The Binlog in Redo feature synchronously writes binary log content to the redo log when a transaction is committed. This reduces the number of synchronous I/O operations to disks and improves database performance.
Prerequisites
The major engine version of the instance is MySQL 8.0.
The minor engine version of the instance is 20200430 or later.
To upgrade the minor engine version, see Upgrade the minor engine version.
The
sync_binlogparameter is set to1and thebinlog_order_commitsparameter is set toOFF. For more information, see Configure parameters.The data replication mode of the instance is set to asynchronous replication. For more information, see Query and modify the data replication mode.
Background information
In critical MySQL business scenarios, to ensure data security, both binary logs and redo logs must be synchronously written to disk when a transaction is committed. This requires the following two parameters to be set to 1:
sync_binlog = 1;
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 1;In native MySQL, each transaction commit requires two synchronous I/O operations (one for binary log persistence and one for redo log persistence), which affects transaction commit efficiency. When using disk storage, the impact of synchronous I/O becomes more significant.
To improve transaction commit efficiency, AliSQL introduced the Binlog in Redo feature (enabled by setting the parameter persist_binlog_to_redo=ON, disabled by default). When a transaction is committed, this feature combines binary log content with the redo log in a single write operation, requiring only one synchronous I/O operation to persist both the redo log and binary log data. This design reduces the two I/O operations needed in native MySQL for separately persisting binary logs and redo logs, significantly reducing database response latency and improving throughput.
Additionally, for high concurrency scenarios where GTID allocation and release cause lock contention, Binlog in Redo implements batch processing optimization through group commit mechanisms to reduce lock conflicts, further ensuring high concurrency performance.
Binary log file writing is performed asynchronously by a backend thread, which periodically appends data to the file in batches, avoiding the file system pressure caused by real-time fsync operations and improving overall I/O efficiency. Even if the database restarts abnormally, the system can automatically repair binary log file integrity by replaying binary log data from the redo log, ensuring data consistency.
The Binlog in Redo feature does not change the format of binary logs. Replication and third-party tools that require binary logs are not affected.
Considerations
After enabling the Binlog in Redo feature, if you need to restore a high-performance local disk instance to a self-managed database using physical backup files, you must use the XtraBackup tool provided by RDS. For information about how to install the XtraBackup tool, see Prepare the tools.
Parameters
persist_binlog_to_redo
This parameter specifies whether to enable the Binlog in Redo feature. This parameter is a global system variable. Valid values: on and off. If you change the value of this parameter, the change immediately takes effect. You do not need to restart your RDS instance.
NoteTo enable this feature, you must set
persist_binlog_to_redotoon, setbinlog_order_commitstooff, and configure the data replication mode of the instance to asynchronous replication.For information about how to configure parameters, see Configure parameters.
For information about how to configure the data replication mode, see Query and modify the data replication mode.
If the
sync_binlogparameter of your instance is not set to 1, configuring the preceding parameters does not enable the Binlog in Redo feature. We recommend that you use the Binlog Parallel Flush feature to optimize instance performance.sync_binlog_interval
The interval at which binary logs are asynchronously stored. This parameter is a global system variable and takes effect when
persist_binlog_to_redo = on. Default value: 50. Unit: milliseconds (ms). In most cases, the default value is recommended. If you change the value of this parameter, the change immediately takes effect. You do not need to restart your RDS instance.
