Cloud-native API Gateway supports full-lifecycle management for Representational State Transfer APIs (REST APIs), from API design, development, and testing to API publishing and unpublishing. The APIs can be operated on through standard HTTP methods and are suitable for scenarios such as API First and fine-grained API control. This topic provides a quick guide through relevant features.
Prerequisites
A Cloud-native API Gateway instance is created. For more information, see Create a Cloud-native API Gateway instance.
API lifecycle management
You can create a REST API by using the console, AI Large Model, or the OpenAPI-based import method.
Create and publish an API in the console
Step 1: Create an API
Log on to the Cloud-native API Gateway console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click API. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
On the API page, click Create API and click Create in the REST API section.
In the Create REST API panel, configure the parameters as prompted.
Parameter
Description
API Name
Specify a custom name for the API that you want to create.
ImportantThe name must be globally unique.
API Protocol
Specify the protocol over which the API is called. Options: HTTP and HTTPS.
Base Path
Specify the basic path of the API. The full path for a specific operation is in the
http(s)://{Domain Name}/{BasePath}/{Operation path}format.Version Management
Specify whether to enable versioning for the API. Different versions of an API are considered as independent APIs that share the same name but different other information. If versioning is enabled, a version tag must be carried in requests to call the API.
After you enable versioning, you must configure versions and usages for APIs.
NoteIf you set Usage to Query, you must configure the Add Query parameter.
If you set Usage to Header, you must configure the Add Header parameter.
Version
Specify an API version if the API that you want to create has multiple versions.
Usage
Specify how you want the API to be called. Valid values: Path, Query, and Header.
If you set the parameter to Path, full access paths are required in API requests. Path format: /API base path/API version/API operation path.
If you set the parameter to Query, you must further configure the Add Query parameter for API callers to add to their requests. Full access path: /API base path/API version/API operation path.
If you set the parameter to Header, you must further configure the Add Header parameter for API callers to add to their requests. Full access path: /API base path/API operation path.
Description
Enter a description for the API.
Step 2: Add an operation
In the API list, click the API that you want to manage. On the API details page, click the API Design tab to add an operation.
If versioning is enabled for the API, you must select a version and then click Add Operation.
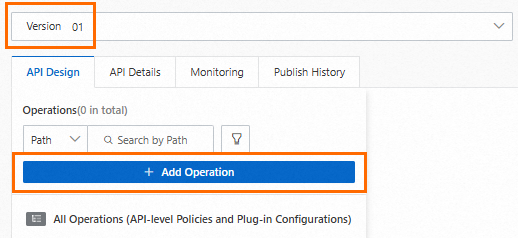
If version management is not enabled for the API, click Add Operation directly.
In the Add Operation panel, configure the parameters and click Add. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Operation Name
Specify a custom name for the operation. The name must be unique within the API.
Operation Path
Specify a path for the operation.
Method
Specify an HTTP method based on which the operation is called. Format: Operation path + Method. The combination must be unique within the API.
Description
Enter a description for the operation.
API Definition
Request Definition
You can define parameters for the Header, Query, Parameter Path, and Body parameters of the API requests.
The following methods are supported for defining variables for Path parameters:
/books/{bookId}
/books/[bookId]
/books/:bookId
The {bookId} method is recommended.
NoteThe request definition is used only to generate SDKs and documents, and is not verified for runtimes.
Response Definition
You can define data structures for different response codes.
The response definition is used only to generate SDKs and documents, and is not verified for runtimes.
Mock
The Mock configuration takes effect only when an API is published with a Mock backend.
Step 3: Publish the API
In the API list, click the API that you want to publish. On the API details page, click Publish API in the upper-right corner.
In the Publish REST API panel, configure the parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Domain Name
Select a domain name to publish the API. The published API can be accessed by using the domain name.
If no domain name is available, click Add Domain Name to create a domain name. For more information, see Create a domain name.
Environment/Gateway/VPC
Select an environment to publish the API. If no environment is available, click Create Environment to create one. For more information, see Manage environments.
ImportantIf the API has been published in this environment before, the published API will be overwritten if you continue to publish it again. Exercise caution when you publish the API.
Scenarios
Select a scenario for which you want to publish the API. Valid values: Mock, Single Service, By Percentage (Multi-service), and By Content (Multi-service).
Mock
In the Mock scenario, mocked responses configured in API operation definitions are returned for requests. If no mocked response is configured, the API operation is inaccessible in this scenario.
