilities are enhanced to optimize the compiled code.
After the preceding optimizations, the E2E throughput is increased by 20% when a 8B LLM is trained.
GPU memory optimization for recomputation
We forecast and analyze the consumption of GPU memory of models by running performance tests on models deployed in different clusters or configured with different parameters and collecting system metrics, such as GPU memory utilization. Based on the results, we suggest the optimal number of activation recomputation layers and integrate it into PyTorch. This allows users to easily benefit from GPU memory optimization. Currently, this feature can be used in the DeepSpeed framework.
ACCL
ACCL is an in-house HPN communication library provided by Alibaba Cloud for Lingjun. It provides ACCL-N for GPU acceleration scenarios. ACCL-N is an HPN library customized based on NCCL. It is completely compatible with NCCL and fixes some bugs in NCCL. ACCL-N also provides higher performance and stability.
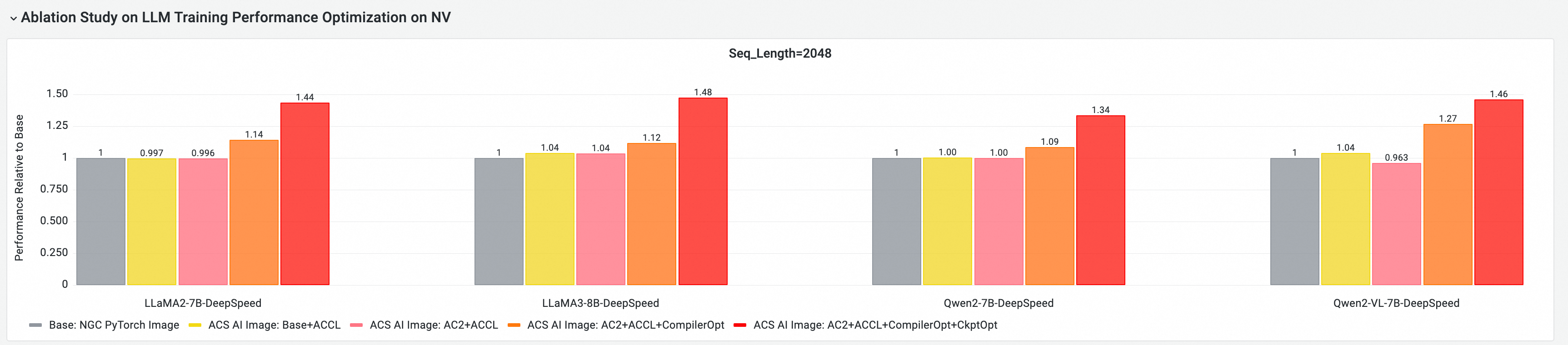
E2E performance gain assessment
Using the cloud-native AI performance evaluation and analysis tool CNP, we conducted comprehensive end-to-end performance comparison analyses with mainstream open-source models and framework configurations against standard base images. Through ablation experiments, we further evaluated the contribution of each optimization component to the overall model training performance.
GPU core component E2E performance contribution analysis.
The following tests are based on 25.07, conducting training E2E performance evaluation and comparative analysis on multi-node GPU clusters, with comparisons including the following:
Base: NGC PyTorch Image.
ACS AI Image: Base+ACCL: Image using the ACCL communication library.
ACS AI Image: AC2+ACCL: Golden image using AC2 Base OS, with no optimizations enabled.
ACS AI Image: AC2+ACCL+CompilerOpt: Golden image using AC2 Base OS, with only torch compile optimization enabled.
ACS AI Image: AC2+ACCL+CompilerOpt+CkptOpt: Golden image using AC2 Base OS, with both torch compile and selective gradient checkpoint optimizations enabled.
Quick Start
The following example content only pulls the training-nv-pytorch image via Docker.
To use the training-nv-pytorch image in ACS, you need to select it from the artifact center page on the console's create workload interface, or specify the image reference through a YAML file.
1. Select image
docker pull egslingjun-registry.cn-wulanchabu.cr.aliyuncs.com/egslingjun/training-nv-pytorch:[tag]2. Call API to enable compiler + recomputation memory optimization
Enable compilation optimization
Using transformers Trainer API:

Enable recomputation memory optimization
export CHECKPOINT_OPTIMIZATION=true
3. Start container
The image includes the built-in model training tool ljperf, which is used to illustrate the steps for starting a container and running training tasks.
LLM class
# Start container and enter
docker run --rm -it --ipc=host --net=host --privileged egslingjun-registry.cn-wulanchabu.cr.aliyuncs.com/egslingjun/training-nv-pytorch:[tag]
# Run training demo
ljperf benchmark --model deepspeed/llama3-8b 4. Usage recommendations
The changes in the image involve libraries such as Pytorch and Deepspeed. Do not reinstall them.
In the deepspeed configuration, leave zero_optimization.stage3_prefetch_bucket_size empty or set to auto.
The environment variable
NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAMEbuilt into this image needs to be adjusted dynamically according to the usage scenario:When a single Pod only requests 1/2/4/8 cards for training/inference tasks: you need to set
NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME=eth0(default configuration in this image).When a single Pod requests all 16 cards of a machine (at this point you can use HPN high-performance network) for training/inference tasks: you need to set
NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME=hpn0.
Known Issues
(None at this time)