In a Kubernetes cluster, an Ingress manages external traffic to internal services and provides Layer 7 load balancing. This topic describes Ingress terms, how an Ingress works, and provides usage instructions.
Terms
In a Kubernetes cluster, an Ingress acts as the access point that exposes internal services and handles most of the service traffic. An Ingress is a Kubernetes resource object used to manage how external traffic accesses internal services. You can configure forwarding rules in an Ingress resource to route traffic to the backend pods of different Services. For more information about the comparison of different Ingresses in ACK, see Comparison among Nginx Ingresses, ALB Ingresses, and MSE Ingresses.
Nginx Ingress Controller
The Kubernetes community maintains the Nginx Ingress Controller. ACK optimizes the community version while maintaining full compatibility and supporting all community annotations.
How it works
For Nginx Ingress resources to work properly, you must deploy an Nginx Ingress Controller in the cluster to parse the Ingress forwarding rules. The Nginx Ingress Controller receives requests, matches them against the Ingress rules, and then forwards them to the corresponding backend Service pods for processing. In Kubernetes, the relationship among a Service, an Nginx Ingress, and the Nginx Ingress Controller is as follows:
A Service is an abstraction of backend services. One Service can represent multiple identical backend services.
An Nginx Ingress defines reverse proxy rules that specify which Service pods receive HTTP or HTTPS requests. For example, requests are routed to different Service pods based on the Host and URL path in each request.
The Nginx Ingress Controller is a component in the Kubernetes cluster that parses Nginx Ingress reverse proxy rules. When an Ingress is added, deleted, or modified, the Nginx Ingress Controller immediately updates its forwarding rules. When the controller receives a request, it forwards the request to the appropriate Service pod based on these rules.
The Nginx Ingress Controller retrieves Ingress resource changes from the API Server, dynamically generates configuration files required by the load balancer (such as nginx.conf), and reloads the load balancer (for example, by running nginx -s reload to reload Nginx) to apply new routing rules.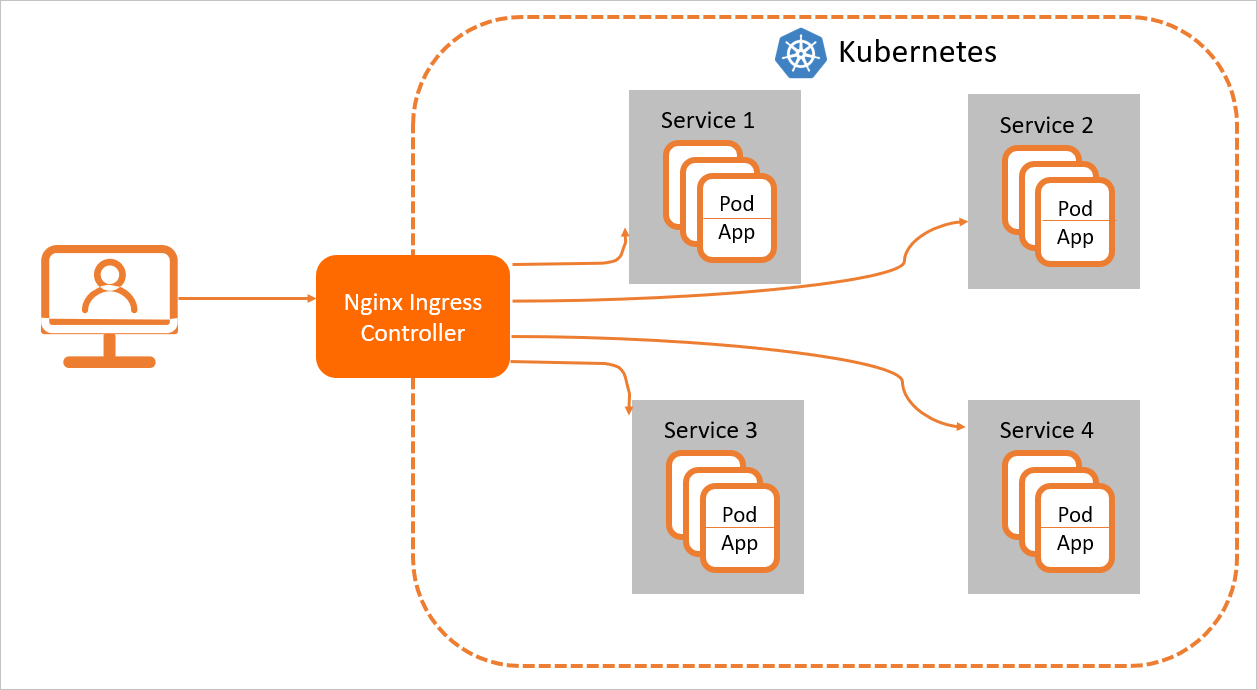
The Nginx Ingress Controller can create an SLB instance by configuring a Service of the LoadBalancer type. This enables external access to internal Kubernetes services through the SLB instance, with access determined by the configured Nginx Ingress rules.
