Events such as sales promotions can cause sudden traffic spikes. These spikes can exceed your system's maximum load, leading to a large backlog of calls that can freeze the entire system. Service Mesh (ASM) provides a local throttling feature. This feature lets you limit traffic on the gateway to protect your system. This topic describes how to configure local throttling for an ingress gateway.
Prerequisites
An ASM instance is created and meets the following requirements:
If you use a commercial ASM instance (Professional or Ultimate Edition), the instance version must be 1.11.5.30 or later. For more information, see Upgrade an ASM instance.
If you use a Standard ASM instance, the instance version must be 1.9 or later. You can use only the native rate limiting feature of Istio to implement local throttling. The reference document varies based on the Istio version. For more information about how to configure local throttling for the latest Istio version, see Enabling Rate Limits using Envoy.
An ingress gateway is deployed. For more information, see Create an ingress gateway.
The bookinfo and nginx services are created. In this topic, the bookinfo service is deployed in the default namespace, and the nginx service is deployed in the foo namespace. For more information about how to create the bookinfo service, see Deploy an application in a cluster associated with an ASM instance.
A gateway rule and a virtual service are created. For more information, see Manage gateway rules and Manage virtual services.
The hey traffic generation tool is installed. For more information, see hey.
Applicable objects
The local throttling feature of ASM applies to ASM gateways and application services that have sidecars injected.
Scenario example description
This topic uses the Bookinfo and Nginx services as examples to demonstrate how to use gateway and service throttling. The Nginx service is deployed separately in the foo namespace to verify the scope of the throttling rule.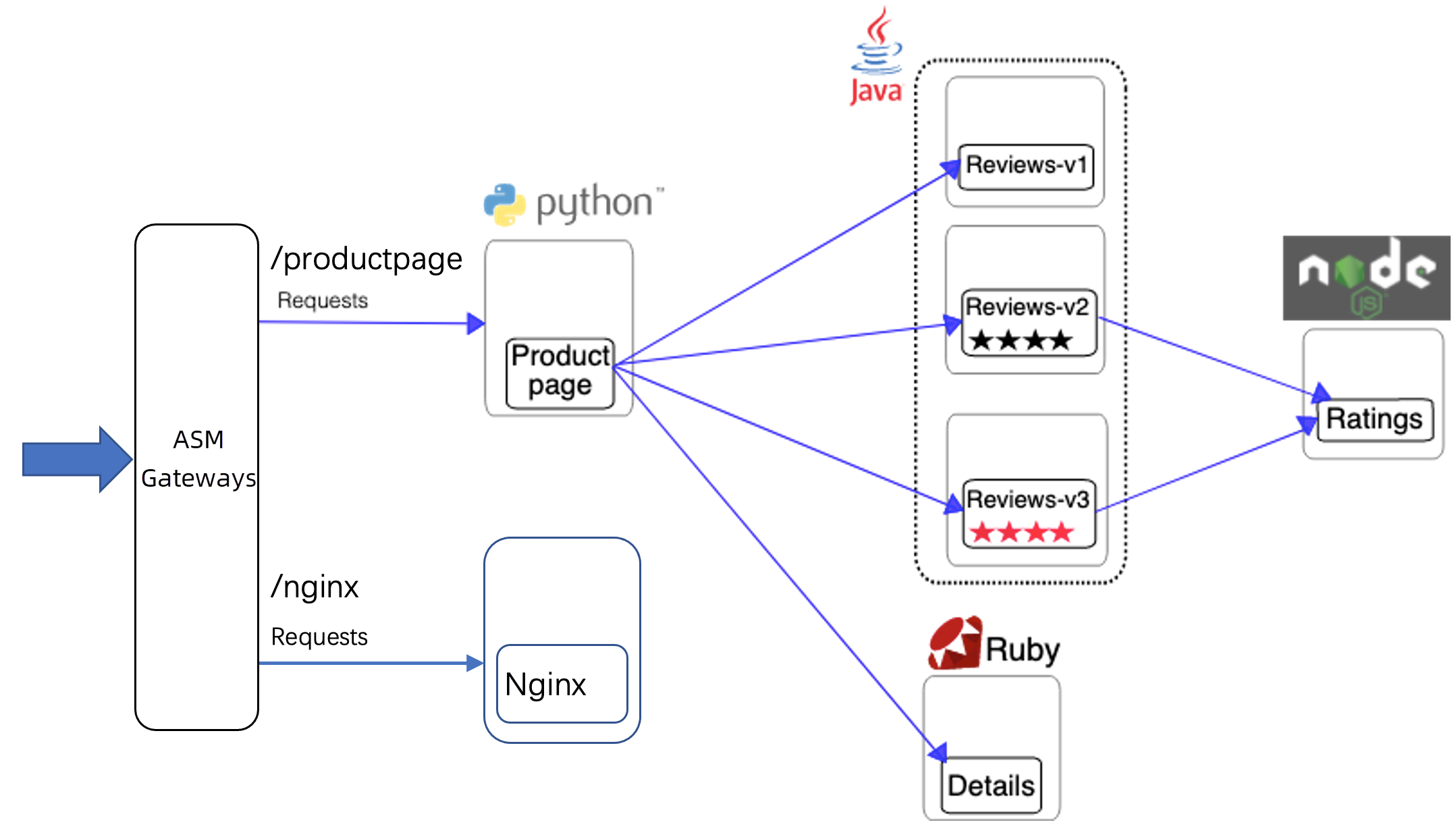
Scenario 1: Configure a throttling rule for a single virtual service route
Configure a throttling rule for the productpage-route-name1 route for the bf2.example.com:80 domain name and port combination. productpage-route-name1 is a route item in the bookinfo virtual service that you created in the Prerequisites section. It matches request paths such as /productpage, /static, /login, and /logout, and forwards the matched requests to the productpage service. After you configure the rule, the rate of traffic to these paths is limited.
