This topic describes how to build an AI customer service system using Dify, Supabase in AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, and a large language model (LLM). This system helps an online clothing store efficiently handle after-sales inquiries, order lookups, and personalized responses. By combining Dify's workflow capabilities, Supabase's real-time data storage, and the LLM's natural language understanding, you can deliver fast, automated responses. This significantly reduces the workload for human agents and improves customer satisfaction.
Background
Supabase in AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL provides powerful database features and real-time data processing capabilities, and is highly compatible with PostgreSQL vector databases. Dify is an open-source development platform for LLM applications that supports the rapid creation of intelligent applications based on the retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) architecture. By integrating Supabase in AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL with Dify, you can easily build an efficient AI customer service system. This system provides users with real-time and accurate service.
This topic uses an online clothing store as an example to show how to build an AI customer service system. The system can handle after-sales inquiries, retrieve order information, and generate personalized responses. This reduces the workload for human agents and improves response speed and customer satisfaction. The main advantages are as follows:
Data-driven, accurate responses: The AI generates responses based on real, structured order and logistics data in Supabase, ensuring that information is accurate.
AI understanding: The AI not only reads data but also analyzes customer intent and sentiment to proactively reassure customers.
Efficient automated processing: Traditional customer service requires agents to manually check systems and type responses. The combination of Dify and Supabase provides automated responses in seconds. This frees up human agents to handle more complex scenarios.
Prerequisites
You have created a Supabase project.
This topic uses Qwen as an example. Obtain an API key to authenticate calls to the LLM.
Procedure
Step 1: Deploy Dify
You can host Dify in the cloud or deploy it locally. This topic describes how to deploy Dify locally.
Run the following commands to deploy Dify.
git clone https://github.com/langgenius/dify.git cd dify/docker cp .env.example .env docker compose up -dGo to
http://<IP_address>/installto register an account and log on. The IP address is that of the server where Dify is running.
Step 2: Connect to the large model
Hover over your profile picture in the upper-right corner and click Settings.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Model Provider. Select and install a model provider. This example uses Qwen.
After the installation is complete, find the model in the list. Click Config, enter the API key, and save your settings.
Step 3: Configure Supabase
In the Dify interface, install the Supabase plugin to use it as external storage or as part of the vector storage.
In the upper-right corner, click Plugins. Then, on the left, click Explore Marketplace.
Search for Supabase and follow the prompts to complete the installation.
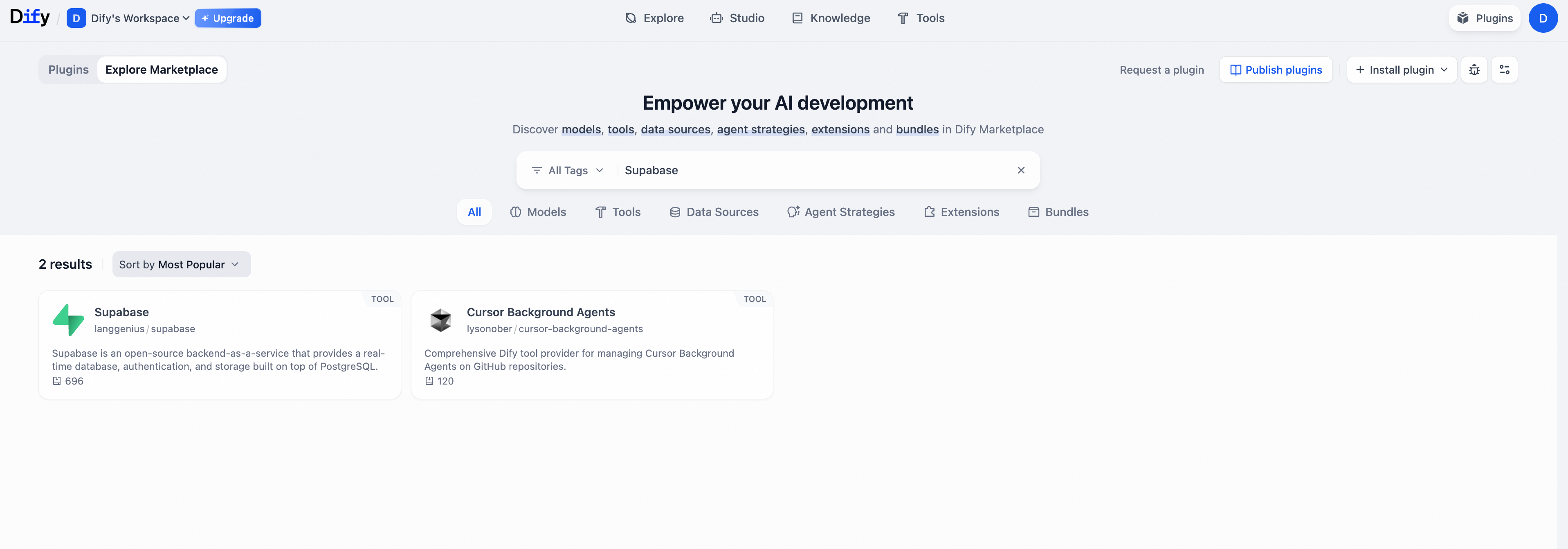
Grant Dify permissions to operate on the Supabase project.
