Cloud Backup provides the data synchronization feature for unstructured file systems. You can synchronize data sources on the source, such as File Storage NAS (NAS) file systems, Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) file systems, S3-Compatible Storage buckets, Object Storage Service (OSS) buckets, Cloud Parallel File Storage (CPFS) file systems, and OSS-Compatible Storage buckets, to the data sources on the destination (including Alibaba Cloud). This topic provides an overview of the data synchronization feature of Cloud Backup, including the introduction, working mechanism, procedure, and cost of the data synchronization feature.
Introduction
The data synchronization feature is an online service provided by Cloud Backup to synchronize data sources on the source, such as NAS file systems, HDFS file systems, S3-Compatible Storage buckets, OSS buckets, CPFS file systems, and OSS-Compatible Storage buckets, to the data sources on the destination (including Alibaba Cloud).

The Cloud Backup client for Windows does not support mounting of Network File System (NFS) file systems. If NFS files systems exist on the source or destination, select the Cloud Backup client for Linux when you create a synchronization plan.
Neither OSS nor S3-Compatible Storage supports synchronization of Archive objects. Only data of objects (including the objects to which symbolic links point) is replicated. Metadata information, such as the read and write permissions on the objects, is not supported.
Benefits
Incremental data synchronization
Incremental synchronization is supported. Synchronization jobs can automatically run on schedule. During incremental synchronization, only changed files are synchronized, significantly improving the synchronization efficiency.
Ease of use
Cloud data sources are natively supported and easy to configure.
Ultra-high performance
Compared with traditional copy tools, the optimized data transmission channel helps improve the data synchronization performance significantly.
How data synchronization works
Install and activate a Cloud Backup client on one or more on-premises servers. Then, Log on to the Cloud Backup console to add source and destination data sources.
Create a synchronization plan. When you run a synchronization job, the Cloud Backup client group scans the specified folders to identify the files to be synchronized, and uploads the incremental data to the cloud.
Cloud Backup allows you to synchronize data to Alibaba Cloud over the Internet, virtual private networks (VPNs), or Express Connect circuits. If you synchronize data over the Internet, make sure that the servers where the Cloud Backup client is installed can access the Internet. You do not need to expose the IP addresses of the servers to the Internet.
Procedure
To synchronize data in the Cloud Backup console, perform the following steps:

Before you synchronize data from HDFS file systems, on-premises NAS file systems, S3-Compatible Storage buckets, CPFS file systems, OSS buckets, and OSS-Compatible Storage buckets, you must install a Cloud Backup client on the servers where the data sources are located. The client is used to establish data connections and manage services with Cloud Backup.
You are not charged for activating Cloud Backup. You are not charged for using the data synchronization feature of Cloud Backup. You are charged for using NAS to read files over the Internet and store files. You are charged for using OSS to store files. For more information, see Billing overview of NAS and Billing overview of OSS.
Before you synchronize data from HDFS file systems, on-premises NAS file systems, S3-Compatible Storage buckets, CPFS file systems, OSS buckets, and OSS-Compatible Storage buckets, you must install a Cloud Backup client on the servers where the data synchronization jobs are executed. The servers must be connected to the network where the data sources reside. The client is used to establish data connections and manage services with Cloud Backup.
In the Cloud Backup console, add data sources such as HDFS file systems, on-premises NAS file systems, S3-Compatible Storage buckets, CPFS file systems, OSS buckets, and OSS-Compatible Storage buckets.
Create a data synchronization plan. Cloud Backup runs the plan and continuously synchronizes data based on the plan. The data synchronization feature is only responsible for data synchronization and cannot guarantee data consistency or integrity. After the synchronization job is complete, you must perform a full validation of the synchronized data and verify the data consistency between the source and destination yourself.
Ensure that you verify the transmitted data at the destination after the data synchronization job is complete to ensure accuracy. Any losses or consequences resulting from data loss due to failure to verify the data at the destination before deleting the source data will be your sole responsibility.
Limits
The Cloud Backup client for Windows does not support mounting of Network File System (NFS) file systems. If NFS files systems exist on the source or destination, select the Cloud Backup client for Linux when you create a synchronization plan.
Neither OSS nor S3-Compatible Storage supports synchronization of Archive objects. Only data of objects (including the objects to which symbolic links point) is replicated. Metadata information, such as the read and write permissions on the objects, is not supported.
Incremental file list (ChangeList)
Cloud Backup synchronizes data based on an incremental file list. You do not need to perform a full scan. This reduces the file scanning cost and improves synchronization efficiency. When you create a synchronization plan, if the selected data source is an OSS bucket or an S3-Compatible Storage bucket, you can use the custom incremental file list for synchronization.
An incremental file list is a CSV table that contains the information about the files to be synchronized on the data source. Each row in the table represents a file. The Name field indicates a path relative to the synchronization path of a data source. The following figure shows a
changeList1.csvtable. The Name field is a required column that records the files to be synchronized. Other columns are not supported.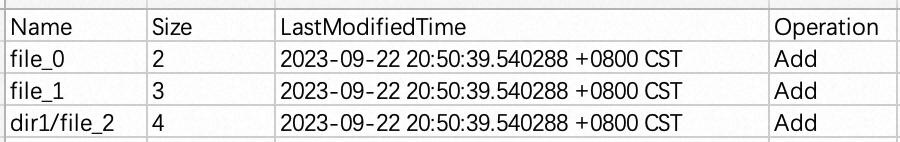 Note
NoteThe values in the Name column must be unique. If the same file name is used, files with the same name overwrite each other during data synchronization.
The value of the Name field cannot be a directory and must be a file.
When you create a synchronization plan, enter the path where the incremental file list is located. When a data synchronization job starts, Cloud Backup reads all CSV files in the path on the source, parses the files, and transfers the files to be synchronized to the destination.
NoteFor example, when you create a plan for synchronization from OSS to NAS, you can use an incremental file list to specify the files to be synchronized. If the incremental file lists
changeList1.csvandchangeList2.csvare stored in the path/changeliston the source, the value of the path for the incremental file lists is/changelist.After the files in each CSV table are processed, the CSV table is moved to the
/Completedlevel of the directory.Directory of the CSV table before processing
Directory of the CSV table after processing
/changelist/changeList1.csv /changelist/changeList2.csv/changelist/Completed/changeList1.csv /changelist/Completed/changeList2.csv
Billing
You are not charged for using the data synchronization feature of Cloud Backup.
You are charged for using NAS to store files. For more information, see Billing overview of NAS.
You are charged for using OSS to store files. For more information, see Billing overview of OSS.