Create a local throttling rule.
-
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
-
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Create.
On the Create page, configure the following parameters as needed and click OK.
For more information about the configuration items, see ASMLocalRateLimiter CRD reference.
Configuration area
Configuration item
Description
Basic throttling information
Namespace
The namespace of the workload to which the local rate limiting rule applies. In this example, you must select istio-system because all ASM gateways are deployed in the istio-system namespace.
Name
A custom name for the local throttling configuration. For this example, enter ingressgateway.
Effective workload type
The type of workload for which throttling takes effect. You can select Apply to Application Service or Apply to Gateway. In this example, select Apply To Gateway.
Associated workload
If the effective workload type is set to Gateway, you can associate the workload using the Select Gateway Rule option. The local rate limiting configuration is then associated with the same gateway workload as the selected gateway rule. For this example, select bookinfo-gateway.
Throttling rule list
Gateway domain name
The domain name declared in the gateway rule. The rate limiting rule takes effect for the specified port and domain name combination. In this example, select bf2.example.com.
Gateway port
The port declared in the gateway rule. The throttling rule applies to the combination of the specified port and domain name. For this example, select 80.
Match virtual service route
Select the route declared in the virtual service that is associated with the gateway rule. The throttling rule will take effect for the specified virtual service route. For this example, select productpage-route-name1.
Throttling configuration
Specify the length of the detection time window and the number of allowed requests within that window for the token bucket algorithm. If the number of requests sent within the time window exceeds the allowed number, the requests are throttled. For this example, use the following configurations:
Set Time Window For Throttling Detection to 1 second.
Set Number of requests allowed in the time window to 10.
The preceding configurations indicate that no more than 10 requests can be sent to the workloads of this service within 1 second.
Advanced options
Click Show Advanced Settings to specify some advanced behaviors for when throttling occurs. You can configure the advanced options as needed. In this example, enter
{"ret_code": xxx,"message": "Your request be limited"}in the Custom Throttling Response Body field.The following YAML files show the local throttling configuration.
If you do not configure advanced options, a default response is returned when throttling is triggered.
If you configure advanced options, a custom response is returned when throttling is triggered.
-
In the hey tool, run the following commands to continuously generate a high volume of traffic.
hey -host bf2.example.com -c 10 -n 100000 http://<ASM gateway IP address>/productpagehey -host bf2.example.com -c 10 -n 100000 http://<ASM gateway IP address>/nginxRun the following command to access the /productpage path of the gateway.
curl -H 'host: bf2.example.com' http://<ASM gateway IP address>/productpage -vExpected output:
< HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests < Content-Length: 18 < Content-Type: text/plain < Date: Thu, 13 Jan 2022 03:03:09 GMT < Server: istio-envoy < local_rate_limitedThe output shows that access to the bookinfo service is throttled.
Run the following command to access the /nginx path of the gateway.
curl -H 'host: bf2.example.com' http://${ASM_GATEWAY_IP}/nginx -vThe response does not include a 429 status code. This indicates that access is not throttled.
Scenario 2: Configure a throttling rule for a domain name and port combination on the gateway
Configure a throttling rule for the bf2.example.com:80 domain name and port combination. This limits traffic to all paths for this combination.
Configure a throttling rule.
-
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
-
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Create.
On the Create page, configure the following parameters as needed and click OK.
For more information about the configuration items, see ASMLocalRateLimiter CRD reference.
Configuration area
Configuration item
Description
Basic throttling information
Namespace
The namespace of the workload for which the local rate limiting rule takes effect. In this example, you must select istio-system because all ASM gateways are deployed in the istio-system namespace.
Name
A custom name for the local throttling configuration. For this example, enter ingressgateway.
Effective workload type
The type of workload on which throttling takes effect. You can select Application Service or Gateway. In this example, Gateway is selected.
Associated workload
If the effective workload type is set to apply to a gateway, you can associate the workload using the Select Gateway Rule option. The local rate limiting configuration is then associated with the same gateway workload as the selected gateway rule. In this example, select bookinfo-gateway.
Throttling rule list
Gateway domain name
Select the domain name declared in the gateway rule. The rate limiting rule takes effect for the specified combination of the port and domain name. In this example, select bf2.example.com.
