In unique-certificate-per-device authentication mode, an application server applies for a unique access credential for each device from the corresponding ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker. The access credential of a device consists of the client ID, AccessKey ID, and AccessKey secret of the device. When a client establishes a connection to an ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker, you must configure the Username and Password parameters based on the access credential of the device for authentication. You can activate the device and transfer data between the device and ApsaraMQ for MQTT only after the authentication is passed.
Terms
Term | Description |
device access credential | The globally unique credential that is issued by the ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker to an ApsaraMQ for MQTT client. A device access credential consists of the AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret, and client ID of the client. When a client establishes a connection to an ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker, you must configure the Username and Password parameters in the authentication request by using the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in the device access credential based on the predefined rules. |
application server | The server that you use to manage local accounts and apply for and manage device access credentials on behalf of clients. |
ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker | The server that ApsaraMQ for MQTT uses for permission authentication and messaging. An ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker processes authentication-related requests that are initiated by an application server and works as an intermediary for messaging between clients. |
Calculation method
This section describes the rules based on which you can specify the Username and Password parameters in the CONNECT packet that an ApsaraMQ for MQTT client sends to an ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker to perform unique-certificate-per-device authentication. For more information, see Authentication overview.
Username
A valid value of the Username parameter consists of the authentication mode name, the AccessKey ID of the client, and the instance ID. The three parts are separated with vertical bars (|). If you want to enable unique-certificate-per-device authentication, set the authentication mode to DeviceCredential.
For example, if an ApsaraMQ for MQTT client with the ID GID_Test@@@0001 uses the AccessKey ID YYYYY to access an ApsaraMQ for MQTT instance with the ID mqtt-xxxxx, set the Username parameter to DeviceCredential|YYYYY|mqtt-xxxxx.
For more information about client IDs, see Terms.
Password
The Password parameter specifies the signature calculation result of the client ID. The following example shows how to calculate the signature of a client ID:
An ApsaraMQ for MQTT client with the ID GID_Test@@@0001 uses XXXXX as the AccessKey secret.
Calculate the signature of the string-to-sign GID_Test@@@0001 by using the HMAC SHA-1 algorithm to obtain a binary array. The AccessKey secret XXXXX is used as the key for the HMAC calculation. Encode the binary array in Base64 to obtain the final signature string for the Password parameter.
Each programming language comes with a function library for the implementation of the HMAC SHA-1 algorithm. You can use the corresponding functions based on your business requirements.
Process
When you use the unique-certificate-per-device authentication mode, deploy your application server based on the following process. During initialization, make sure that your ApsaraMQ for MQTT client can interact with your application server to obtain and update the device access credential.
Figure 1. Authentication process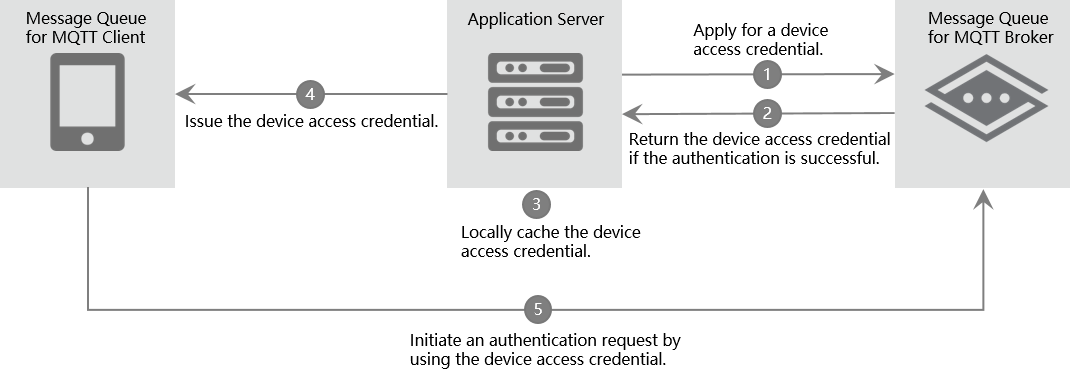
The following items describe the steps of unique-certificate-per-device authentication:
The application server sends an API request to the ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker to apply for a device access credential for the ApsaraMQ for MQTT client.
The ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker authenticates the request. If the broker determines that the request is valid, the broker issues the corresponding device access credential.
The application server stores the returned device access credential in the local cache and maps the device access credential to the client. Caching of device access credentials provides the following benefits:
Device access credentials do not need to be updated unless they are leaked on the client. When the client reconnects to the broker, the application server can return a device access credential to the client directly from the cache. This eliminates the overhead of calling an API operation to apply for an access credential.
If the ApsaraMQ for MQTT client applies for a new device access credential and an error occurs on the ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker, the application server returns the previously applied device access credential for local disaster recovery.
The application server issues the requested device access credential to the corresponding ApsaraMQ for MQTT client.
The ApsaraMQ for MQTT client sends an authentication request to connect to the ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker. The relevant parameters in the authentication request are configured by using the information contained in the device access credential based on the predefined rules. After the ApsaraMQ for MQTT client passes the authentication, it can send and receive messages.
Limits
Instance specifications
The access credential quota provided for devices by an ApsaraMQ for MQTT instance is equal to the maximum number of connections specified for the instance. When the upper limit is reached, you cannot apply for access credentials for new devices. You can upgrade the instance configurations to increase the quota for access credentials. For more information, see Renew an instance and upgrade or downgrade the configurations of an instance.
When you use the unique-certificate-per-device authentication mode, we recommend that you call the UnRegisterDeviceCredential operation to delete device access credentials that are no longer used at the earliest opportunity to save the quota.
ApsaraMQ for MQTT clients
An ApsaraMQ for MQTT client includes the Username and Password parameters in the authentication request each time the client establishes a connection to an ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker. Make sure that the Username and Password parameters are configured by using the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in the device access credential based on the predefined rules.
To eliminate the need to apply for the same device access credential each time an ApsaraMQ for MQTT client reconnects to the ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker, the client must persistently store the device access credential that is returned by the application server. This helps prevent the application server from unexpectedly quitting when a large number of ApsaraMQ for MQTT clients connect to the ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker at the same time.
Application servers
The application server must manage mappings between device access credentials and ApsaraMQ for MQTT clients. This eliminates the need to repeatedly call the credential application operation for the same client.
The application server must implement local disaster recovery. This helps ensure business continuity in scenarios in which the ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker becomes temporarily unavailable.
Related API operations
You can call the corresponding API operations to perform unique-certificate-per-device authentication. An application server is responsible for the application and management of device access credentials. It interacts with an ApsaraMQ for MQTT broker by calling API operations over HTTPS.
Each API operation requires identity verification that is performed by using an AccessKey pair and a request signature. ApsaraMQ for MQTT provides API operations that allow you to create, query, delete, and update device access credentials. For more information, see Unique-certificate-per-device authentication operations.