Obtain the URL and service role key for your Supabase project. For more information, see Get API Keys.
In the Plugins list, find the installed Supabase plugin. Click the card and select API Key Authorization Configuration.
In the dialog box that appears, configure the authorization information and save your settings.
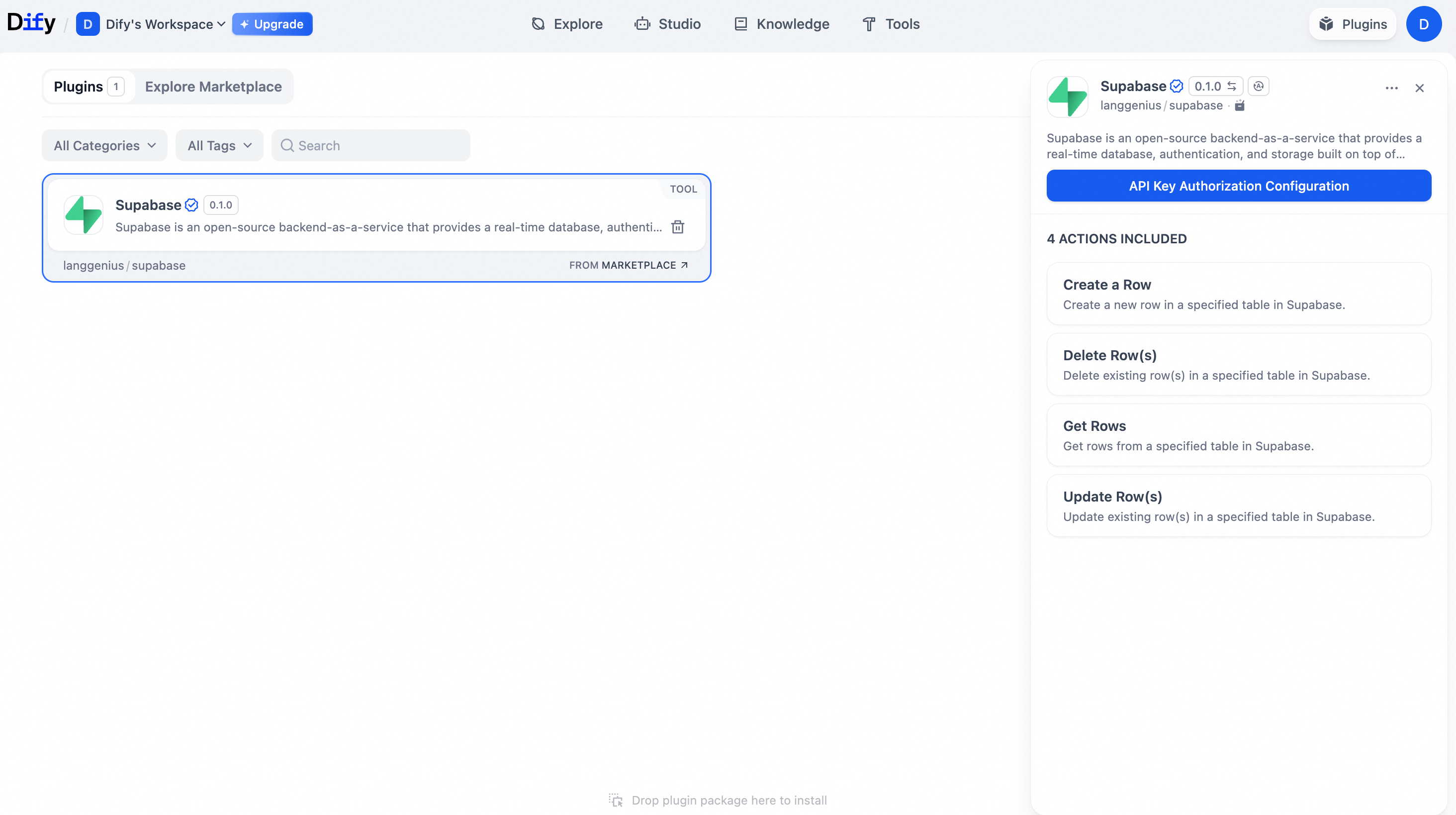
Step 4: Prepare Supabase test data
Create an orders table and insert test data.
