Nova is the new-generation vector search engine for AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL V7.0. It provides excellent query performance and high cost-effectiveness. It has two modes: disk-based (Novad) and memory-optimized (Novam). The Novad mode is cost-effective, while the Novam mode is for high-performance scenarios. This topic describes how to select and create a Nova index.
Advantages
Compared to traditional Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) indexes, Nova indexes have the following core advantages:
Improved query performance: Faster vector queries.
Optimized memory efficiency: The Novad disk-based index reduces memory usage and is more cost-effective.
Increased write throughput: Decoupling data writes from the index building process improves the write efficiency for vector data.
Prerequisites
An AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL V7.0 instance with minor engine version 7.4.2.0 or later is required. To use this feature, you must contact technical support to upgrade your instance.
Capacity assessment and index selection
Nova indexes have two modes: disk-based (Novad) and memory-optimized (Novam).
Disk-based (Novad): This mode uses a hybrid graph and partition index. HNSW resides in memory, and the Inverted File (IVF) index is stored on disk. This design is disk I/O-friendly and ensures stable performance when the index size significantly exceeds the available memory. The Novad mode is less dependent on memory, provides much better index building performance, and uses far less disk space than the Novam mode. This mode is ideal for large-scale, low-cost retrieval scenarios. It offers significant cost advantages for data volumes in the tens or hundreds of billions.
Memory-optimized (Novam): This mode uses a graph index. Its performance improves as more memory is allocated. It automatically accesses the disk when memory is insufficient. With sufficient memory, the Novam mode provides better query performance than the Novad mode on an instance with the same specifications. This mode is ideal for high-performance scenarios, such as real-time recommendations.
The Nova index runs regular optimization tasks in the background. These tasks may consume resources even when there are no active workloads.
The following tables provide recommended resource specifications for different vector dimensions and numbers of vectors. These recommendations are for reference only. You may need to add more resources to support larger data volumes.
Novad
Vector dimensions | Number of vectors | Recommended total compute resources |
128 | < 320 M | 8 cores |
256 | < 160 M | |
512 | < 80 M | |
768 | < 50 M | |
1024 | < 40 M | |
1536 | < 26 M | |
2048 | < 20 M | |
128 | < 640 M | 16 cores |
256 | < 320 M | |
512 | < 160 M | |
768 | < 100 M | |
1024 | < 80 M | |
1536 | < 60 M | |
2048 | < 40 MB | |
128 | < 1.28 B | 32 cores |
256 | < 640 M | |
512 | < 320 M | |
768 | < 200 M | |
1024 | < 160 M | |
1536 | < 120 M | |
2048 | < 80 M | |
128 | < 5.12 B | 128 cores |
256 | < 2.56 B | |
512 | < 1.28 B | |
768 | < 800 M | |
1024 | < 640 M | |
1536 | < 480 M | |
2048 | < 320 M | |
128 | <200B | 4096 cores |
256 | < 100 B | |
512 | < 50 B | |
768 | Less than 33 B | |
1024 | <25 B | |
1536 | < 16 B | |
2048 | Less than 12 B | |
128 | < 1.6 T | 32768 c |
256 | < 800 B | |
512 | < 400 B | |
768 | < 260 B | |
1024 | <200B | |
1536 | < 130 B | |
2048 | < 100 B |
Novam
Vector dimensions | Number of vectors | Recommended total compute resources |
128 | < 32 M | 8 cores |
256 | < 16 M | |
512 | Less than 8 MB | |
768 | < 5 M | |
1024 | <4 MB | |
1536 | < 2.6 M | |
2048 | < 2 MB | |
128 | < 64 M | 16 cores |
256 | <32 MB | |
512 | < 16 M | |
768 | < 10 M | |
1024 | <8 MB | |
1536 | < 5 M | |
2048 | < 4 MB | |
128 | < 128 M | 32 cores |
256 | < 64 M | |
512 | < 32 M | |
768 | < 20 M | |
1024 | < 16 M | |
1536 | < 10 M | |
2048 | < 8 MB |
Syntax
CREATE INDEX [INDEX_NAME]
ON [SCHEMA_NAME].[TABLE_NAME]
USING ANN(COLUMN_NAME)
WITH (DIM=<DIMENSION>,
ALGORITHM=<ALGORITHM>,
DISTANCEMEASURE=<MEASURE>,
...);Parameters:
INDEX_NAME: The name of the index.
SCHEMA_NAME: The name of the schema (namespace).