If you want to publish an API to the Mock scenario, you must make sure that a mocked response is configured for at least one operation in the API. Otherwise, the API fails to be published.
Single Service
In this scenario, all traffic is directed to a specific backend service.
By Percentage (Multi-service)
Traffic is directed to configured backend services based on configured weights.
NoteThe weights of all services must sum up to 100.
By Content (Multi-service)
Traffic is directed to corresponding backend services based on the match conditions. If you select Default next to Match Condition, traffic is directed to the configured backend service when no other rules are hit.
The following match condition types are supported: equal to, prefix, and regular expression.
Supported parameter types: Query and Header.
The "and" operation logic is used between multiple match conditions.
ImportantYou can select Default for only one entry.
Backend Services
Associate backend services with the environment/gateway/VPC. If no backend service is available, click Create Service to create a service. For more information, see Create a service.
Description
Enter a description for the published API.
Step 4: Debug the API
In the API list, click the API that you want to manage. On the API details page, click the operation that you want to debug and then click Debugging Operation.
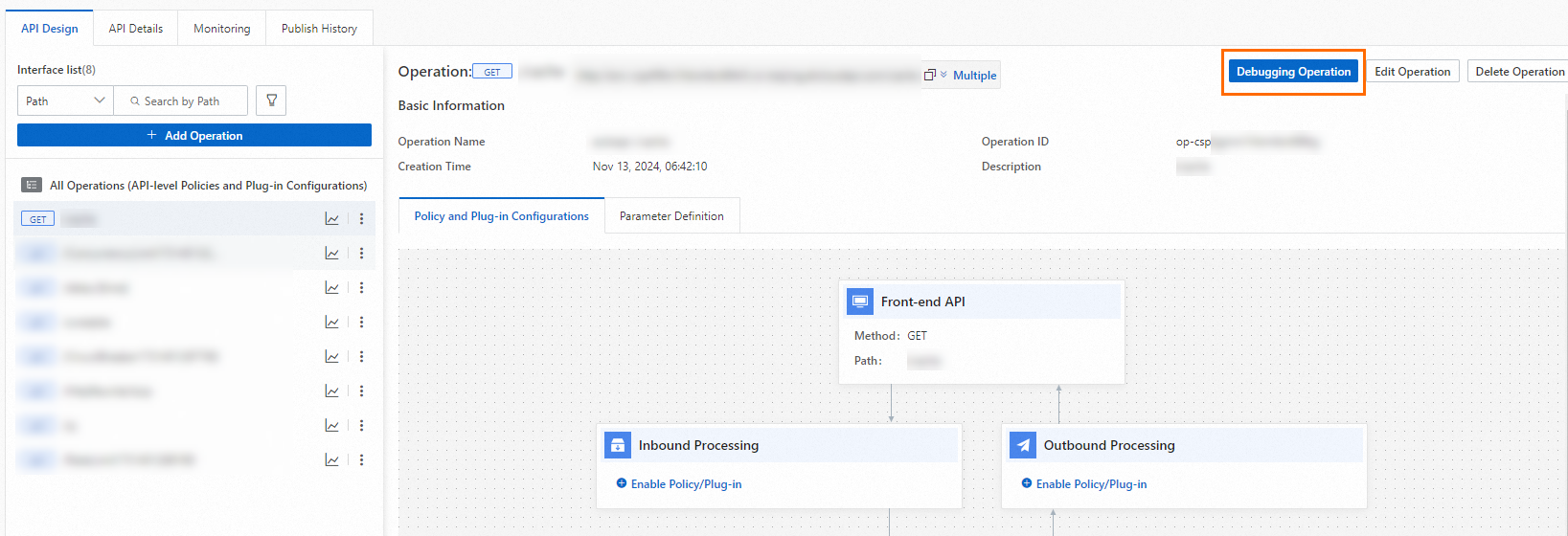
In the Operation to Be Debugged panel, configure the parameters and click Send Request to debug the operation.
