If a system fault or an incorrect operation occurs on a Tablestore instance, restore table data from a backup vault to the source instance or another specified instance. You can restore only one table at a time.
Prerequisites
You have created a Tablestore backup plan and completed a backup.
Billing details
Restoring data to Tablestore incurs data write throughput fees that are charged by Tablestore. For more information, see Tablestore billing methods.
For the first 30 days, Cloud Backup offers Tablestore backup free of charge. After 30 days, Tablestore backup is billed as follows:
During backup: Cloud Backup charges for backup storage capacity. Tablestore does not charge for read traffic.
During restoration: Cloud Backup does not charge for restoration. Tablestore charges fees for data restoration.
Notes
If you use a KMS key for encryption during a backup, you cannot restore the backup data from the backup vault if the KMS key is disabled or deleted.
Cloud Backup does not support restoring data directly to a table that contains a secondary index. To restore data, you must delete the secondary index from the destination table before you run the restore job. After the data is restored, you can recreate the secondary index. Recreating a secondary index is free of charge.
Procedure
After you create a backup plan, the first backup job is a full backup. Subsequent backup jobs are incremental backups by default.
Go to the Create Restore Job panel.
Log on to the Cloud Backup console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the Actions column of the desired instance, click Restore or choose .
If you click Restore, the source instance is the current instance and cannot be changed. If you choose Restore To this Instance, the destination instance is automatically set to the source instance, but you can change it as needed.
In the Create Restore Job panel, configure the parameters for the restore job.
Set the data restoration parameters.
Parameter
Description
Source Database
This parameter appears only when you click Restore.
The name of the source database. This parameter cannot be changed. You can only restore data from this instance to a specified instance.
Source Vault
These parameters appear only when you choose Restore to This Instance.
Select the backed-up instance that you want to restore from the specified backup vault. Select an instance as needed.
Backed Up Instance
Recoverable Tables
From the Recoverable Tables list, select the name of the table to restore. The table names in this list come from the tables you specified for backup. Tables that were not backed up do not appear in this list. A single restore job can restore the data and search indexes of only one table.
NoteWhen you select a table to restore, if the destination table does not exist, the restore job creates a new table based on the backed-up table.
Recoverable Time Point
From the Recoverable Time Point list, select a restorable time range. The time points are based on the running time of the backup plan that you specified.
Choose Recovery Point
Select a restorable point in time. Drag the timeline slider to set a specific time point.
By default, the system regenerates auto-increment columns and restores search indexes. Change the restore options as needed.
Restore Option
Description
Regenerate Auto-increment Columns
Regenerates the auto-increment column for the data table during data restoration. The Regenerate Auto-increment Columns switch is enabled and cannot be changed.
ImportantIf the table did not have an auto-increment primary key column when it was backed up, this setting has no effect.
When you restore a table with an auto-increment column, only regenerating the auto-increment column is supported, and only putRow operations are restored. In an incremental backup, Cloud Backup ignores updateRow and deleteRow operations on tables with auto-increment columns. If you performed multiple `putRow` operations on the same row in the source table (where the values of other primary key columns are the same), each `putRow` operation creates a new row after restoration. This is because the values of the auto-increment column are regenerated.
Restore Search Indexes
Specifies whether to restore the search indexes associated with the table. Restore Search Indexes is enabled by default. If you do not need to restore the search indexes, disable Restore Search Indexes.
ImportantIf the table did not have a search index when it was backed up, this setting has no effect.
Click Next.
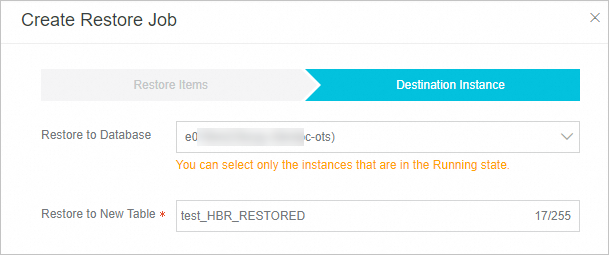
Set the Destination Instance.
Parameter
Description
Restore to Database
From the Restore to Database list, select the name of the database to restore to. The database names in this list come from all Tablestore resources under your account. If you specify a different Tablestore instance, you can restore Tablestore data across instances within the same account and region.
Restore to New Table
The system generates a new table name for the restoration by default. Change the table name as needed.
ImportantWhen restoring to the source table, select the same table name as the backup.
When restoring across Tablestore instances, do not use the name of an existing table for the new table.
The restore job overwrites rows in the destination table that have the same primary key. Other rows are not affected.
If you restore to an existing table, the schema of the destination table must be the same as the source table. You also need to set a proper max version offset and time to live for the destination table to prevent write failures during restoration or data from expiring immediately after restoration. If the schema of the destination table is different from the backed-up table, the restoration may fail.
Click OK.
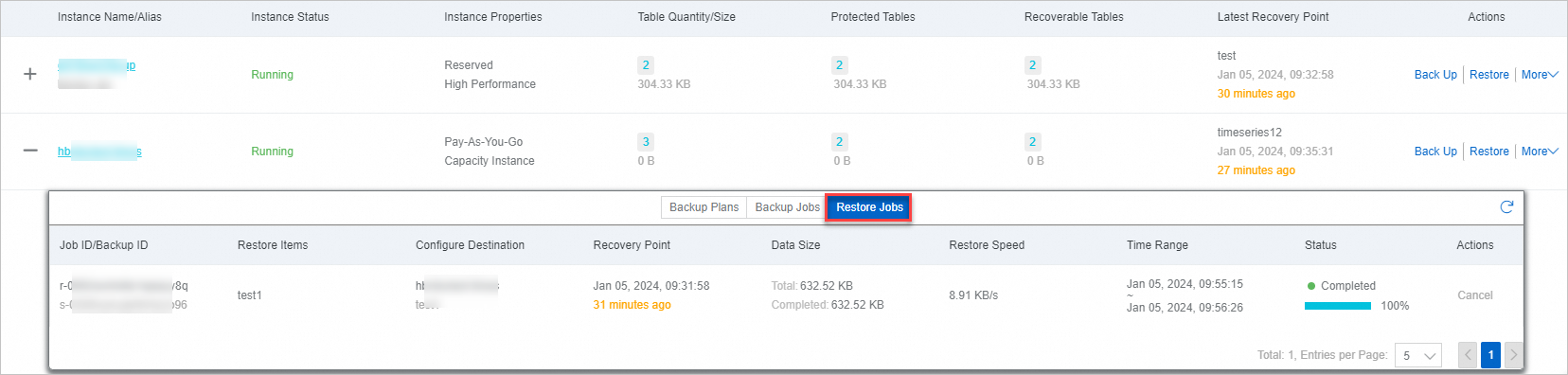
After the restore job is created, view its progress in the Status column on the Restore Jobs tab. When the Status changes to Completed and the progress reaches 100%, the data restoration is complete.
After the restoration is complete, log on to the Tablestore console to verify the restored data in the destination instance.
References
Cloud Backup provides resource plans for different backup scenarios. Purchase a resource plan at a discount to reduce costs. For more information, see Purchase a resource plan.
For more information about the product, see What is Cloud Backup?.