This topic describes the definition, model relationship, internal attributes, behavior constraints, and usage notes for messages in ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ.
Definition
A message is the smallest unit of data transmission in ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ. A producer encapsulates the payload and extended attributes of business data into a message and sends the message to an ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ broker. The broker then delivers the message to a consumer based on the relevant semantics.
The message model of ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ has the following features:
Immutability
A message is an event that is generated. After the message is generated, the content of the message does not change. Even if the message passes through a transmission channel, the content of the message remains the same. The messages that consumers obtain are read-only messages.
Persistence
By default, ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ persists messages by storing them in files on the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ broker. This ensures that messages can be traced and recovered in the event of a system failure.
Model relationship
The following figure shows the position of messages in the domain model of ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ.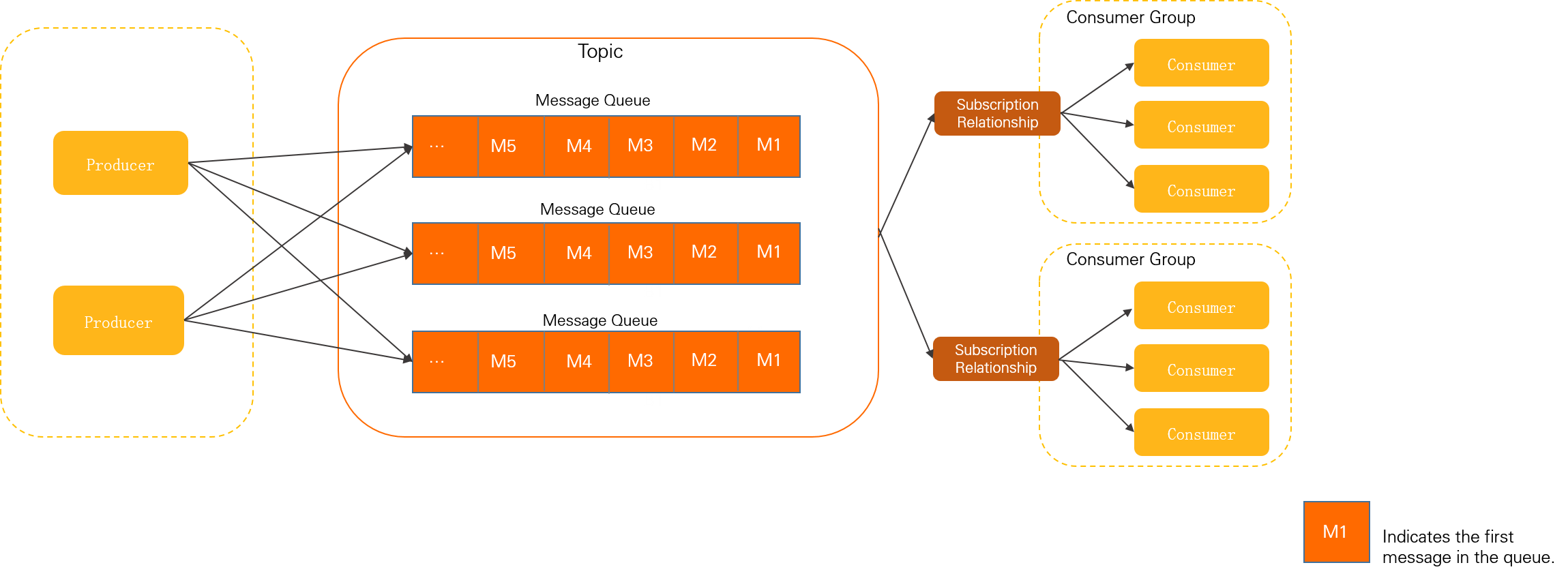
Messages are initialized by producers and sent to the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ broker.
Messages are stored in queues in the order they are received by the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ broker.
Consumers obtain and consume messages from the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ broker according to their subscription relationships.
Internal attributes
System attributes
Topic name
Definition: The name of the topic to which a message belongs. The topic name is globally unique within a cluster. For more information, see Topics.
Value: Obtained from the SDK interface.
Lite topic name
Definition: The name of the lite topic to which the message belongs. If the topic type is Lite, the name is globally unique within that topic. For more information, see Lite topic model.
Value: Obtained from the SDK interface.
Message queue
Definition: The queue where the message is stored. For more information, see Message queues.
Value: Specified and populated by the broker.
Message offset
Definition: The position of the message within its queue. For more information, see Consumption progress.
Value: Specified and populated by the broker. Valid values: 0 to Long.Max.
Message ID
Definition: The unique identifier of a message. Each message ID is globally unique within the cluster.
Value: Automatically generated by the producer client. A message ID is a 32-character string that consists of digits and uppercase letters.
(Optional) Index key list
(Optional) Filter tag
Definition: The tag used to filter messages. Consumers can filter messages by tags to receive only messages that have the specified tags.
Value: Defined by the producer client.
Constraint: You can specify only one tag for a message.
(Optional) Scheduled time
Definition: In scheduled delivery scenarios, this is the timestamp in milliseconds when the message is delivered. For more information, see Scheduled and delayed messages.
Value: Defined by the message producer.
Constraints:
Subscription and pay-as-you-go Standard Edition instances, and Serverless Standard and Professional Edition instances: A maximum of 7 days.
Subscription and pay-as-you-go Professional Edition and Platinum Edition instances: A maximum of 40 days.
For more information, see Quotas and limits.
Message sending time
Definition: The local timestamp in milliseconds of the producer client when the message is sent.
Value: Populated by the producer client.
Note: The client clock may differ from the broker clock. The message sending time is based on the client clock.
Message retention timestamp
Definition: The local timestamp in milliseconds of the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ broker when the message is stored.
For scheduled messages and transactional messages, the message retention time is the broker time that is displayed for the consumer when the message takes effect.
Value: Populated by the broker.
Note: The client clock may differ from the broker clock. The message retention time is based on the broker clock.
Number of consumption retries
Definition: The number of times that the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ broker redelivers a message after consumption fails. The number of retries increases by 1 after each retry attempt. For more information, see Consumption retry.
Value: Marked by the broker. The number of retries is 0 for the first consumption attempt. After a consumption failure, the number of retries for the first retry attempt is 1.
Custom attributes for messages
Message load
Message load
Definition: The payload of a business message.
Value: Serialized and encoded by the producer and transmitted as a binary byte array.
Constraints: For more information, see Parameter limits.
Behavior constraints
The size of a message cannot exceed the upper limit. If the size of a message exceeds the corresponding upper limit, the message fails to be sent.
The default maximum message sizes are as follows:
Normal and ordered messages: 4 MB
Transactional, scheduled, and delayed messages: 64 KB
Usage notes
Overloaded transmission is not recommended for a single message.
As a messaging middleware, ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ is designed to transmit business event data. We recommend that you control the data size of a single message. An excessively large message can increase the load on the network transport layer and is not ideal for features such as retries and traffic shaping.
If an overloaded transmission is required in the production environment, we recommend that you split the message based on a fixed size or use the file storage method.
Immutability of messages
In ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ 5.x brokers, messages are immutable. Consumers obtain read-only message views.
Because 3.x and 4.x versions do not have immutability constraints, you must re-initialize the messages if you want to forward them.