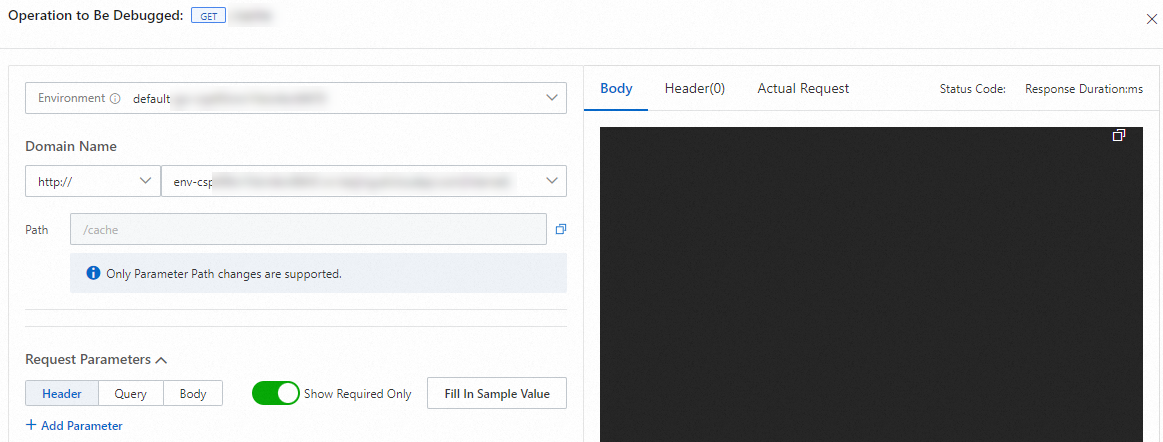
Step 5: Use a domain name to access the API
On the API page, click the API that you want to manage. On the page that appears, click the API Details tab.
On the API Details tab, you can view the publish information of the API.
In the Release Information section, you can see two domain name types:
Second-level domain name: a public domain name that is automatically generated by the system and can be used to directly access the API. This domain name is provided for debugging the API and can be used to make a maximum of 100 calls per day.
Custom domain name: a custom domain name that you configure when you publish the API. You must map the CNAME of the custom domain name to the public second-level domain name to access the API. This domain name is exempted from the 100-calls-per-day limit.
The ultimate accessible path is http(s)://{domain name}/{BasePath}/API operation path.
Step 6: Unpublish the API
In the API list, click the API that you want to manage. On the API details page, click the API Details tab.
In the Release Information section, find the release record that you want to manage and click Unpublish in the Actions column.
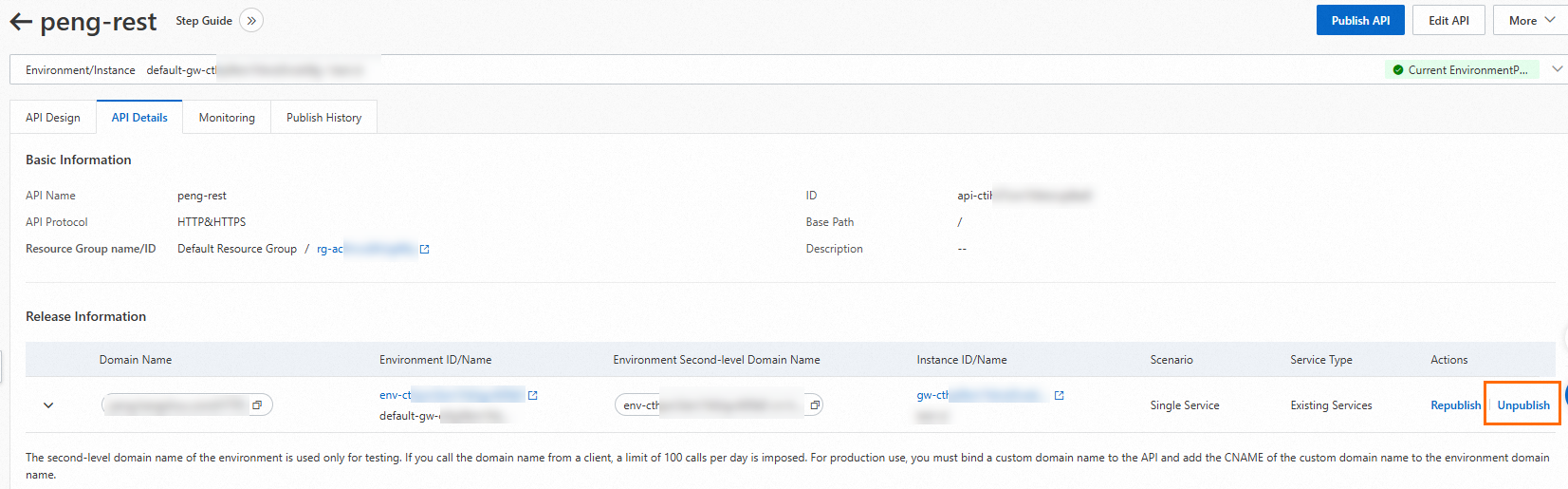
In the dialog box that appears, click Unpublish.