In the Supabase Dashboard, click SQL Editor in the navigation pane on the left. Copy the following SQL statement and click Run to quickly insert the test data.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS orders (
order_id TEXT PRIMARY KEY, -- Order ID
customer_name TEXT NOT NULL, -- Customer name
product_name TEXT NOT NULL, -- Product name
product_size TEXT NOT NULL, -- Product size
current_status TEXT NOT NULL, -- Logistics status
last_updated TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE NOT NULL, -- Last update time
estimated_delivery DATE -- Estimated delivery date
);
INSERT INTO orders (
order_id,
customer_name,
product_name,
product_size,
current_status,
last_updated,
estimated_delivery
) VALUES (
'ORD12345',
'Zhang***',
'French retro blue dress',
'M',
'Arrived at [Hangzhou] distribution center, waiting for dispatch to [Ningbo]',
'2025-08-16 14:20:00+08',
'2025-08-20'
);Step 5: Create an E-commerce customer service workflow
In the Dify interface, click Studio > Chatflow at the top, and then create an application.
Configure the nodes as follows. For more information about node configuration, see workflow.
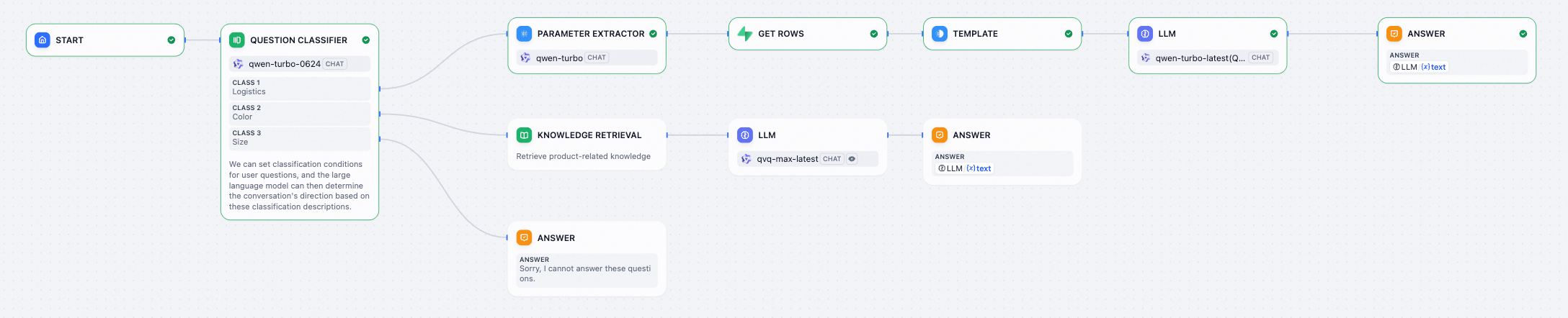
In this example, the question classifier is configured with three categories: Logistics, Color, and Size. You can add more categories as needed. The classifier identifies logistics status inquiries and extracts the specific order number. The nodes in the Logistics category flow are configured as follows:
Node
Configuration
Parameter Extractor
INPUT VARIABLE: sys.query.
EXTRACT PARAMETERS:
Name: order_id.
Type: String.
Description: The customer's order number. It must be an alphanumeric combination starting with "ORD", such as ORD12345 or ORD67890. Extract only strings that match this format.
Required: Yes.
GET ROWS
Configure this node for the AI assistant to send an API request to Supabase to query the logistics status.
When adding the node, select Tools > Supabase > Get Rows.
On the right side of the node configuration, select the configured API Keys.
INPUT VARIABLE:
Table Name: orders
Limit: 100
Filter: order_id
Template
Set INPUT VARIABLE. For the variable value, select json under Get Rows.
LLM
The AI assistant combines the queried logistics information with the customer's sentiment and generates a response based on the prompt.
CONTEXT: Select output under Template.
SYSTEM: Copy the following prompt to SYSTEM, and type "/" within the <context></context> XML tags to insert the context.
Use the following context, placed within the <context></context> XML tags, as your learned knowledge. <context> <Type "/" here to insert the context> </context> When answering the user: If you don't know the answer, say that you don't know. If you are unsure, ask for clarification. Avoid mentioning that you are getting information from the context. Answer in the same language as the user's question.
Answer
Set Answer to text under LLM.
Test example
User question
Hello, my order is #ORD12345 for that dress. The logistics haven't been updated, and I need to wear it soon. When will it arrive? Could it be lost?AI response
Hello, regarding your order #ORD12345, the current logistics status shows that the item has arrived at the Hangzhou distribution center and is expected to be delivered to Ningbo within 2 days. Please rest assured that the item has a complete tracking system during transit and will not be lost. We recommend that you continue to monitor the logistics information. We will notify you immediately if there are any issues.