This topic describes the features, architecture, benefits, scenarios, and usage of RDS for SQL Server serverless instances to help you understand and start using them.
You can also join the RDS Serverless DingTalk user group (Group ID: 41925003105) for consultation, communication, and feedback.
To ensure product stability and user experience, Alibaba Cloud will discontinue the sale of RDS for SQL Server serverless instances on November 3, 2025, and will stop providing related technical support on June 1, 2026. This includes, but is not limited to, new feature iterations and technical issue fixes. To ensure your product experience, convert your RDS for SQL Server serverless instances to pay-as-you-go instances as soon as possible.
Official launch
Serverless RDS instances are officially launched on March 20, 2023. You can create a serverless RDS instance in the ApsaraDB RDS console.
Serverless RDS instances are available in the China (Hong Kong) and Singapore regions.
You can create a serverless RDS instance that runs SQL Server 2016 SE, SQL Server 2017 SE, or SQL Server 2019 SE on RDS High-availability Edition.
If you use a RAM user to create a serverless RDS instance, the AliyunRDSFullAccess policy must be attached to the RAM user. For more information, see Use RAM for resource authorization.
Service level agreement (SLA) commitments are not applicable to your serverless RDS instance or to the availability and liability of any relevant services. Alibaba Cloud shall not be liable for the adverse impacts of your use of serverless RDS instances and relevant services.
Introduction to serverless instances
RDS for SQL Server serverless instances can automatically scale computing resources based on workload peaks and troughs. This allows them to quickly respond to business changes while optimizing costs and improving efficiency.
The following figure compares the resource utilization and capacity changes between a regular instance and a serverless instance for a fluctuating workload.
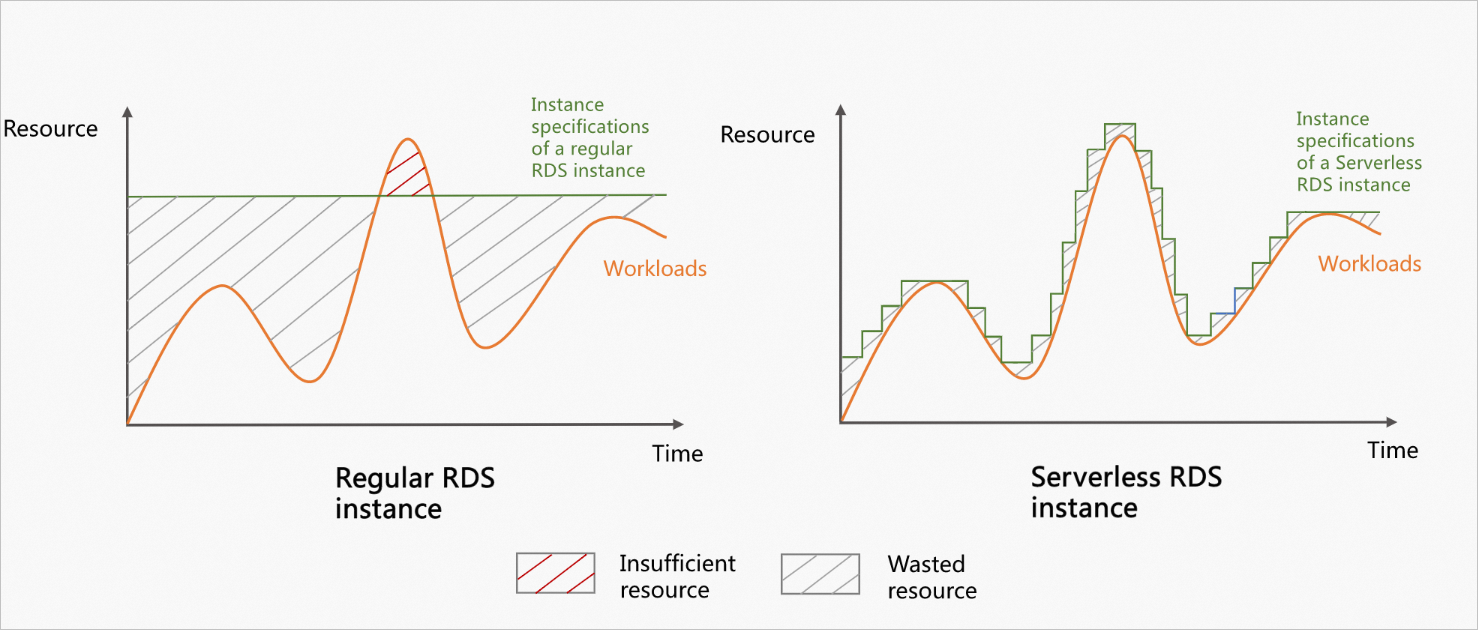
The figure shows the following information about a fluctuating workload:
Regular instance: Wastes resources during off-peak hours and has insufficient resources during peak hours, which affects service performance.