ImportantAfter the API is unpublished, you can no longer access the operations in the API by using an associated domain name. Exercise caution when you unpublish an API.
Create and publish an API by using an OpenAPI file
Step 1: Create an API
Log on to the Cloud-native API Gateway console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click API. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
On the API page, click Create API and click Import in the REST API section.
In the Create File based on OpenAPI panel, set the API parameters and click Precheck and Create.
Parameter
Description
API Name
Specify a custom name for the API that you want to create. The API name must be globally unique.
Upload Method
Specify a method to import the API. Valid values: Local File and Import OSS File.
OpenAPI File
Drag a file to the displayed box or click View Local File to select a local file. The file cannot exceed 30 MB in size.
Version Management
Specify whether to enable versioning for the API. Different versions of an API are considered as independent APIs that share the same name but different other information. If versioning is enabled, a version tag must be carried in requests to call the API.
After you enable versioning, you must configure versions and usages for APIs.
NoteIf you set Usage to Query, you must configure the Add Query parameter.
If you set Usage to Header, you must configure the Add Header parameter.
Version
Specify an API version if the API that you want to create has multiple versions.
Usage
Specify how you want the API to be called. Valid values: Path, Query, and Header.
If you set the parameter to Path, full access paths are required in API requests. Path format: /API base path/API version/API operation path.
If you set the parameter to Query, you must further configure the Add Query parameter for API callers to add to their requests. Full access path: /API base path/API version/API operation path.
If you set the parameter to Header, you must further configure the Add Header parameter for API callers to add to their requests. Full access path: /API base path/API operation path.
Description
Enter a description for the API.
After the API is created, you can view the operations defined in the OpenAPI file in the operations list.
Step 2: Publish the API
In the API list, click the API that you want to publish. On the API details page, click Publish API in the upper-right corner.
In the Publish REST API panel, configure the parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Domain Name
Select a domain name to publish the API. The published API can be accessed by using the domain name.
If no domain name is available, click Add Domain Name to create a domain name. For more information, see Create a domain name.
Environment/Gateway/VPC
Select an environment to publish the API. If no environment is available, click Create Environment to create one. For more information, see Manage environments.
ImportantIf the API has been published in this environment before, the published API will be overwritten if you continue to publish it again. Exercise caution when you publish the API.
Scenarios
Select a scenario for which you want to publish the API. Valid values: Mock, Single Service, By Percentage (Multi-service), and By Content (Multi-service).
Mock
In the Mock scenario, mocked responses configured in API operation definitions are returned for requests. If no mocked response is configured, the API operation is inaccessible in this scenario.
If you want to publish an API to the Mock scenario, you must make sure that a mocked response is configured for at least one operation in the API. Otherwise, the API fails to be published.
Single Service
In this scenario, all traffic is directed to a specific backend service.
By Percentage (Multi-service)
Traffic is directed to configured backend services based on configured weights.
NoteThe weights of all services must sum up to 100.
By Content (Multi-service)
Traffic is directed to corresponding backend services based on the match conditions. If you select Default next to Match Condition, traffic is directed to the configured backend service when no other rules are hit.
The following match condition types are supported: equal to, prefix, and regular expression.
Supported parameter types: Query and Header.
The "and" operation logic is used between multiple match conditions.
ImportantYou can select Default for only one entry.
Backend Services
Associate backend services with the environment/gateway/VPC. If no backend service is available, click Create Service to create a service. For more information, see Create a service.
Description
Enter a description for the published API.
Step 3: Debug the API
In the API list, click the API that you want to manage. On the API details page, click the operation that you want to debug and then click Debugging Operation.

In the Operation to Be Debugged panel, configure the parameters and click Send Request to debug the operation.

Step 4: Use a domain name to access the API
On the API page, click the API that you want to manage. On the page that appears, click the API Details tab.
On the API Details tab, you can view the publish information of the API.
In the Release Information section, you can see two domain name types:
Second-level domain name: a public domain name that is automatically generated by the system and can be used to directly access the API. This domain name is provided for debugging the API and can be used to make a maximum of 100 calls per day.
Custom domain name: a custom domain name that you configure when you publish the API. You must map the CNAME of the custom domain name to the public second-level domain name to access the API. This domain name is exempted from the 100-calls-per-day limit.
The ultimate accessible path is http(s)://{domain name}/{BasePath}/API operation path.
Step 5: Unpublish the API
In the API list, click the API that you want to manage. On the API details page, click the API Details tab.

