Overview
Background information
To build a cloud network architecture that supports high security and efficiency, create a dedicated virtual private cloud (VPC) that functions as a demilitarized zone (DMZ) to isolate the internal network (trusted zone) from the Internet (untrusted zone). The DMZ VPC allows you to control Internet access. This design helps you build an application access gateway that can withstand high-concurrency traffic, control access to the Internet, and improve the utilization of Internet bandwidth. In addition, you can combine the architecture with security services to enhance protection for your internal network and protect your cloud services from attacks. This topic describes the design principles and key points of a DMZ VPC and provides complete design solutions and best practices to help you optimize your cloud infrastructure and improve its security and high availability.
Terms
VPC: A VPC is a custom private network that you can create on Alibaba Cloud. VPCs are logically isolated from each other at Layer 2. You can create and manage cloud service instances in your VPC, such as Elastic Compute Service (ECS), Server Load Balancer (SLB), and ApsaraDB RDS.
Transit routers: Transit routers provide multiple network communication and route management features. For example, you can use transit routers to connect network instances, create custom route tables, add routes, and add routing policies.
Application Load Balancer (ALB): ALB is an Alibaba Cloud service that runs at the application layer and is optimized to balance traffic over HTTP, HTTPS, and Quick UDP Internet Connections (QUIC). ALB is highly elastic and can process large volumes of Layer 7 traffic on demand.
Network Load Balancer (NLB): NLB is a Layer 4 load balancing service intended for the Internet of Everything (IoE) era. NLB offers ultra-high performance and can automatically scale on demand. NLB is ideal for services that require high concurrency.
Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB): GWLB is a Layer 3 load balancing service that distributes traffic from ports to Network Virtual Appliances (NVAs) in server groups based on IP listeners. GWLB is ideal for deploying high availability NVAs.
NAT Gateway: NAT Gateway is an Alibaba Cloud service that provides address translation. You can use NAT Gateway to hide cloud service addresses to improve network security.
Elastic IP Address (EIP): An EIP is a public IP address that you can purchase and hold as an independent resource. An EIP is a NAT IP address provisioned on the Internet-facing gateway of Alibaba Cloud and is mapped to the associated cloud resource by using NAT. After EIPs are associated with cloud resources, the cloud resources can use the EIPs to communicate with the Internet.
Internet Shared Bandwidth: Internet Shared Bandwidth supports bandwidth sharing and multiplexing within a region. After you create an Internet Shared Bandwidth instance in a region, you can add EIPs in the region to the Internet Shared Bandwidth instance. The EIPs can share the Internet Shared Bandwidth instance. This reduces Internet bandwidth costs.
Network Intelligence Service (NIS): NIS provides a set of AIOps tools for you to manage the entire lifecycle of cloud networks from network planning to network O&M. For example, you can use NIS to perform traffic analysis, network inspections, network performance monitoring, network diagnostics, path analysis, and topology creation. NIS helps you optimize your network architecture, improve network O&M efficiency, and reduce network operations costs.
Design principles
When you design a DMZ, we recommend that you combine the network architecture with SLB, NAT Gateway, Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN), transit routers, Internet Shared Bandwidth, EIPs, and security services to improve network flexibility and scalability while maintaining data security, application security, and application reliability. When you design a DMZ, follow these key principles:
Stability: A DMZ not only isolates the internal network from the Internet, but also determines the availability and continuity of services. Therefore, you must design a stable DMZ.
High performance and efficiency: If your business experiences large traffic fluctuations, the DMZ must be able to dynamically scale resources to scale out sufficient resources during peak hours and scale in resource during off-peak hours. This improves resource utilization.
Security compliance: The DMZ must block external risks and help the enterprise meet the security compliance requirements of the industry, such as finance. Therefore, you must also design attack defense and intrusion detection mechanisms.
Principle of least privilege (PoLP): To harden system security, allow system components to access and operate minimum resources.
Key design
Stability
To improve architecture stability, we recommend that you select at least two zones when you create an NLB or ALB instance, transit router, or NAT gateway. Deploy the backend servers in different vSwitches in different zones to implement zone disaster recovery.
Security
Basic protection:
Add ALB and NLB instances to security groups to implement access control on external services.
