This topic describes how to perform major compactions.
Background information
The storage engine of ApsaraDB for OceanBase is based on the LSM-tree architecture. Data is divided into static baseline data (stored in SSTables) and dynamic incremental data (stored in MemTables). An SSTable is read-only and stored on the disk. After an SSTable is generated, it is not modified. A MemTable can be read and written and is stored in the memory. Data related to DML operations, such as inserting, updating, and deleting, is first written into the MemTable. After the size of the MemTable reaches the specified threshold, its data is compacted with the baseline data and stored in the SSTable on the disk. For more information, see Overview.
When the size of the MemTable exceeds the specified threshold, the data in this MemTable is transferred to an SSTable to release the memory. This process is called minor compaction. For more information about minor compaction, see Minor compaction.
A minor compaction generates a new SSTable. When the number of minor compactions exceeds the specified threshold or during off-peak hours of a day, the system merges the baseline SSTables and the incremental SSTables generated by minor compactions into one SSTable. This process is called major compaction. For more information about major compaction, see Major compaction.
Applicable scenarios
Scheduled major compaction: You do not need to manually initiate a major compaction. You can set scheduled major compaction tasks to trigger major compactions in off-peak hours.
Manual major compaction: You can manually initiate a major compaction at any time based on your business condition.
NoteA major compaction affects business performance. To ensure stable business operation, we recommend that you perform major compactions during off-peak hours.
Procedure
Log on to the ApsaraDB for OceanBase console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Instances.
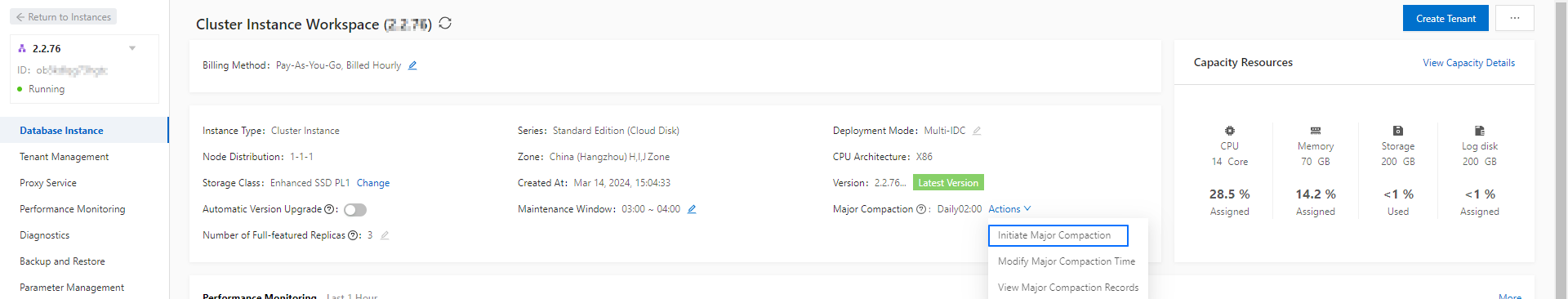
In the instance list, click the name of the target cluster instance to go to the Cluster Instance Workspace page.
On the Cluster Instance Workspace page, click Actions and choose Initiate Major Compaction.
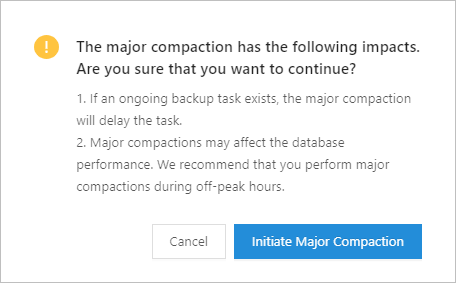
In the dialog box that appears, click Initiate Major Compaction to initiate a major compaction.
NoteIf a backup task is running when you initiate a major compaction, the backup process will be postponed.
A major compaction affects database performance. We recommend that you perform major compactions during off-peak hours.