This topic describes how to use the one-click cloud migration feature to migrate a self-managed PostgreSQL database on an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance or in an on-premises data center to ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL. This feature uses physical streaming replication and provides a fast, simple, and stable migration process that supports a wide range of scenarios to improve migration efficiency.
Prerequisites
The target ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance must meet the following requirements:
The major version of the instance must be the same as that of the self-managed PostgreSQL database. PostgreSQL 10 and later are supported.
NoteTo migrate across major versions, such as from PostgreSQL 10 to ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL 13, you must first complete the one-click cloud migration as described in this document. Then, you can upgrade the major version of the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. For more information, see Upgrade the major version of a database.
The instance must be a primary instance. Read-only instances do not support one-click cloud migration.
The storage class of the instance must be cloud disk.
The instance must be empty. The available storage space must be greater than or equal to the total data size of the self-managed PostgreSQL database.
The self-managed PostgreSQL database must meet the following requirements:
Network
Migration source
Network configuration requirements
A self-managed PostgreSQL database on an Alibaba Cloud ECS instance or an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance
The source ECS instance or ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance must be in the same VPC as the target ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. If they are in different VPCs, you must use Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) to connect them. For more information, see Cloud Enterprise Network.
A self-managed PostgreSQL database in an on-premises data center that is connected to a VPC
You must establish a private network connection between the on-premises data center and the target ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. For more information about the configuration, see Connect a VPC to an on-premises IDC.
If you migrate a self-managed PostgreSQL database from an ECS instance, you must configure the security group of the ECS instance. For more information, see (Optional) Configure an ECS security group.
The postgresql.conf file is configured. For more information, see Configure the postgresql.conf file.
A migration account is created. For more information, see Create a migration account.
The pg_hba.conf file is updated. For more information, see Update the pg_hba.conf file.
The server firewall is configured. For more information, see Configure the server firewall.
Notes
Read and write operations are allowed on the self-managed PostgreSQL database during the cloud migration task. However, do not perform other operations on the source instance, such as another migration, a restart, or an instance upgrade or downgrade.
Step 1: Run a cloud migration evaluation
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
In the navigation pane on the left, click One-Click Cloud Migration/Disaster Recovery. Then, click the Feasibility Evaluation tab.
In the Select Scenario and Source Type step of the configuration wizard, set Scenario to Cloud Migration, select a migration source, and then click Next.
In the Target Instance Configuration step, click Next.
In the Source Instance Configuration step, select the check boxes for all configuration items that you have completed, and then click Next.
NoteFor more information about the Source Instance Configuration step, see (Optional) Configure an ECS security group, Create a migration account, and Update the pg_hba.conf file.
In the Start Feasibility Evaluation step, you can configure the source instance information.
Parameter
Description
Migration Task Name
The system automatically generates a name. No changes are needed.
Source VPC IP/DNS
For a one-click migration of a self-managed PostgreSQL database on an ECS instance, configure the private IP of the ECS instance. For more information, see View IP addresses.
For a one-click cloud migration of a self-managed PostgreSQL database in an on-premises data center, enter the private IP address of the data center.
Source Instance Port
The port of the self-managed PostgreSQL database. Run the
netstat -a | grep PGSQLcommand to view the port.Username
migratetest, the database account that you created in the Create a migration account step.Password
123456, the password for the database account that you created in the Create a migration account step.Click Create Feasibility Evaluation Task.
NoteThe instance status changes to Maintaining Instance during the feasibility evaluation task.
When the migration evaluation is complete, you can view the status of the task in the Cloud Migration list on the Feasibility Evaluation tab.
You can proceed to the cloud migration step only if the Status is Successful. For more information, see Step 2: Migrate to the cloud.
If the Status is Failed, you can click View Report in the Actions column and resolve the issue based on the error message. For more information about common errors, see Interpret a cloud migration evaluation report.
After you resolve the error, click Re-evaluate in the Actions column to run the evaluation task again.

Step 2: Migrate to the cloud
You can perform this step only after the cloud migration evaluation is successful.
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
In the left navigation pane, click One-Click Cloud Migration/Disaster Recovery. On the Cloud Migration tab, click Create Cloud Migration Task.
In the Create Cloud Migration Task window, select the successful cloud migration evaluation task from the Associated Evaluation Task list. This is the task from Step 1: Run a cloud migration evaluation.