Stress testing
Test environment
Application server: an Alibaba Cloud Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance
RDS instance type: 32 cores, 128 GB memory, ESSD disk
RDS edition: RDS High-availability Edition with asynchronous data replication
Test case
Sysbench provides the following test cases:
oltp_update_non_index
oltp_write_only
Test results
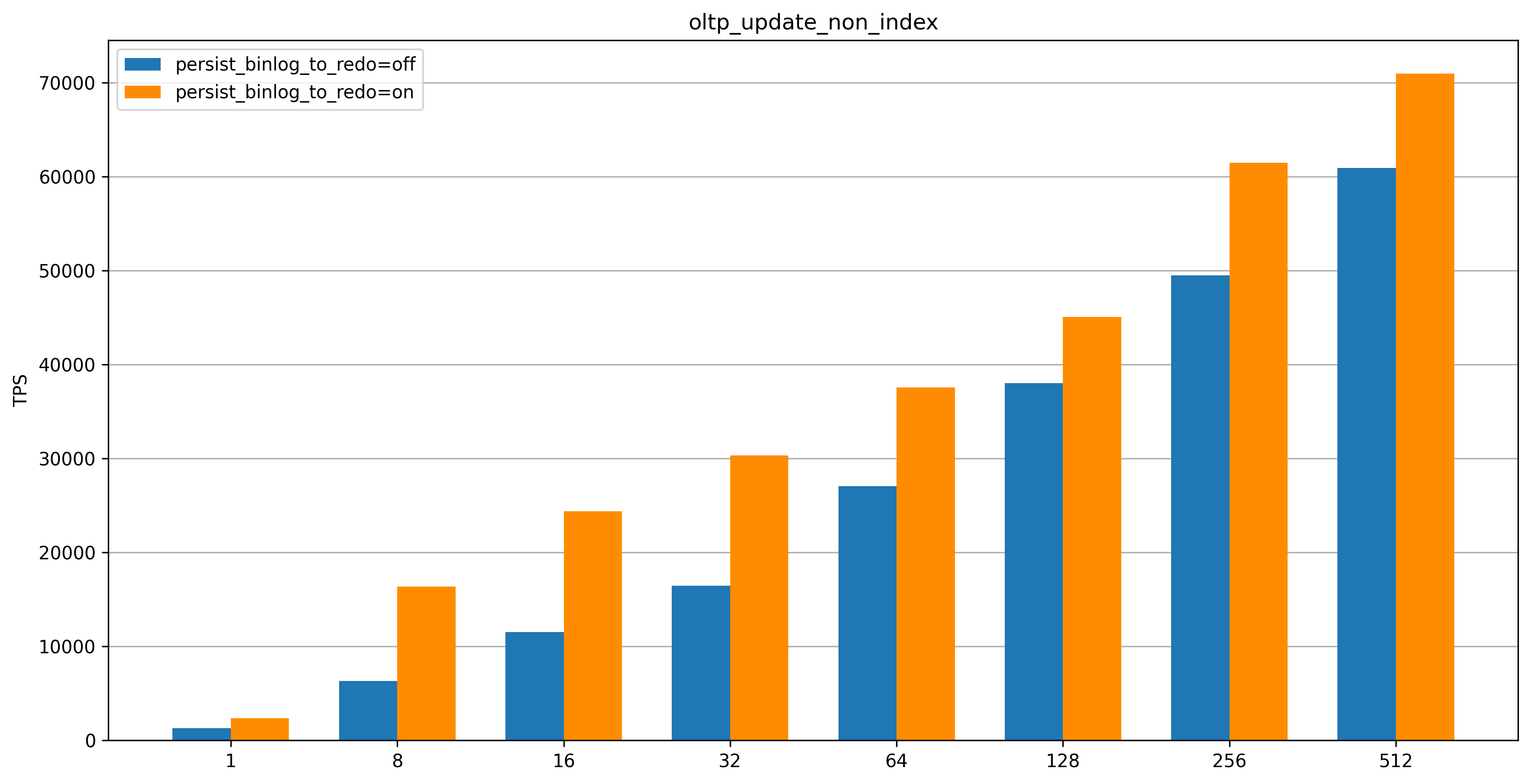
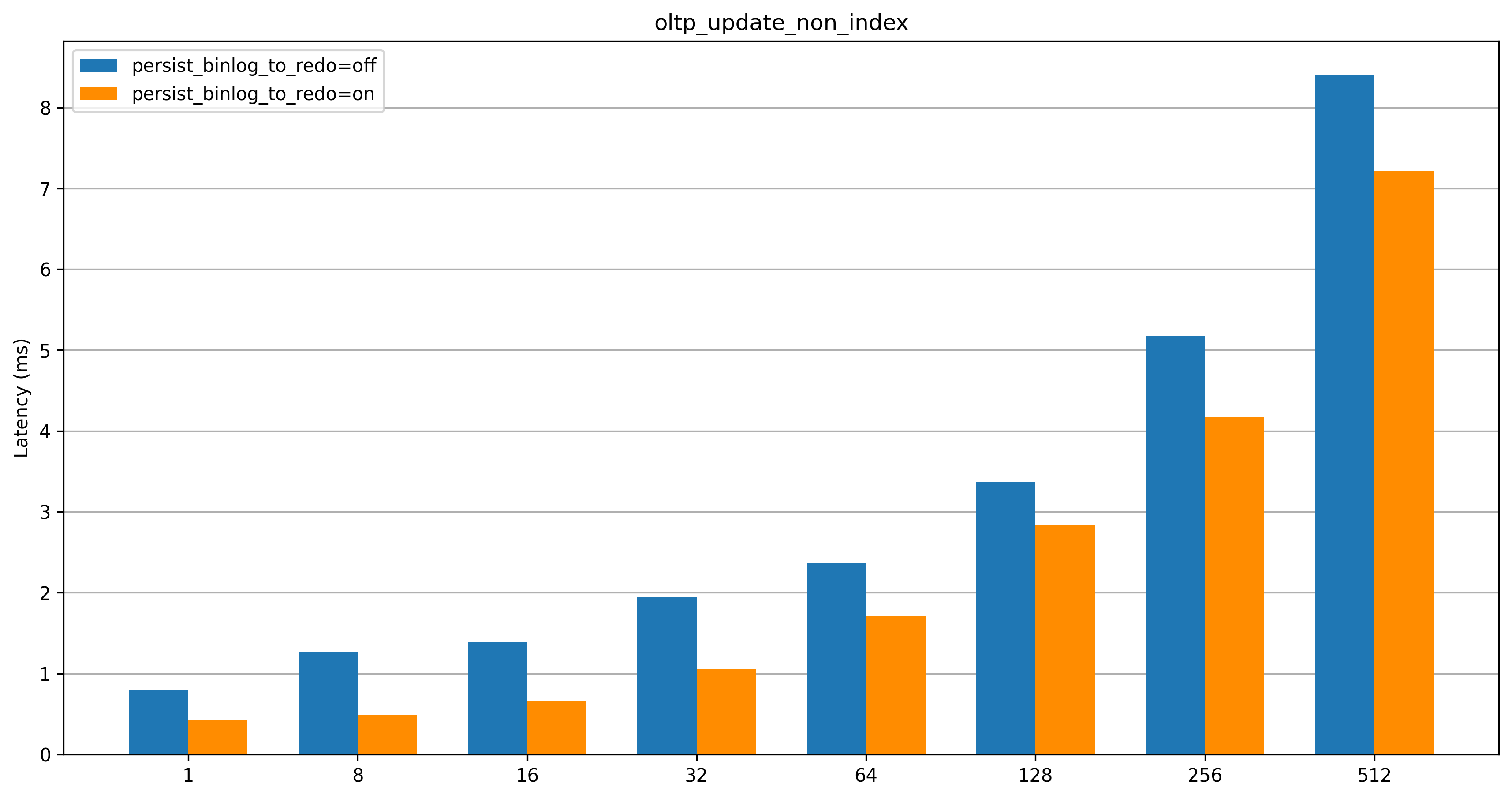
oltp_update_non_index
After the Binlog in Redo feature is enabled, the TPS significantly improves in low-concurrency scenarios and noticeably improves in high-concurrency scenarios, with lower latency.