We recommend that you enable the SNAT feature for NAT gateways and control Internet access for backend servers based on your business requirements. This reduces the potential security risks.
Advanced protection:
Anti-DDoS: Associate EIPs protected by Anti-DDoS Pro/Premium with the internal-facing NLB or ALB instance in the DMZ VPC to mitigate DDoS attacks at the Tbit/s level. Before you can use EIPs protected by Anti-DDoS Pro/Premium, you must activate Anti-DDoS Origin and select the pay-as-you-go billing method.
Web Application Firewall: Purchase a WAF-enabled ALB instance and migrate your web services to the WAF-enabled ALB instance. Instead of integration with WAF 2.0 in transparent proxy mode, ALB is integrated with WAF 3.0 in service integration mode. Listening and forwarding are performed by ALB instead of WAF. Forwarding services and security services are decoupled from each other to ensure compatibility and performance stability.
Internet firewall: Enable the Internet firewall and turn on automatic protection for new assets. The Internet firewall is automatically enabled for public IP addresses that are newly added to your Alibaba Cloud account.
Third-party firewall: Combine with GWLB to design a third-party firewall, such as Palo Alto Networks and Fortinet.
Performance
You can combine EIPs with Internet Shared Bandwidth to increase the inbound and outbound throughput to 100 Gbit/s, which can withstand higher traffic spikes.
Each NAT gateway supports a throughout of 10 gigabits and millions of connections to support large-scale businesses in the cloud.
To ensure robust scalability in cases of traffic spikes, we recommend that you enable dynamic IP address allocation when you create an ALB instance.
NLB offers ultra-high performance and can automatically scale on demand. An NLB instance supports up to 100 million concurrent connections.
Observability
Use NIS to analyze Internet traffic and performance and detect anomalies.
Insight providers: You can use insight providers to obtain real-time information about Internet quality assessment, learn about Internet quality degradation in a timely manner, and receive Internet quality events and event impact analysis.
Internet traffic analytics: You can view the volume of Internet traffic on the Traffic Statistics and Traffic Map tabs in the NIS console. NIS displays the ranking of inbound or outbound traffic by region or instance in the form of 1-tuple (cloud IP addresses), 2-tuples (cloud IP addresses and peer IP addresses), and 5-tuples (cloud IP addresses, cloud ports, protocols, peer IP addresses, and peer ports).
