A transit router provides the flow log feature. A flow log captures traffic information transmitted over the transit router and its network connections. These connections include inter-region, VPC, VPN, ECR, and VBR connections. The flow log delivers the captured information to Simple Log Service. You can then query and analyze the logs in the Simple Log Service console to understand traffic on the transit router. Flow logs capture traffic outside the data path and do not affect network performance.
Only Enterprise Edition transit routers and their connected resources support the flow log feature. You must first upgrade Basic Edition transit routers.
Flow log overview
How flow logs work

A flow log captures traffic information within a specified aggregation interval. You can set the aggregation interval to 1 minute or 10 minutes. During the aggregation interval, the flow log aggregates the captured traffic information and delivers it to Simple Log Service. You can query and analyze the flow logs in the Simple Log Service console to understand traffic details. For example:
View traffic details for inter-region, VPC, VPN, ECR, or VBR connections.
Analyze traffic that does not match any routes.
Analyze traffic that matches a blackhole route.
Capture direction
The capture direction of traffic information varies based on the resource:
Inter-region connection: Only outbound traffic from the current transit router is captured (the
directionfield isout). To capture bidirectional traffic, you must also enable the flow log for the inter-region connection on the peer transit router.VPC, VPN, ECR, and VBR connections: Both inbound (the
directionfield isin) and outbound (thedirectionfield isout) traffic are captured.TR: Captures traffic of all network instance connections created on the transit router. The capture direction follows the preceding rules.
Log fields
A flow log can record the following fields. The flow log feature makes a best effort to capture traffic information. If some fields are empty after you create a flow log for a resource, it indicates that the resource does not support recording those fields or the information for those fields is missing.
Field | Description | Flow log version that introduced the field |
account-id | The ID of the Alibaba Cloud account to which the Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) instance belongs. | 2 |
attachment-id | The ID of the network instance connection. | 2 |
bytes | The number of bytes in the data packets. | 2 |
cen-id | The ID of the CEN instance. | 2 |
direction | The direction of the traffic.
For more information, see Capture direction. | 2 |
dscp | The Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) value of the data packet. When a flow log captures traffic of an inter-region connection, this field records the DSCP value modified by the traffic marking policy. | 3 |
dst-region-id | The ID of the region where the network instance connection is deployed. When traffic of an inter-region connection is captured, this field indicates the ID of the region where the destination transit router is deployed. | 2 |
dstaddr | The destination IP address. | 2 |
dstport | The destination port. | 2 |
end | The timestamp that indicates when the aggregation interval ends. The value is a UNIX timestamp. It represents the total amount of time in seconds that has elapsed from 00:00:00 Thursday, 1 January 1970 UTC to the end of the current aggregation interval. | 2 |
flowlog-resource-type | The type of resource for which the flow log is enabled. Valid values:
| 3 |
packets | The number of packets. | 2 |
packets-lost-blackhole | The number of packets dropped because they matched a blackhole route. | 3 |
packets-lost-mtu-exceeded | The number of packets dropped because the MTU was exceeded. | 3 |
packets-lost-no-route | The number of packets dropped because no matching route was found. | 3 |
packets-lost-ttl-expired | The number of packets dropped because the TTL expired. Note This type of packet drop usually occurs due to a network loop. | 3 |
protocol | The protocol of the packets. | 2 |
src-region-id | The ID of the region where the network instance connection is deployed. When traffic of an inter-region connection is captured, this field indicates the ID of the region where the source transit router is deployed. | 2 |
srcaddr | The source address. | 2 |
srcport | The source port. | 2 |
start | The timestamp that indicates when the aggregation interval starts. The value is a UNIX timestamp. It represents the total amount of time in seconds that has elapsed from 00:00:00 Thursday, 1 January 1970 UTC to the start of the current aggregation interval. | 2 |
tr-dst-az-id | The ID of the zone where the ENI of the destination transit router is located. This field is recorded only when traffic to a VPC-connected instance in the same region is captured. | 3 |
tr-dst-eni | The ID of the ENI of the destination transit router. This field is recorded only when traffic to a VPC-connected instance in the same region is captured. | 3 |