NoteAfter you select an Associated Evaluation Task, the Source Database Type, Source IP/DNS, Source Instance Port, and Username parameters are automatically populated and do not require configuration.
Click Start Cloud Migration to automatically begin the migration task.
WarningDuring the cloud migration task, the instance status changes to Migrating Data. You can still read from and write to the self-managed PostgreSQL database. However, do not perform other operations, such as starting another migration, restarting the instance, or upgrading or downgrading the instance. These operations will cause the migration task to fail.
Perform a switchover.
In the cloud migration task list, click the link in the Cloud Migration Phase column to view the task's progress.

When the migration enters the Incremental Synchronization phase, click Switch To Cloud in the Actions column. This promotes the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance to the primary database, which then begins to provide services.
In the Switch To Cloud window, set the source instance to read-only or stop write operations from your application.
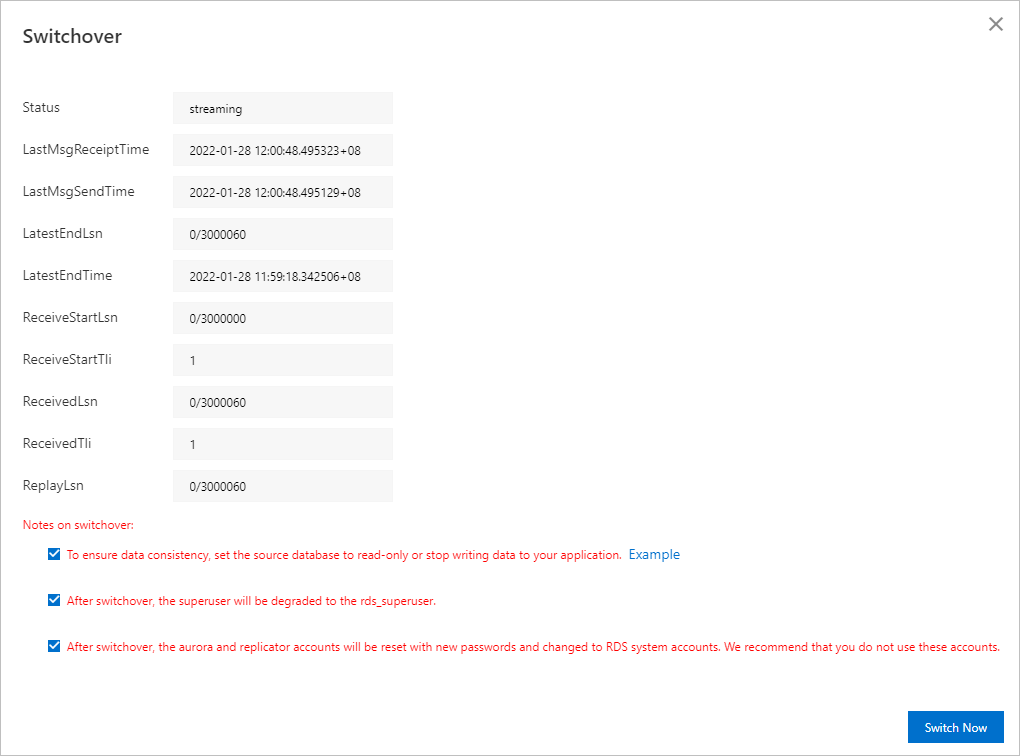 Note
NoteSet the source instance to read-only:
If the source instance is an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance, configure it as follows:
You can use the Set instance parameters feature to set the rds_force_trans_ro_non_sup parameter of the source instance to on.
Run the following statement to interrupt all existing sessions.
SELECT pg_terminate_backend(pid) FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE usename not in ('replicator', 'monitor', 'pgsql', 'aurora') AND pid != pg_backend_pid();
If the source instance is a self-managed database, configure it as follows:
-- Set the database to read-only ALTER SYSTEM SET default_transaction_read_only=on; -- Reload the parameter configuration to apply the changes SELECT pg_reload_conf(); -- Interrupt all existing sessions SELECT pg_terminate_backend(pid) FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE usename not in ('replicator', 'monitor', 'pgsql', 'aurora') AND pid != pg_backend_pid();
Select all the check boxes, click Switch Now, and wait for the migration to complete.