Internet connection quality: The Internet connection quality displays the average latencies between Alibaba Cloud regions and other geolocations. This helps you select a suitable region or zone that has the lowest latency when you deploy services.
Best practices

Overall design
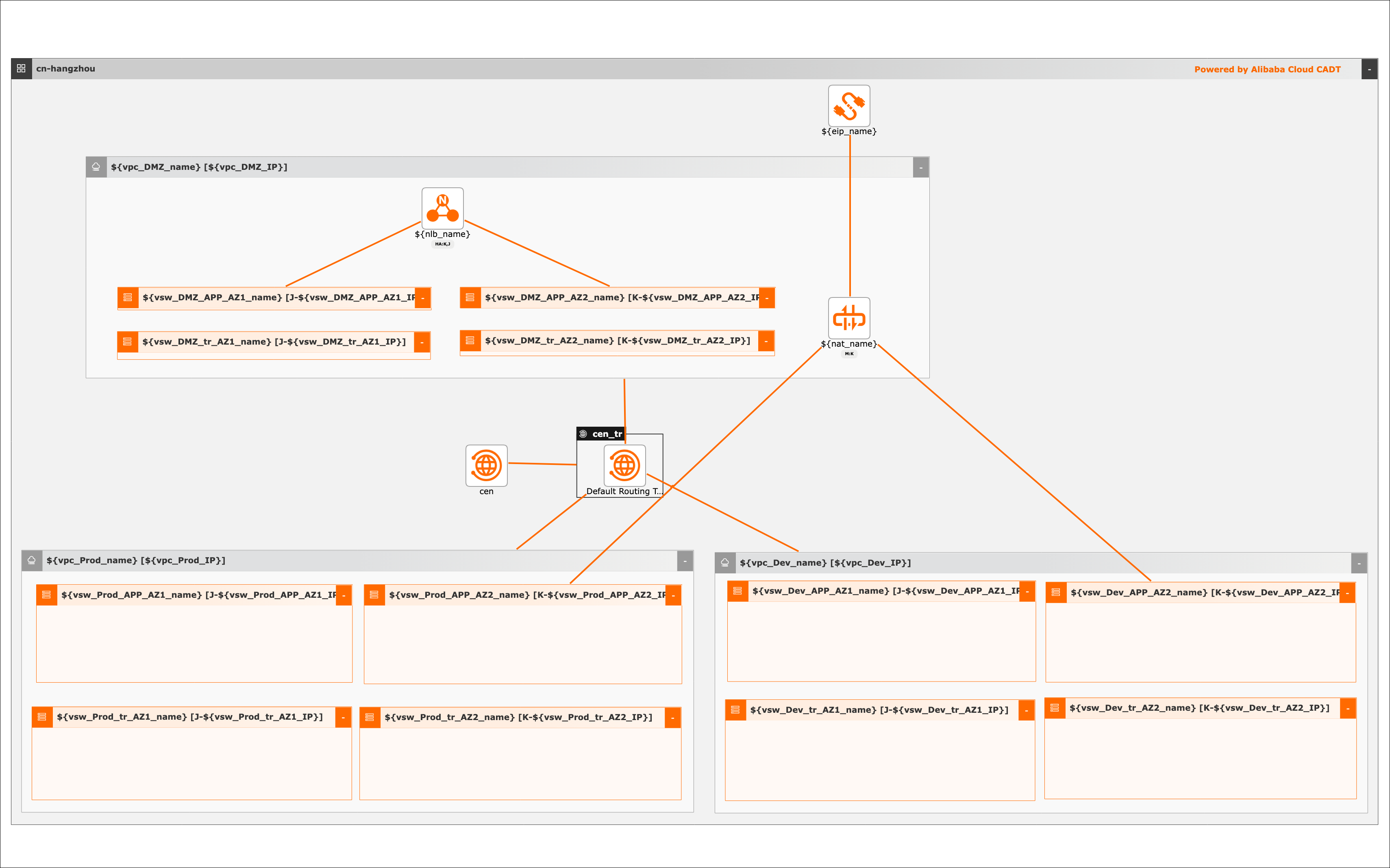
Create a dedicated VPC as a DMZ to isolate the internal network (trusted zone) from the Internet (untrusted zone), and use the DMZ VPC to control Internet access. This design helps you build an application access gateway that can withstand high-concurrency traffic, control access to the Internet, and improve the utilization of Internet bandwidth. In addition, you can combine your architecture with security services to maximize protection for your internal network.
Design of transit routers and route tables
Attach VPCs that contain Internet-facing services and the DMZ VPC to a transit router. In the service VPCs, configure the
0.0.0.0/0route that points to the transit router. After you add this route, Internet traffic is forwarded to the default route.We recommend that the transit router uses the system route table, which is also the default route table. In the route, add a custom route whose destination CIDR block is
0.0.0.0/0and next hop is the DMZ VPC to route Internet traffic to the DMZ VPC. When Internet traffic goes through the SLB instance and NAT gateway, the system converts the destination IP address to the private IP address and queries routes in the route table before forwarding the traffic to the destination VPC.
Design of the DMZ VPC
Use an IPv4 or IPv6 gateway as the Internet egress and ingress to control Internet access.
Public bandwidth:
Internet Shared bandwidth supports various metering methods, including pay-by-bandwidth (subscription and pay-as-you-go), pay-by-95th-percentile bandwidth, and pay-by-data-transfer. EIPs added to the same Internet Shared bandwidth instance can share the bandwidth resources of the Internet Shared bandwidth instance and are limited by the Internet Shared bandwidth.
CDT Internet data transfers support the pay-by-data-transfer metering method. CDT also supports tiered pricing per region per account.
NAT gateway deployment:
Deploy NAT gateways in a dedicated vSwitch. Deploy an independent NAT gateway in the zone of the service vSwitch that requires Internet access. This ensures that Internet access of NAT gateways in other zones is not affected if the zone fails.
We recommend that you disable DNAT and enable only SNAT. Configure SNAT policies to control access from private networks to the Internet. To prevent risks, you can also allow ping commands on EIPs that are associated with the NAT gateway.
