To monitor Python applications deployed on Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) and Container Compute Service (ACS), you must install the ack-onepilot component for Application Real-Time Monitoring Service (ARMS) and modify the corresponding Dockerfile. This lets you view monitoring data, such as application topologies, API calls, and call trace analysis, in the ARMS console. This topic describes how to install the agent for Python applications deployed on Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) and Container Compute Service (ACS).
If you have any questions when you use the Python agent, see FAQ about the Python agent. If the document does not resolve your issue, you can contact us through the DingTalk group (ID: 159215000379).
To ensure that you can use the latest features of the Python agent, the latest version of the agent is installed by default each time you use the aliyun-bootstrap component or the non-intrusive installation method. To manually specify an agent version, see the How do I install an agent for a specific region and version? section in FAQ about the Python agent.
Prerequisites
An ACK or ACS cluster is created.
For ACK clusters: Create an ACK dedicated cluster (new creations are discontinued), Create an ACK managed cluster, or Create an ACK Serverless cluster.
For ACS clusters: Create an ACS cluster.
A namespace is created. For more information, see Manage namespaces and quotas. This topic uses arms-demo as an example namespace name.
Your Python and framework versions are supported. For more information, see Python libraries supported by Application Monitoring.
Notes
If your application starts with uvicorn, choose one of the following configuration methods.
Method 1: Add the following statement to the first line of the uvicorn entry file to import the Python agent.
from aliyun.opentelemetry.instrumentation.auto_instrumentation import sitecustomizeMethod 2: Replace uvicorn with gunicorn and add the
aliyun-instrumentprefix to the gunicorn command.Example:
uvicorn app:app --workers 4 --port=9090 --host 0.0.0.0Change the command to:
aliyun-instrument gunicorn -w 4 -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker -b 0.0.0.0:8000 app:appNoteThe aliyun-instrument instruction handles the initialization and non-intrusive instrumentation of the ARMS Python agent.
If your application starts with uWSGI, see Install the Python agent for a Django or Flask project that starts with uWSGI.
If you use gevent coroutines, you must set the
GEVENT_ENABLE=trueenvironment variable.For example, if your program contains the following code:
from gevent import monkey monkey.patch_all()You must set the environment variable as follows:
GEVENT_ENABLE=true
Step 1: Install the ARMS agent installer (ack-onepilot)
Log on to the ACK console. On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Add-ons. In the upper-right corner, search for ack-onepilot.
ImportantMake sure that the version of ack-onepilot is 3.2.4 or later.
Click Install on the ack-onepilot card.
NoteBy default, the ack-onepilot component supports 1,000 pods. For every additional 1,000 pods in the cluster, you must add 0.5 CPU cores and 512 MB memory for the component.
In the dialog box that appears, configure the parameters and click OK. We recommend that you use the default values.
NoteAfter you install ack-onepilot, you can upgrade, configure, or uninstall it on the Add-ons page.
- Important
If the version of the ack-onepilot component that you installed is later than 5.0.0, you can skip Step 2 and proceed to Step 3. This provides a fully non-intrusive installation experience for Python applications.
Step 2: Modify the Dockerfile
Download the agent installer from the Python Package Index (PyPI) repository.
pip3 install aliyun-bootstrapUse aliyun-bootstrap to install the agent.
# The region ID of the Alibaba Cloud account. ARMS_REGION_ID=xxx aliyun-bootstrap -a installNoteTo install a specific version of the Python agent, run the following command:
# Replace ${version} with the actual version number. aliyun-bootstrap -a install -v ${version}For more information about all released versions of the Python agent, see Python agent release notes.
Start the application using the ARMS Python agent.
aliyun-instrument python app.pyBuild the image.
The following code provides a complete example of a Dockerfile:
Step 3: Grant access permissions to ARMS resources
ACK managed clusters
If an ARMS Addon Token does not exist in the ACK managed cluster, manually grant permissions to access ARMS resources. If an ARMS Addon Token already exists, skip to Step 4.
If a cluster has ARMS Addon Token, ARMS performs password-free authorization on the cluster. ARMS Addon Token may not exist in some ACK managed clusters. We recommend that you check whether an ACK managed cluster has ARMS Addon Token before you use ARMS to monitor applications in the cluster. If the cluster has no ARMS Addon Token, you must authorize the cluster to access ARMS.
