Alibaba Cloud Container Compute Service (ACS) supports Advanced Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (AHPA). AHPA predicts future resource demand by learning and analyzing historical data to dynamically adjust the number of pod replicas. AHPA scales out pods and prefetches resources ahead of predicted demand peaks. This enhances the response speed and stability of your business. Conversely, AHPA scales down resources ahead of predicted demand troughs to save resource costs.
Background information
You can enable Managed Service for Prometheus for the AHPA controller to collect the historical metric data of your application. The AHPA controller makes scaling decisions based on the collected data. The AHPA controller uses machine learning algorithms to predict the number of pods that may be required by your business within the next 24 hours. The AHPA controller is suitable for scenarios where the workloads dynamically change. The AHPA controller provides proactive and passive prediction policies to ensure timely pod scaling and resource prefetching so that your business can withstand traffic spikes. This enhances the response speed, performance, and stability of your business and also helps reduce resource costs. For more information, see AHPA overview.
Prerequisites
An ACS cluster is created. For more information, see Create an ACS cluster.
Managed Service for Prometheus is enabled. For more information about how to enable Managed Service for Prometheus, see Use Managed Service for Prometheus to monitor ACS clusters.
Step 1: Install the AHPA controller
Log on to the ACS console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its ID. In the left-side navigation pane of the cluster details page, choose Operations > Add-ons.
On the Add-ons page, click the Others tab. Find AHPA Controller and click Install. Then, follow the on-screen instructions to install the AHPA controller.
Step 2: Add Prometheus as a data source for AHPA
Log on to the ARMS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the upper part of the Instances page, select the region where your Prometheus instance is deployed. Select the Prometheus instance that is named after your ACS cluster. General-purpose is displayed in the Instance Type column for the Prometheus instance. Click Settings in the Actions column. In the HTTP API URL (Grafana Read URL) section, record the following information:
If access tokens are enabled, you must configure an access token for your cluster.
View and record the internal endpoint.
Specify the endpoint of the Prometheus instance in the cluster configurations.
Create a file named application-intelligence.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
prometheusUrl: the endpoint of the Prometheus instance.token: the access token of the Prometheus instance.
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: application-intelligence namespace: kube-system data: prometheusUrl: "http://cn-hangzhou-intranet.arms.aliyuncs.com:9443/api/v1/prometheus/da9d7dece901db4c9fc7f5b9c40****/158120454317****/cc6df477a982145d986e3f79c985a****/cn-hangzhou" token: "eyJhxxxxx"NoteIf you want to view the Prometheus metrics displayed on the AHPA dashboard, set the following parameters in the Configmap:
prometheus_writer_url: Specify the internal remote write endpoint of the Prometheus instance.prometheus_writer_ak: Specify the AccessKey ID of the Alibaba Cloud account.prometheus_writer_sk: Specify the AccessKey secret of the Alibaba Cloud account.
Run the following command to create the application-intelligence ConfigMap:
kubectl apply -f application-intelligence.yaml
Configure Managed Service for Prometheus to monitor AHPA.
Log on to the ARMS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, click Integrate Other Components to go to the Integration Center page. Type AHPA in the search box and click the search icon. Click the AHPA card after it appears.
Configure Managed Service for Prometheus to monitor AHPA.
On the ACK AHPA page, choose Select a Kubernetes cluster > Select Cluster. Select your ACS cluster from the drop-down list.
Configure the parameters in the Configuration Information section based on the following table. Click OK.
Parameter
Description
Exporter Name
The name must be unique among the exporters used to collect monitoring data from AHPA.
metrics collection interval (seconds)
The interval at which you want the service to collect monitoring data.
After the Integration Status Check step is complete, click Integration Management. On the page that appears, you can find that Managed Service for Prometheus is enabled for AHPA.
Step 3: Deploy a test service
Deploy a test service that consists of a Deployment named fib-deployment and a Service named fib-svc. Deploy an application named fib-loader that is used to send requests to the test service to simulate traffic fluctuation. Then, deploy Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) to scale the test service. This way, you can compare the HPA scaling results with the AHPA prediction results.