References for Nginx Ingress
ALB Ingress Controller
The ALB Ingress Controller provides enhanced Ingress traffic management that uses Alibaba Cloud Application Load Balancer (ALB). It is compatible with Nginx Ingress, supports complex business routing and automatic certificate discovery, and handles HTTP, HTTPS, and QUIC protocols. The ALB Ingress Controller is designed for cloud-native environments and meets the requirements for high elasticity and large-scale Layer 7 traffic processing.
How it works
The ALB Ingress controller retrieves the changes to Ingresses from the API server and dynamically generates AlbConfig objects when Ingresses changes are detected. Then, the ALB Ingress controller performs the following operations in sequence: create ALB instances, configure listeners, create Ingress rules, and configure backend server groups. The Services, the Ingresses, and the AlbConfigs object interact with each other in the following ways:
A Service is an abstraction of an application that is deployed in a group of replicated pods.
An Ingress contains reverse proxy rules. It controls the Services to which HTTP or HTTPS requests are routed. For example, an Ingress routes requests to different Services based on the hosts and URLs in the requests.
An AlbConfig is a custom resource definition (CRD) that the ALB Ingress controller uses to configure ALB instances and listeners. An AlbConfig object corresponds to one ALB instance.
The ALB instance associated with an AlbConfig is fully managed by the Controller. Do not modify the instance in the ALB console. Modifying the instance in the console may cause the Ingress services to become abnormal.
References for ALB Ingress
APIG Ingress Controller
APIG Ingress provides Ingress traffic management that uses the cloud-native API gateway. It is an upgraded version of the MSE cloud-native gateway and is compatible with Nginx Ingress and over 50 Nginx Ingress annotations, which covers more than 90% of Nginx Ingress scenarios. It supports simultaneous phased releases of multiple service versions, flexible service governance, and comprehensive security protection, and meets the traffic governance needs of large-scale cloud-native distributed applications.
Components
APIG Controller:
The APIG Controller is a control plane, not a network data plane. It manages cloud-native API gateway instances and their configurations. The APIG Controller does not process any service traffic. It operates in bypass mode and manages the cloud-native API gateway instances that handle the actual service traffic.
In the cluster, install the APIG Controller component. Use the ApigConfig Custom Resource Definition (CRD) provided by the component to declaratively manage cloud-native API gateway instances and set the listener options of the gateway for Ingress resources.
Cloud-native API gateway:
The APIG Controller creates the cloud-native API gateway based on the configured ApigConfig resource. The gateway consists of a control plane and a data plane.
Control plane: The control plane listens for resources such as Ingress, IngressClass, and Service in the associated container service cluster. It parses these resources and sends the resulting configurations to the data plane in real time.
Data plane: The data plane implements the traffic governance configurations. It processes external requests based on the rules from the control plane and forwards the requests to the backend target services.
How it works
The APIG Controller listens for ApigConfig resources created in the cluster. It dynamically maintains the lifecycle of the corresponding cloud-native API gateway instance and the association between the gateway and the container service cluster in real time.
The control plane of the cloud-native API gateway retrieves Ingress resource changes from the API server of the associated container service cluster. It then dynamically updates the routing rules for the gateway. When the cloud-native API gateway receives a request, it matches the request with the Ingress forwarding rules and forwards it to the pods of the corresponding backend Service.
In Kubernetes, the relationship between Service, Ingress, IngressClass, ApigConfig, and the APIG Controller is as follows:
Service: An abstraction of a real backend service. A Service can represent multiple identical backend services.
Ingress: A set of reverse proxy rules that specify which Service an HTTP or HTTPS request should be forwarded to. For example, requests can be forwarded to different services based on the host and URL path in the request.
IngressClass: Describes an Ingress processor implementation in a Kubernetes cluster. Ingress resources associated with this IngressClass are parsed by that processor. You must also use the Parameter field of the IngressClass to associate an ApigConfig (a cloud-native API gateway). This gateway then implements the traffic management rules described in the parsed Ingress resource.
ApigConfig: A CRD provided by the APIG Controller. It describes the basic information of a cloud-native API gateway instance.
APIG Controller: Not a network data plane, but a control plane that manages cloud-native API gateway instances and configurations. The APIG Controller listens for ApigConfig resources in the cluster and coordinates the cloud-native API gateway instance to implement the traffic management rules described in the Ingress resources.
The following figure shows how the APIG Controller works.

References for APIG Ingress
MSE Ingress Controller
MSE Ingress provides enhanced Ingress traffic management that uses the MSE cloud-native gateway. It is compatible with Nginx Ingress and over 50 Nginx Ingress annotations, which covers more than 90% of Nginx Ingress scenarios. It supports simultaneous phased releases of multiple service versions, flexible service governance, and comprehensive security protection, and meets the traffic governance needs of large-scale cloud-native distributed applications.
How it works
Components
MSE Ingress controller:
The MSE Ingress controller is not a network data plane, but is a control plane that manages MSE cloud-native gateways and their configurations. The MSE Ingress controller does not process any service requests. The MSE Ingress controller works as a traffic bypass to manage MSE cloud-native gateways that process service traffic.