TABLE_NAME: The name of the table.
COLUMN_NAME: The name of the vector index column.
Other vector index parameters:
Parameter
Description
Default value
Valid values
dim
The vector dimensions.
None (Required)
[1, 8192]
algorithm
The index algorithm:
novam: A graph index without quantization compression.
novad: A partitioned index with rabitq quantization.
hnswflat: An HNSW index without quantization compression.
hnswflat
(novam, novad, hnswflat)
distancemeasure
The supported similarity distance measure algorithms:
L2: Builds an index using the squared Euclidean distance function. This is typically used for image similarity retrieval scenarios. Formula:
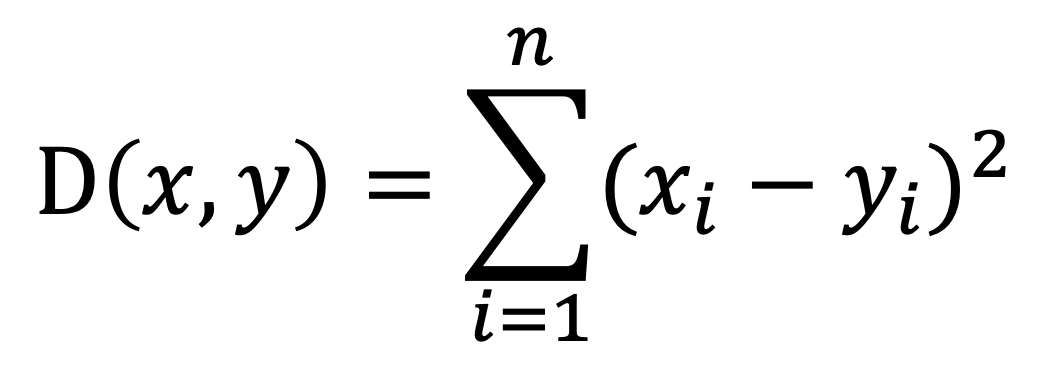
IP: Builds an index using the inverse inner product distance function. This is typically used as a substitute for cosine similarity after vector normalization. Formula:
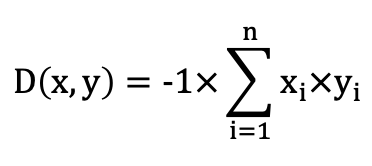
COSINE: Builds an index using the cosine distance function. This is typically used for text similarity retrieval scenarios. Formula:
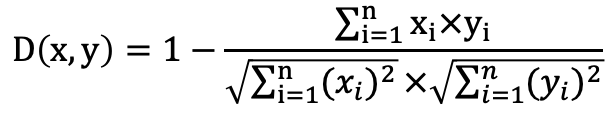
l2
(L2, IP, COSINE)
max_delta_vecs
The maximum number of vectors in a write batch.
1048576
[1024, 1073741824]
hnsw_m
The number of neighbors in Novam. A larger value generally results in a higher-quality graph but a longer build time.
16
[10, 1000]
hnsw_ef_construction
The size of the candidate set for searching during Novam index building. A larger value generally results in a higher-quality graph but a longer build time.
64
[40, 4000]
base_slice_log2_size
The log base 2 of the file shard size for Novam.
24
[10, 30]
nlist
The number of lists for Novad.
1024
[2, 1073741824]
accel_m
The number of neighbors in the acceleration layer for Novad.
16
[8, 1024]
accel_efc
The size of the candidate set for building the acceleration layer for Novad.
128
[1, 32768]
rabitq_bits
The number of bits for rabitq compression.
1
[1, 8]
max_cluster_vecs
The maximum number of vectors for a single file center point in Novad.
65536
[1, 10000000]
Examples
Create a sample table.
CREATE TABLE chunks ( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, chunk VARCHAR(1024), intime TIMESTAMP, url VARCHAR(1024), feature REAL[] ) DISTRIBUTED BY (id);Create a Nova index on the vector column.
Create a Novad vector index that uses the cosine similarity measure.
CREATE INDEX idx_feature_novad_cosine ON chunks USING ann(feature) WITH ( dim=1536, algorithm=novad, distancemeasure=cosine, nlist=4096, rabitq_bits=1 );Create a Novam vector index that uses the Euclidean distance measure.
CREATE INDEX idx_feature_novam_l2 ON chunks USING ann(feature) WITH ( dim=1536, algorithm=novam, distancemeasure=l2, hnsw_m=32, hnsw_ef_construction=200 );