ACK dedicated cluster/registered cluster
To monitor an application deployed in an ACK dedicated cluster or registered cluster, make sure that the AliyunARMSFullAccess and AliyunSTSAssumeRoleAccess permissions are granted to your Resouce Access Management (RAM) user.
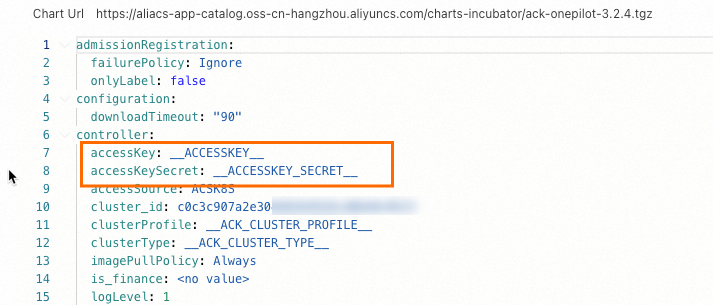
After installing the ack-onepilot component, enter the AccessKey ID and AccessKey Secret of the account in the configuration file of ack-onepilot.
Method 1: Input in Hem
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, click the cluster you want to manage. In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, choose . Then, click Update next to ack-onepilot.
Replace
accessKeyandaccessKeySecretwith the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the account and click OK.NoteThe AccessKey Secret is only visible during initial creation of an Alibaba Cloud AccessKey pair and cannot be retrieved afterward. This design mitigates leakage risks. Securely store the Secret immediately.
Restart the Deployment.
Method 2: Import through Kubernetes Secrets
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, click the cluster you want to manage. In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, choose .
Click Create. In the panel that appears, click Add and add the AccessKey ID and AccessKey Secret for ack-onepilot.
NoteThe AccessKey Secret is only visible during initial creation of an Alibaba Cloud AccessKey pair and cannot be retrieved afterward. This design mitigates leakage risks. Securely store the Secret immediately.

In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click the ack-onepilot component. Generally, it is named ack-onepilot-ack-onepilot in the ack-onepilot namespace.
In the upper-right corner of the page that appears, click Edit.
Scroll down until you see the Environments section. Click Add, add the environment variables
ONE_PILOT_ACCESSKEYandONE_PILOT_ACCESSKEY_SECRET, reference the Secrets in Kubernetes Secrets, and click OK.
ASK/ECI cluster
To monitor applications in an ACK Serverless (ASK) cluster or applications in a Kubernetes cluster connected to Elastic Container Instance, you must first authorize the cluster to access ARMS on the Cloud Resource Access Authorization page. Then, restart all pods on which the ack-onepilot component is deployed.
Step 4: Enable ARMS Application Monitoring for the Python application
If the version of the ack-onepilot component that you installed is later than 5.0.0, the component automatically downloads and injects the Python agent package during this step. You do not need to manually modify the startup command in the Dockerfile. This provides a fully non-intrusive installation experience.
The Python agent package is downloaded and injected by an init container. By default, the init container consumes 0.5 cores and 250 MB of resources, and its execution may take about 10 seconds. These resources are released after the initialization is complete. You can adjust the resource quota for the init container to change its execution speed using the following environment variables:
PYTHON_INIT_RESOURCE_REQUESTS_CPU: The CPU request for the Python application init container. Example: 500m.
PYTHON_INIT_RESOURCE_REQUESTS_MEM: The memory request for the Python application init container. Example: 250Mi.
PYTHON_INIT_RESOURCE_LIMIT_CPU: The CPU limit for the Python application init container. Example: 1000m.
PYTHON_INIT_RESOURCE_LIMIT_MEM: The memory limit for the Python application init container. Example: 500Mi.
This feature is in beta. If you have any questions while using this non-intrusive injection feature, contact us through the DingTalk group (ID: 159215000379).
The following template is a complete YAML example for creating a deployment and enabling ARMS Application Monitoring:
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Deployments page, find the target application and choose from the Actions column.
Click Create From YAML to create a new application.