Create a file named demo.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
Run the following command to deploy a test service:
kubectl apply -f demo.yaml
Step 4: Create an AHPA policy in a declarative manner
To configure an AHPA policy, perform the following steps:
Create a file named ahpa-demo.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1 kind: AdvancedHorizontalPodAutoscaler metadata: name: ahpa-demo spec: scaleStrategy: observer metrics: - type: Resource resource: name: cpu target: type: Utilization averageUtilization: 40 scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: fib-deployment maxReplicas: 100 minReplicas: 2 stabilizationWindowSeconds: 300 prediction: quantile: 95 scaleUpForward: 180 instanceBounds: - startTime: "2021-12-16 00:00:00" endTime: "2031-12-16 00:00:00" bounds: - cron: "* 0-8 ? * MON-FRI" maxReplicas: 15 minReplicas: 4 - cron: "* 9-15 ? * MON-FRI" maxReplicas: 15 minReplicas: 10 - cron: "* 16-23 ? * MON-FRI" maxReplicas: 20 minReplicas: 15The following table describes some of the parameters that are specified in the preceding code block.
Parameter
Required
Description
scaleTargetRef
Yes
The Deployment that you want to manage.
metrics
Yes
The metrics based on which the AHPA policy is implemented. The following metrics are supported: CPU, GPU, memory, queries per second (QPS), and response time (RT).
target
Yes
The scaling threshold. If you specify
averageUtilization: 40, the scaling threshold of CPU utilization is 40%.scaleStrategy
No
The scaling mode of AHPA. Default value:
observer. Valid values:auto: AHPA automatically performs scaling activities.observer: AHPA observes the resource usage and does not perform scaling activities. You can use the observer mode to check whether AHPA works as expected.scalingUpOnly: AHPA performs only scale-out operations and does not perform scale-in operations.proactive: Only active predictions take effect.reactive: Only passive predictions take effect.
maxReplicas
Yes
The maximum number of replicated pods that can be provisioned for the application.
minReplicas
Yes
The minimum number of replicated pods that must run for the application.
stabilizationWindowSeconds
No
The cooldown period of scale-in activities. Default value: 300. Unit: seconds.
prediction.quantile
Yes
A quantile that indicates the probability of the actual metric value not reaching the scaling threshold. A larger value indicates a higher probability. Valid values: 0 to 1. Default value: 0.99. The value is accurate to two decimal places. We recommend that you set the parameter to a value from 0.90 to 0.99.
prediction. scaleUpForward
Yes
The duration of a cold start. The value represents the time period from the point in time when a pod is created to the point in time when the pod enters the Ready state.
instanceBounds
No
The time period during which the number of pods is limited by the maximum number of pods and the minimum number of pods defined by AHPA.
startTime: the start time of the scaling operation.
endTime: the end time of the scaling operation.
instanceBounds.bounds.cron
No
This parameter is used to create a scheduled scaling job. A cron expression consists of five fields that are separated by spaces. For example, the cron expression
- cron: "* 0-8 ? * MON-FRI"specifies the time period from 00:00:00 to 08:00:00 on Monday to Friday each month.The following table describes the fields that are contained in a cron expression. For more information, see Cron expressions.
Field
Required
Valid value
Valid special character
Minutes
Yes
0~59
* / , -
Hours
Yes
0~23
* / , -
Day of Month
Yes
1~31
* / , – ?
Month
Yes
1 to 12 or JAN to DEC
* / , -
Day of Week
No
0 to 6 or SUN to SAT
* / , – ?
NoteThe Month and Day of Week fields are not case-sensitive. For example, you can specify
SUN,Sun, orsun.The default value of the Day of Week field is
*.The following list describes the special characters:
*: specifies an arbitrary value./: specifies an increment.,: separates a list of values.-: specifies a range.?: specifies a placeholder.
Run the following command to apply the AHPA policy:
kubectl apply -f ahpa-demo.yaml
Step 5: View the prediction results
On the Integration Management page, click the name of your cluster on the Container Service tab. Select ACK AHPA in the Addon Type section. Click the Dashboards tab. Then, click ahpa-dashboard. On the page that appears, you can view data in the AHPA dashboard.
The Service metrics displayed on the AHPA dashboard display the CPU utilization, current number of pods, and predicted number of pods.
The CPU Utilization & Actual POD chart displays the average CPU utilization and the current number of pods of the Deployment.
The Actual and Predicted CPU Usage chart displays the CPU usage of the pods in the Deployment and the predicted CPU usage. If the predicted CPU usage is higher than the current CPU usage, the CPU capacity predicted by AHPA is sufficient to run the application.
In the Pod Trends section, you can view the current number of pods, the recommended number of pods, and the proactively predicted number of pods.
Current number of pods: the number of pods that are running.
Recommended number of pods: the number of pods recommended by AHPA for the application. The value is generated based on the result of proactive prediction, the result of passive prediction, and the maximum and minimum numbers of pods within the current time period.
Proactively predicted number of pods: the number of pods proactively predicted by AHPA based on historical metric data and the pattern of workload fluctuations.