Serverless instance:
Resources are scaled in response to workload changes. This minimizes idle resources, improves resource utilization, and reduces costs.
Resources are scaled to match the workload requirements during peak hours. This ensures that services are not affected and improves system stability.
You are charged based on the actual resources that are used to run your workloads. This is different from the fixed-price payment model and can significantly reduce costs.
No manual configuration changes are required. This improves Operations and Maintenance (O&M) efficiency and the experience for O&M administrators and developers.
The instance is optimized for high-throughput write scenarios and high-concurrency services. It also provides elastic scaling capabilities, which makes it suitable for scenarios that have large data volumes and typical peak and trough access patterns.
Architecture

Benefits of serverless instances
Lower costs: For startups, RDS for SQL Server serverless instances do not require you to manage underlying infrastructure or related services. They are ready to use after creation and provide stable and efficient data access services. You are charged only for the resources that you use.
Automatic elastic scaling of computing resources: The computing resources required for read and write operations can be elastically scaled. You do not need to schedule scale-out or scale-in operations. This greatly reduces O&M costs and system risks.
Fully managed and maintenance-free: All O&M tasks, such as version upgrades, system deployment, scaling, and alert handling, are handled by the Alibaba Cloud professional team. These tasks are transparent to you, do not affect your services, and ensure continuous service availability. This provides a truly maintenance-free experience.
High availability: RDS for SQL Server serverless instances use a high-availability architecture.
Limits
Compared with regular RDS for SQL Server instances, RDS for SQL Server serverless instances do not support changing the time zone or character set, connecting to a self-managed domain, configuring Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), configuring Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption, enabling disk encryption, upgrading the major engine version, or updating the minor engine version.
Serverless instances use the pay-as-you-go billing method. However, because they are sold based on RDS Capacity Units (RCUs), you cannot change the billing method of a serverless instance to subscription.
Serverless instances do not support the creation of read-only instances. You can create a primary instance that uses RDS Cluster Edition and then create read-only instances for the primary instance. For more information, see Create an RDS for SQL Server instance and Overview of read-only RDS for SQL Server instances.
You cannot create database accounts with system administrator (SA) permissions or host accounts on a serverless instance. For more information, see Accounts and permissions.
Billing
For more information, see Serverless billing.
Scenarios
Scenarios with significant workload fluctuations, such as development and testing environments.
Software as a Service (SaaS) scenarios, such as website building for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Educational scenarios, such as teaching and student experiments.
Scenarios with unpredictable workloads, such as Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing.
Users with fluctuating or unpredictable workloads.
Scenarios that involve intermittent scheduled tasks.
Individual developers.
Usage
You can create a serverless instance. For more information, see Create an RDS for SQL Server serverless instance.
You can manually adjust the scaling range of RDS Capacity Units (RCUs) as needed. The serverless instance automatically scales RCUs up or down within the specified range based on the actual workload. For more information, see Change the scaling range of RCUs.
If the current storage capacity of your serverless instance no longer meets your business requirements, you can manually expand the storage capacity. For more information, see Expand storage capacity.