In the YAML file, add the following
labelsunder `spec.template.metadata`.labels: aliyun.com/app-language: python # Required for Python applications. Specifies that this is a Python application. armsPilotAutoEnable: 'on' armsPilotCreateAppName: "deployment-name" # The display name of the application in ARMS.ImportantIf the version of the ack-onepilot component that you installed is later than 5.0.0, the component automatically downloads and injects the Python agent package during this step. This provides a fully non-intrusive installation experience. If you do not want to use this feature, or if you have already manually installed the Python agent in the container, we recommend that you disable the non-intrusive injection feature for Python using the following label:
labels: aliyun.com/app-language: python # Required for Python applications. Specifies that this is a Python application. armsPilotAutoEnable: 'on' armsPilotCreateAppName: "deployment-name" # The display name of the application in ARMS. armsAutoInstrumentationEnable: "off" # Disables the non-intrusive injection feature for Python applications.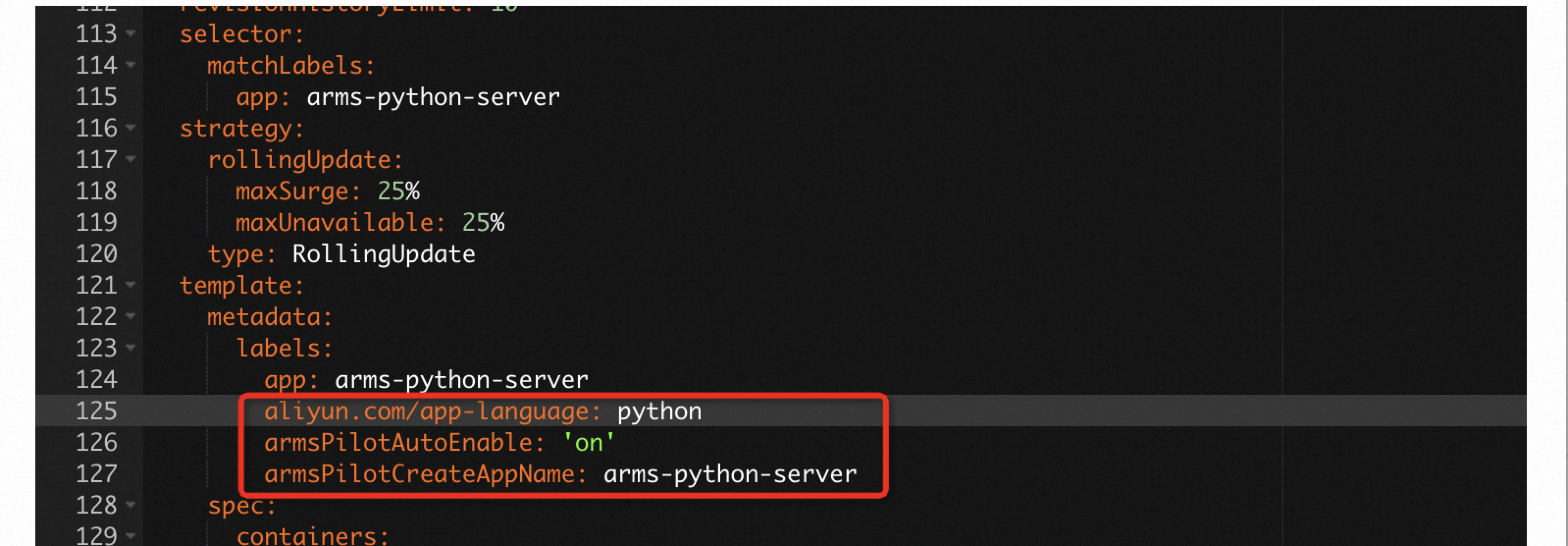
Click Update.
Result
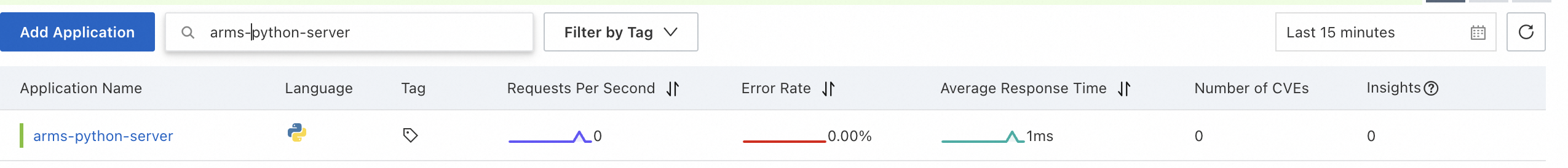
The agent installation is successful if the Python application appears on the page in the ARMS console and begins to report data within about one minute.
 > Edit YAML
> Edit YAML