SLB deployment: Deploy SLB instances in a dedicated vSwitch. You can deploy the SLB instance across zones to improve service reliability. We recommend that you use NLB for Layer 4 load balancing and ALB for Layer 7 load balancing.
For more information about the configurations of route tables, see Deploy one VPC in a region.
DMZ VPCs are suitable for enterprises that have a controllable volume of inbound and outbound Internet traffic. If you have a large volume of inbound Internet traffic, you can combine a DMZ VPC with a distributed ingress. The only difference is that the SLB instance which functions as the ingress is deployed in each service VPC.
(Optional) Security
Internet-to-cloud protection: We recommend that you enable the Internet firewall.
Cloud-to-Internet protection: We recommend that you enable the Internet firewall for the public IP addresses of ECS instances and EIPs. We recommend that you enable a NAT firewall for NAT gateways and a VPC firewall for VPCs.
Scenarios
A unified DMZ is a standard configuration in the network architecture of a large-scale or medium-scale enterprise, especially in the finance, retail, manufacturing, and public service industries and multinational corporations. The importance of a DMZ is high recognized by these industries. A DMZ increases the robustness, security, and maintainability of the entire architecture, and is applicable to the following scenarios:
Centralized control of cloud behaviors: In a cloud environment, enterprises need to centrally control the behaviors of each business in Internet scenarios to prevent risks. A DMZ allows the enterprise to regulate and monitor all inbound and outbound Internet traffic, and ensures that the enterprise meets the security and compliance requirements. For example, you can use a DMZ to regulate web access, file transfer, and remote access.
Protection for cloud businesses: Security is the prerequisite for an enterprise to deploy businesses in the cloud. The design of a DMZ is highly important and must take into consideration multiple dimensions, such as security, cost-effectiveness, simplified O&M, and attack mitigation. You can build a multi-layer defense line based on Cloud Firewall, Anti-DDoS, and WAF to effectively mitigate attacks from the Internet and detect and block anomalies in the internal network.
Log audit and compliance reporting for logistics enterprises: The Internet businesses of logistics enterprises contain a large volume of sensitive user data. To meet regulatory requirements, logistics enterprises must monitor all traffic to protect data security and user privacy. Meanwhile, logistics enterprises need to record and audit all inbound and outbound traffic to facilitate security event investigations. A DMZ configured with flow logs and traffic mirroring helps logistics enterprises efficiently collect and analyze the log data of all Internet traffic and meet compliance requirements for data transmission. In addition, it provides traces for security events.
Design a DMZ by using Terraform
DMZ design
Item | References |
Website of Terraform modules | |
GitHub URL | |
Examples |
Coding process:
Divide the production, test, and DMZ environment, and deploy multiple VPCs and vSwitches in each environment.
Create a CEN instance and a transit router. Attach the VPCs to the CEN instance by connecting the VPCs to the transit router.
Add routes to the default route table of the transit router to route Internet traffic.
Create an NLB instance in the VPC of the DMZ, and add the servers in the production environment to the NLB instance as backend servers.
Create a NAT gateway in the VPC of the DMZ, associate an EIP with the NAT gateway, and enable only SNAT for the NAT gateway. Configure routes to allow instances in the test environment to access the Internet by using the EIP of the NAT gateway.
Required resources:
3 VPCs
12 vSwitches
1 CEN instance
1 transit router
1 NLB instance
1 Internet NAT gateway
1 EIP
Virtualize the architecture on CADT
DMZ design
Scenario | Item | References |
Design a DMZ | Template ID | H1IH327YSFQ11L18 |
Template library address | ||
Sample code |
Visualized deployment architecture
Procedure
Visualization deployment
Create required cloud resources, including 3 VPCs, 12 vSwitches, and 1 NAT gateway.
Create an application based on a template. The default region is China (Hangzhou). Create the cloud resources, instead of using existing cloud resources.
Save and verify the application, and calculate the fees. In this example, all cloud resources are billed on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Confirm the configurations, select a protocol, and start the deployment of all resources. Routes are automatically configured.
API calls
Call the corresponding API operations to deploy and use cloud resources.
Refer to the documentation to initialize the configurations by using a command-line interface (CLI).
Refer to the sample YAML file to deploy and output the architecture.
If you want to change the region, change the value of the area_id field. For example, change cn-hangzhou to cn-shanghai.