You must install the MSE Ingress Controller component in your ACK cluster, use the MseIngressConfig CRDs provided by this component to manage cloud-native gateways based on annotations, and configure Ingress resource listening items for the gateways.
For more information about how to install the MSE Ingress controller component, see Manage the MSE Ingress Controller component.
MSE cloud-native gateways: MSE cloud-native gateways are created based on the MseIngressConfig CRDs that you configured. An MSE cloud-native gateway consists of a control plane and a data plane.
Control plane: monitors resources such as Ingresses, Ingress classes, and Services in an associated ACK cluster. After the resources are parsed, the parsed resource configurations are sent to the gateway data plane in real time.
Data plane: implements traffic governance. The data plane processes external requests based on the governance rules that are sent from the control plane, and routes the requests to your destination backend Service.
Workflow
The MSE Ingress controller monitors the resource that is defined by an MseIngressConfig CRD in an ACK cluster and dynamically maintains the lifecycle of the cloud-native gateway that corresponds to the resource and the association between the gateway and ACK cluster in real time.
The control plane of the cloud-native gateway obtains the changes of Ingress resources by using the API server of the associated ACK cluster, and dynamically updates the routing rules of the gateway. After the cloud-native gateway receives a request, the gateway matches the request with an Ingress routing rule and routes the request to the pod that corresponds to the backend Service based on the matched routing rule.
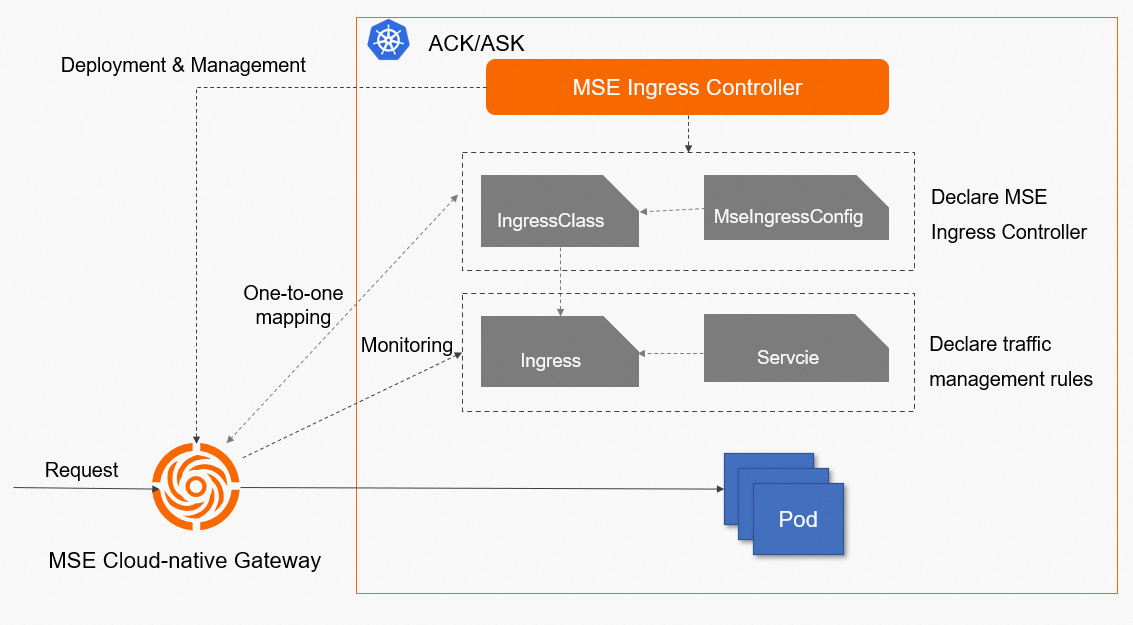
In a Kubernetes cluster, Services, Ingresses, Ingress classes, MseIngressConfigs, and MSE Ingress controller work in the following process:
Service: an abstraction of real backend services. One service can represent multiple identical backend services.
Ingress: a set of reverse proxy rules. An Ingress specifies the service to which HTTP requests or HTTPS requests are routed. For example, an Ingress routes requests to different Services based on the hostnames and URLs in the requests.
Ingress class: a description of the Ingress processor. An Ingress class is used to declare the implementation of an Ingress processor in a Kubernetes cluster. The Ingress resources that are associated with the Ingress class are parsed by the Ingress processor. You must associate an MseIngressConfig with the Parameter field of the Ingress class to implement the traffic management rule that is specified in the parsed Ingress resource description.
MseIngressConfig: a CRD that is provided by MSE Ingress Controller. An MseIngressConfig CRD provides basic information about a cloud-native gateway.
MSE Ingress Controller: a control plane that manages MSE cloud-native gateways and their configurations. MSE Ingress Controller is not a network data plane. The MSE Ingress controller is used to monitor Ingress resources defined by MseIngressConfig CRDs in a cluster and coordinate MSE cloud-native gateways to implement the traffic management rule that is specified in the parsed Ingress resource description.
The following figure shows how the MSE Ingress controller works.