tr-dst-resource-account-id | The ID of the Alibaba Cloud account to which the destination network instance belongs. | 3 |
tr-dst-resource-id | The ID of the destination network instance. If the destination resource of the traffic is in a different region from the current transit router, this field records the ID of the peer transit router. | 3 |
tr-dst-vsw-id | The ID of the vSwitch to which the ENI of the destination transit router belongs. This field is recorded only when traffic to a VPC-connected instance in the same region is captured. | 3 |
tr-id | The ID of the transit router to which the flow log belongs. | 3 |
tr-pair-attachment-id | Records the ID of the inbound or outbound network instance connection based on the traffic direction:
| 3 |
tr-src-az-id | The ID of the zone where the ENI of the source transit router is located. This field is recorded only when traffic from a VPC-connected instance in the same region is captured. | 3 |
tr-src-eni | The ID of the ENI of the source transit router. This field is recorded only when traffic from a VPC-connected instance in the same region is captured. | 3 |
tr-src-resource-account-id | The ID of the Alibaba Cloud account to which the source network instance belongs. | 3 |
tr-src-resource-id | The ID of the source network instance. | 3 |
tr-src-vsw-id | The ID of the vSwitch to which the ENI of the source transit router belongs. This field is recorded only when traffic from a VPC-connected instance in the same region is captured. | 3 |
type | The traffic type. Valid values:
| 3 |
version | The version of the flow log. | 3 |
Limits
Flow logs do not support capturing multicast traffic.
If you want to use fields from a newer version for an existing flow log, you must delete the flow log and create a new one.
By default, a new flow log uses the latest version. The latest version is compatible with all fields from previous versions. You can view the version of a flow log in the Cloud Enterprise Network console.
The transit router flow log does not record a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection if it contains only connection establishment, reset, or termination packets.
For example, if a TCP connection does not complete the three-way handshake, or if a client's connection request is reset by a firewall, the flow log does not record the connection. This design prevents TCP scan attacks from generating many flow logs.
Billing overview
When you use the flow log feature of a transit router, the following fees are incurred:
Network log extraction fees
Transit Router charges network log extraction fees for the extracted logs.
NoteNetwork log extraction fees are not currently charged. You will be notified of the billing start time.
Simple Log Service fees
The traffic information captured by flow logs is stored in Alibaba Cloud Simple Log Service. You can view and analyze the data in Simple Log Service. Simple Log Service charges for data storage and queries. For more information, see Billing overview of Simple Log Service.
Prerequisites
Before you create a flow log for a resource, make sure that the required resource exists. To create the required resources, see the following topics:
Create a flow log
Log on to the CEN console.
On the Instances page, click the ID of the CEN instance that you want to manage.
On the tab, find the transit router instance associated with the resource where you want to enable flow logs, and click its instance ID.
On the TransitRouter instance details page, click the Flow Log tab.
If Simple Log Service is not activated for your Alibaba Cloud account, activate it before you use the flow log feature.
On the Flow Log tab, click Enable Now. On the Simple Log Service page, review and select the Simple Log Service Agreement, and then click Enable Now. After the service is enabled, return to the Flow Log tab.
NoteIf Simple Log Service is already activated for your Alibaba Cloud account, skip this step.
On the Flow Logs tab, click Create Flow Log.
In the Create Flow Log dialog box, set the following parameters and click Confirm.
Configuration item
Description
Name
Enter a name for the flow log.
Description
Enter a description for the flow log.
Region
The system displays the region of the current transit router by default.
Transit Router Instance ID
The system displays the ID of the current transit router by default.
Instance
First, select a resource type. Then, select the resource whose traffic you want to capture. The following resource types are supported:
TR
If you select this resource type, you do not need to select a resource. The system enables the flow log feature for all VPC, VPN, ECR, VBR, and inter-region connections under the transit router in the current region.
Inter-region connection
VPC connection
VPN connection
ECR connection
VBR connection
Simple Log Service Project
Select a project to manage flow logs.
You can select an existing project or create a new one. You can only select or create a project in the same region as the current transit router.