The AHPA prediction results are generated based on historical data within the last seven days. Therefore, you must wait seven days after you apply the AHPA policy. To apply the AHPA policy to an existing application, select the Deployment used to run the application in the AHPA dashboard.
In this example, the AHPA policy uses the observer scaling mode. The following figure compares the AHPA prediction results with the HPA scaling results. You can use the comparison results to check whether the AHPA prediction results meet the expectations.
The following figure compares the AHPA prediction results with the HPA scaling results.
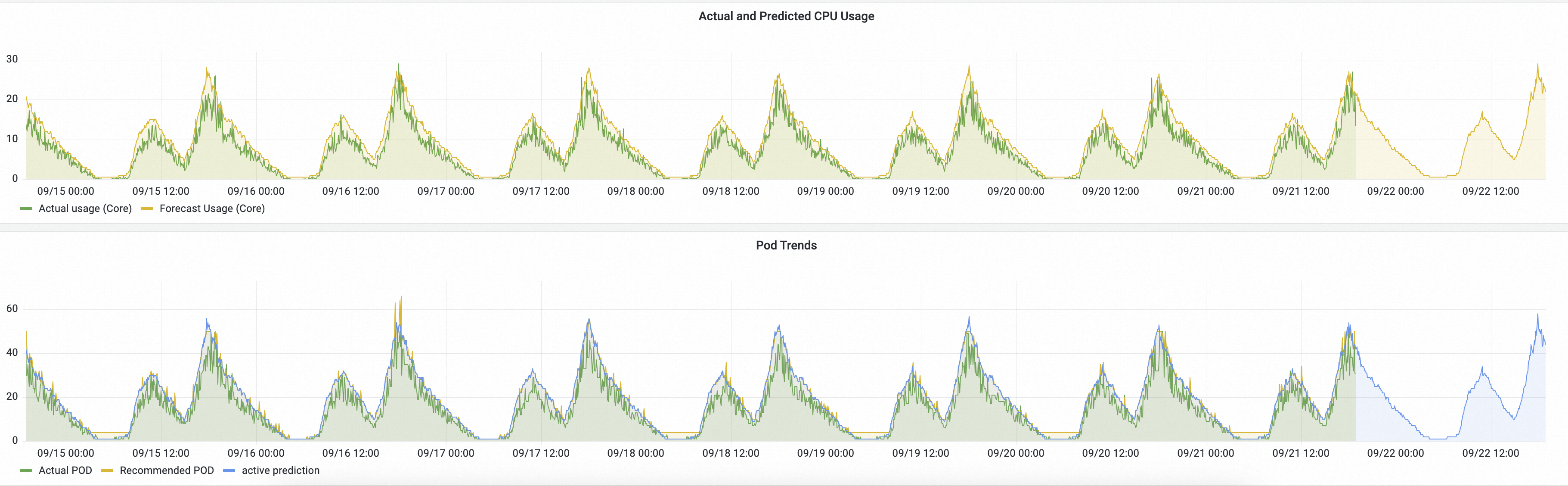
The figure provides the following information:
Actual and Predicted CPU Usage: The actual CPU usage based on HPA is represented by a green line. The CPU usage predicted by AHPA is represented by a yellow line.
The preceding figure shows that the predicted CPU usage is higher than the actual CPU usage. This indicates that the predicted CPU capacity is sufficient.
The preceding figure shows that the predicted CPU usage reaches a specific value earlier than the actual CPU usage. This indicates that the required resources are prepared in advance.
Pod Trends: The actual number of pods provisioned by HPA is represented by a green line. The number of pods predicted by AHPA is represented by a yellow line.
The preceding figure shows that the value represented by the yellow line is less than the value represented by the green line. This indicates that the predicted number of pods is less than the actual number of pods.
The preceding figure shows that the yellow curve is smoother than the green curve. This indicates that the changes in pod number are mild by using the AHPA scaling service, which improves business stability.
The results show that AHPA can use predictive scaling to handle fluctuating workloads as expected. After you confirm the prediction results, you can set the scaleStrategy parameter in the AHPA policy to auto, which allows AHPA to automatically scale pods.
Key AHPA metrics
Metric | Description |
ahpa_proactive_pods | The proactively predicted number of pods. |
ahpa_reactive_pods | The passively predicted number of pods. |
ahpa_requested_pods | The recommended number of pods. |
ahpa_max_pods | The maximum number of pods. |
ahpa_min_pods | The minimum number of pods. |
ahpa_target_metric | The scaling threshold. |