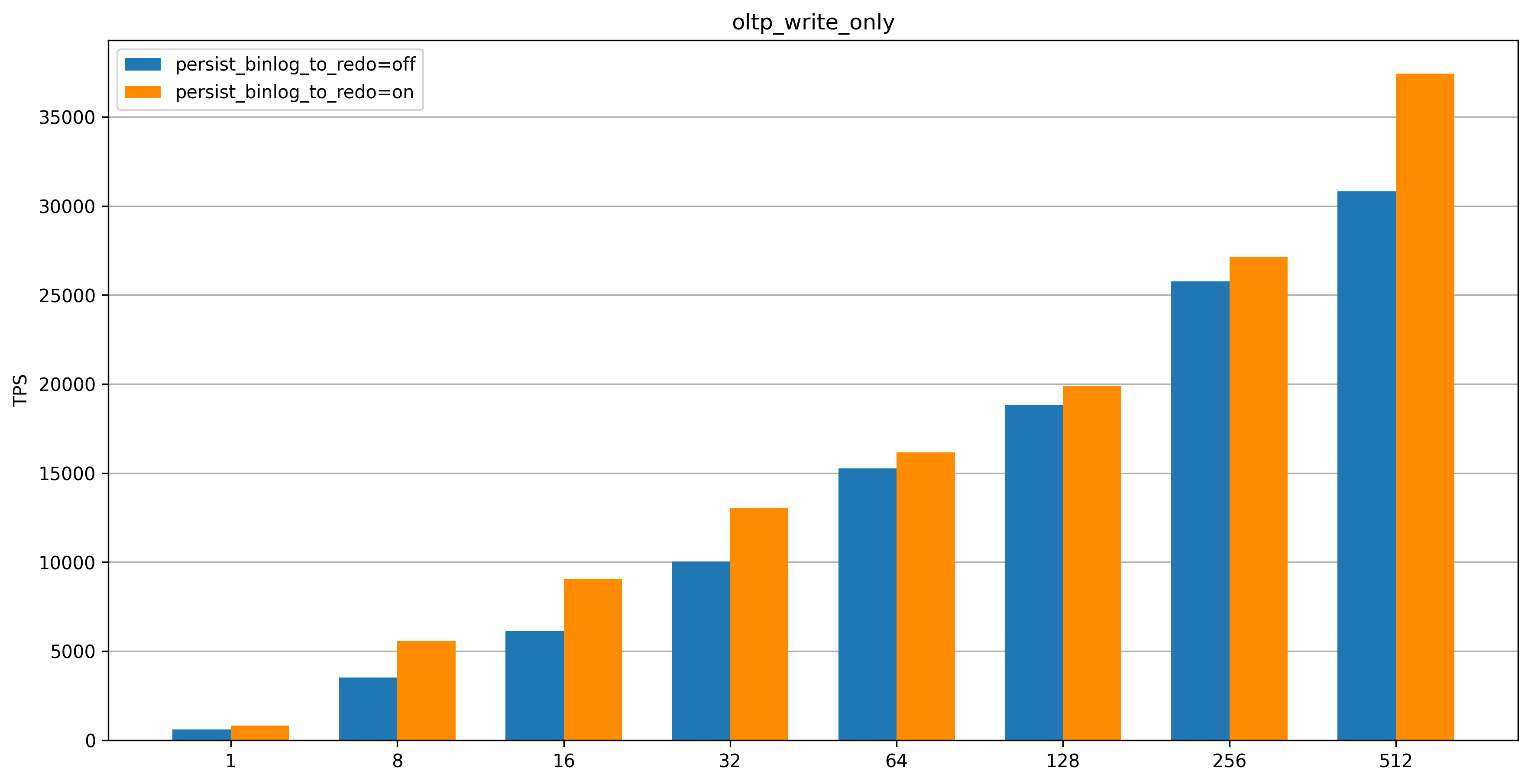
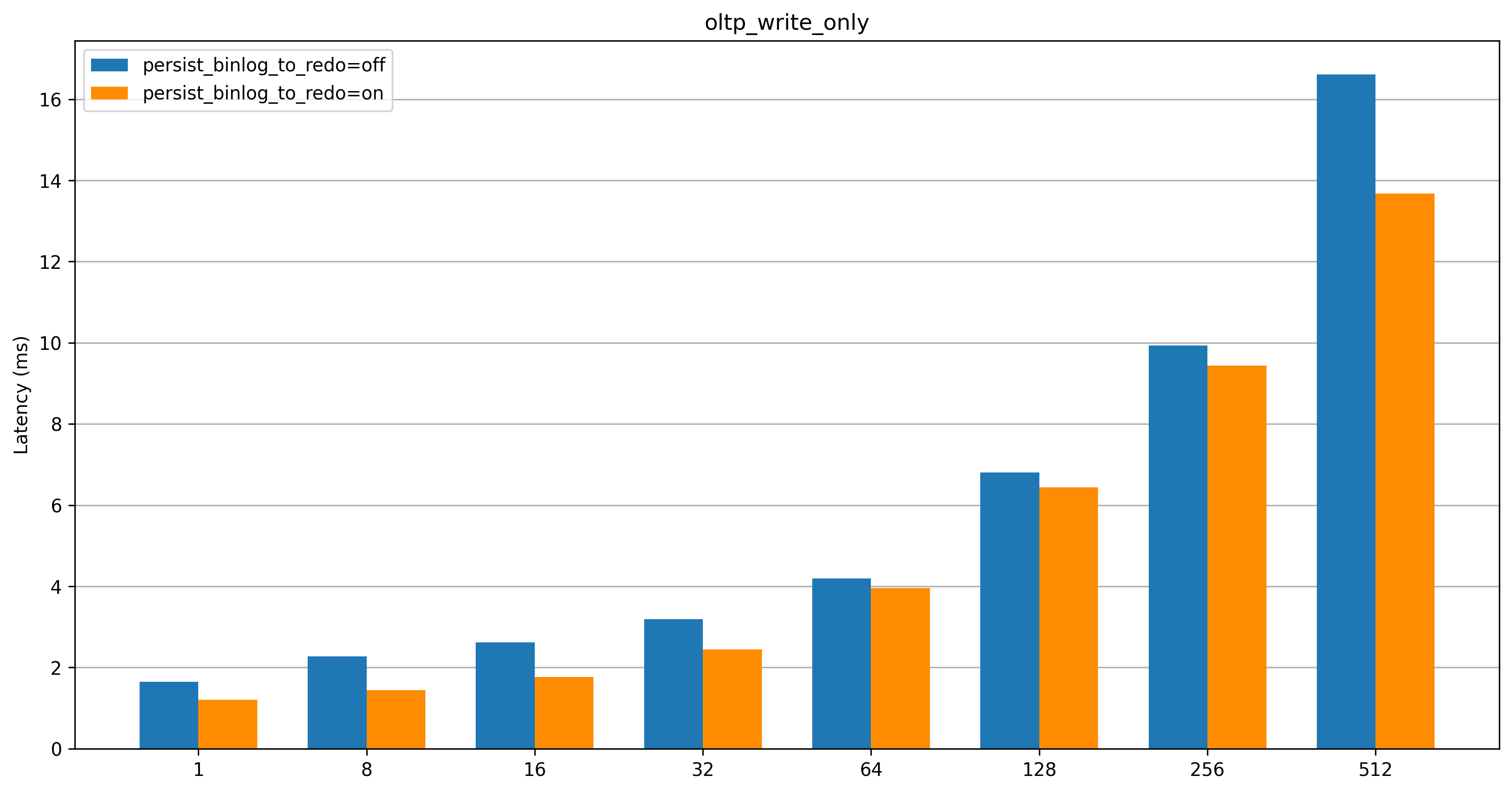
oltp_write_only
After the Binlog in Redo feature is enabled, the TPS significantly improves in both low-concurrency and high-concurrency scenarios, with lower latency.
Test conclusion
The oltp_update_non_index test case contains only single-statement transactions with a high number of transaction commits. The oltp_write_only test case contains multi-statement transactions (two UPDATE statements, one DELETE statement, and one INSERT statement) with fewer transaction commits than the oltp_update_non_index test case. Therefore, the performance improvement for the oltp_update_non_index test case is more significant than that for the oltp_write_only test case.
When the number of concurrent connections is less than 64, the Binlog in Redo feature significantly improves performance and reduces latency, which is effective for most practical scenarios.
When the number of concurrent connections is greater than 256, the Binlog in Redo feature provides higher peak performance and lower latency, which better handles traffic spikes.