Simple Log Service Logstore
Select a Logstore to store flow logs.
You can select an existing Logstore or create a new one.
Log Format
Select the fields that you want to record in the flow log. The following formats are supported:
Default Format (default)
Uses the fields selected by the system. You cannot add or remove fields in this format.
Custom Format
In addition to the required fields (srcaddr, dstaddr, and bytes), you can customize the fields to be recorded.
After you select a log format, the system automatically generates the log format as a string (as shown below). Click Copy Selected Format. You can use the copied format to create flow logs of the same format in batches when you call the API.
${srcaddr}${dstaddr}${bytes}${version}${flowlog-resource-type}${account-id}${cen-id}${tr-id}${src-region-id}${dst-region-id}${attachment-id}${tr-pair-attachment-id}${tr-src-resource-account-id}${tr-dst-resource-account-id}${tr-src-resource-id}${tr-dst-resource-id}${tr-src-vsw-id}${tr-dst-vsw-id}${tr-src-eni}${tr-dst-eni}${tr-src-az-id}${tr-dst-az-id}${srcport}${dstport}${protocol}${dscp}${packets}${start}${end}${type}${packets-lost-no-route}${packets-lost-blackhole}${packets-lost-mtu-exceeded}${packets-lost-ttl-expired}${direction}Sampling Interval (minutes)
Select the aggregation interval for the flow log to capture traffic information. Valid values:
1 Minute (default)
10 Minutes
Tag
Add tags to the flow log.
Tag Key: The tag key can be up to 64 characters in length. It cannot be an empty string or start with
acs:oraliyunor containhttp://orhttps://.Tag Value: The tag value can be an empty string with a maximum length of 128 characters. It cannot start with
acs:oraliyunor containhttp://orhttps://.
You can add multiple tags to a flow log. For more information about tags, see Tags.
Service-linked Role Creation Notice
When you create a flow log, the system automatically creates a service-linked role named AliyunServiceRoleForTRFlowLog. The transit router assumes this role to obtain permissions to read and modify Simple Log Service resources. This allows the transit router to call Simple Log Service API operations to collect traffic information from specified resources.
If the AliyunServiceRoleForTRFlowLog role already exists, the system does not create it again. For more information about the policy of the AliyunServiceRoleForTRFlowLog service-linked role, see System access policies of Cloud Enterprise Network.
Query and analyze flow logs
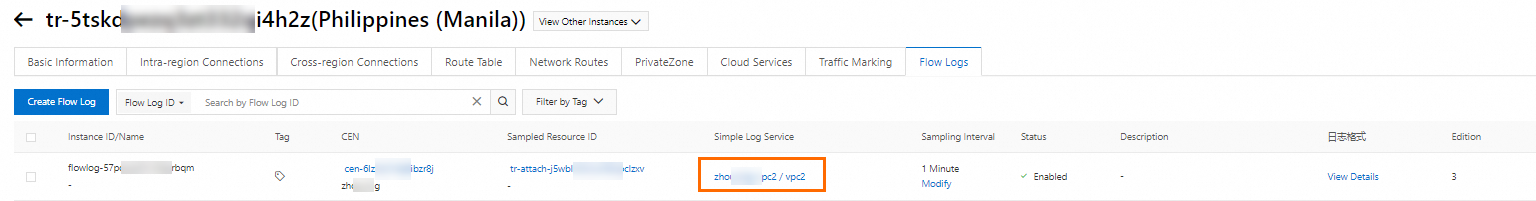
After you create a flow log, it is enabled by default. It takes a few minutes for Simple Log Service to initialize. Once initialized, Simple Log Service automatically starts to record traffic information. You can click the project and logstore names in the Simple Log Service column to navigate to the Simple Log Service console to query and analyze flow logs. For more information about querying and analyzing flow logs, see Simple Log Service Query Overview and Simple Log Service Analysis Overview.
More operations
Operation | Step |
Stop a flow log |
|
Delete a flow log | Deleting a flow log only stops recording traffic information for the related resource. The logs that have been generated are not deleted.
|