In the Release Information section, find the release record that you want to manage and click Unpublish in the Actions column.

In the dialog box that appears, click Unpublish.
ImportantAfter the API is unpublished, you can no longer access the operations in the API by using an associated domain name. Exercise caution when you unpublish an API.
Create and publish an API based on the AI Large Model
Step 1: Create an API
Log on to the Cloud-native API Gateway console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click API. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
On the API page, click Create API and click Create Based on AI Large Model in the REST API section.
In the Create Based on AI Big Model panel, set the parameters as prompted and click Generate a Swagger Example. An API and operations are automatically generated.
Parameter
Description
API Name
Specify a custom name for the API that you want to create.
ImportantThe name must be globally unique.
Scenario
Describe the scenario in which the API is used.
Resources and Operations
Create data objects. You can create up to five data objects.
Name
Enter a name for the data object. Example: book.
Attributes
Enter attributes, such as book title and author, contained in the data object. You can directly paste the definition text or code related to the data model
Add/Delete/Modify/Query
Enter a description about the addition operation. Example: Add xxx by ID or name.
Enter a description about the deletion operation. Example: Delete xxx by ID.
Enter a description about the modification operation. Example: Modify the xxx name.
Enter a description about the query operation. Example: Query xxx by ID.
Others
Enter additional information about your API.
After the large model completes generating the API and operations, click Precheck and Create. In the dialog box that appears, check whether the API and operations generated by the large model are correct.
Click Create API.
Step 2: Publish the API
In the API list, click the API that you want to publish. On the API details page, click Publish API in the upper-right corner.
In the Publish REST API panel, configure the parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Domain Name
Select a domain name to publish the API. The published API can be accessed by using the domain name.
If no domain name is available, click Add Domain Name to create a domain name. For more information, see Create a domain name.
Environment/Gateway/VPC
Select an environment to publish the API. If no environment is available, click Create Environment to create one. For more information, see Manage environments.
ImportantIf the API has been published in this environment before, the published API will be overwritten if you continue to publish it again. Exercise caution when you publish the API.
Scenarios
Select a scenario for which you want to publish the API. Valid values: Mock, Single Service, By Percentage (Multi-service), and By Content (Multi-service).
Mock
In the Mock scenario, mocked responses configured in API operation definitions are returned for requests. If no mocked response is configured, the API operation is inaccessible in this scenario.
If you want to publish an API to the Mock scenario, you must make sure that a mocked response is configured for at least one operation in the API. Otherwise, the API fails to be published.
Single Service
In this scenario, all traffic is directed to a specific backend service.
By Percentage (Multi-service)
Traffic is directed to configured backend services based on configured weights.
NoteThe weights of all services must sum up to 100.
By Content (Multi-service)
Traffic is directed to corresponding backend services based on the match conditions. If you select Default next to Match Condition, traffic is directed to the configured backend service when no other rules are hit.
The following match condition types are supported: equal to, prefix, and regular expression.
Supported parameter types: Query and Header.
The "and" operation logic is used between multiple match conditions.
ImportantYou can select Default for only one entry.
Backend Services
Associate backend services with the environment/gateway/VPC. If no backend service is available, click Create Service to create a service. For more information, see Create a service.
Description
Enter a description for the published API.
Step 3: Debug the API
In the API list, click the API that you want to manage. On the API details page, click the operation that you want to debug and then click Debugging Operation.

In the Operation to Be Debugged panel, configure the parameters and click Send Request to debug the operation.

Step 4: Use a domain name to access the API
On the API page, click the API that you want to manage. On the page that appears, click the API Details tab.
On the API Details tab, you can view the publish information of the API.
In the Release Information section, you can see two domain name types:
Second-level domain name: a public domain name that is automatically generated by the system and can be used to directly access the API. This domain name is provided for debugging the API and can be used to make a maximum of 100 calls per day.
Custom domain name: a custom domain name that you configure when you publish the API. You must map the CNAME of the custom domain name to the public second-level domain name to access the API. This domain name is exempted from the 100-calls-per-day limit.
The ultimate accessible path is http(s)://{domain name}/{BasePath}/API operation path.
Step 5: Unpublish the API
In the API list, click the API that you want to manage. On the API details page, click the API Details tab.

In the Release Information section, find the release record that you want to manage and click Unpublish in the Actions column.

In the dialog box that appears, click Unpublish.
ImportantAfter the API is unpublished, you can no longer access the operations in the API by using an associated domain name. Exercise caution when you unpublish an API.