Gateway port
Select the port declared in the gateway rule. The throttling rule takes effect for the specified port and domain name combination. In this example, select 80.
Match virtual service route
Select a route that is declared in the virtual service associated with the gateway rule. The throttling rule takes effect for the specified virtual service route. For this example, do not select a route. This indicates that the throttling rule takes effect on all routes under the specified domain name and port.
Throttling configuration
Specify the length of the detection time window and the number of allowed requests within that window for the token bucket algorithm. If the number of requests sent within the time window exceeds the allowed number, the requests are throttled. For this example, use the following configurations:
Set Time Window For Throttling Detection to 1 second.
Set Number of requests allowed in the time window to 10.
The preceding configurations indicate that no more than 10 requests can be sent to the workloads of this service within 1 second.
The following YAML file shows the local throttling configuration.
-
In the hey tool, run the following command to continuously generate a high volume of traffic.
hey -host bf2.example.com -c 10 -n 100000 http://${ASM_GATEWAY_IP}/nginxRun the following command to access the /nginx path of the gateway.
curl -H 'host: bf2.example.com' http://${ASM_GATEWAY_IP}/nginx -vThe response
HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requestsindicates that access to the /nginx path on the gateway is throttled.
Scenario 3: Configure a throttling rule for requests with a specific header on a single virtual service route
Configure a throttling rule for the nginx-route-name1 route for the bf2.example.com:80 domain name and port combination. Specify that the rule applies only to requests that contain the ratelimit: "true" header. Other requests on this route are not affected. nginx-route-name1 is a route item in the bookinfo virtual service that you created in the Prerequisites section. It matches the /nginx request path and forwards matched requests to the nginx service.
Configure a throttling rule.
-
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
-
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Create.
On the Create page, configure the following parameters as needed and click OK.
For more information about the configuration items, see ASMLocalRateLimiter CRD reference.
Configuration area
Configuration item
Description
Basic throttling information
Namespace
The namespace for the local rate limiting configuration must be set to the namespace of the workload to which the rate limit applies. In this example, you must select istio-system because all ASM gateways are deployed in the istio-system namespace.
Name
A custom name for the local throttling configuration. For this example, enter ingressgateway.
Effective workload type
The type of workload for which throttling takes effect. You can select Applicable Application or Applicable Gateway. For this example, select Applicable Gateway.
Associated workload
If you set Effective Workload Type to Gateway, you can associate the workload using the Select Gateway Rule option. The local rate limiting configuration is then associated with the same gateway workload as the selected gateway rule. For this example, select bookinfo-gateway.
Throttling rule list
Gateway domain name
Select the domain name declared in the gateway rule. The combination of the specified port and this domain name determines where the rate limiting rule is applied. In this example, select bf2.example.com.
Gateway port
Select the port declared in the gateway rule. The throttling rule applies to the specified port and domain name combination. In this example, select 80.
Match virtual service route
Select a route from the virtual service that is associated with the gateway rule. The throttling rule applies to the specified virtual service route. For this example, select nginx-route-name1.
Match request properties
Specify the request matching rules for the throttling configuration to take effect. For this example, use the following configurations:
For Match Attribute, select Specific Request Header.
Set Request Header Name to ratelimit.
For Matching Method, select Exact Match.
Enter true for Matched Content.
Throttling configuration
Specify the length of the detection time window and the number of allowed requests within that window for the token bucket algorithm. If the number of requests sent within the time window exceeds the allowed number, the requests are throttled. For this example, use the following configurations:
Set Time Window For Throttling Detection to 1 second.
Set Number of requests allowed in the time window to 10.
The preceding configurations indicate that no more than 10 requests can be sent to the workloads of this service within 1 second.
The following YAML file shows the local throttling configuration.
-
In the hey tool, run the following command to continuously generate a high volume of traffic. All requests carry the
ratelimit: trueheader to trigger throttling.hey -host bf2.example.com -H 'ratelimit: true' -c 10 -n 10000 http://${ASM_GATEWAY_IP}/nginxRun the following command to access the
/nginxpath of the gateway.curl -H 'host: bf2.example.com' -H 'ratelimit: true' http://${ASM_GATEWAY_IP}/nginx -vThe response
HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requestsindicates that requests to the/nginxpath of the gateway that carry theratelimit: trueheader are throttled.Run the following command to access the
/nginxpath of the gateway, but without theratelimit: trueheader.curl -H 'host: bf2.example.com' http://${ASM_GATEWAY_IP}/nginx -vThe response does not include a 429 status code. This indicates that requests without the
ratelimit: trueheader are not affected by throttling.
Related operations
Delete the throttling configuration and resume access
Delete the throttling rule.
-
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
-
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Traffic Protection and Scheduling page, find the throttling rule that you want to delete and click Delete in the Actions column. In the Confirm dialog box, click OK.
-
Run the following command to access the
/nginxpath of the gateway.curl -H 'host: bf2.example.com' http://${ASM_GATEWAY_IP}/nginx -vThe response does not include a 429 status code. This indicates that access is not throttled.