AnalyticDB for MySQL Enterprise Edition, Basic Edition, Data Lakehouse Edition, and Data Warehouse Edition support the task orchestration feature of Data Management (DMS) to orchestrate, schedule, manage, and monitor AnalyticDB for MySQL tasks. This topic describes how to use DMS to develop and schedule tasks.
Background information
Challenges and requirements of event scheduling
Traditional database event schedulers, such as MySQL Event Scheduler, are powerful but have some limitations:
High technical requirements: You must be familiar with the specific SQL syntax for defining events, such as
CREATE EVENTandALTER EVENT. The configuration cannot be completed on a simple user interface.Strong dependency on the database kernel: The kernel must support the event scheduler, and the scheduler must be enabled.
Limited to a single database: Scheduling can only be performed for a single database. You cannot schedule events across different databases or integrate with other tools.
Difficult to track: You cannot view the execution status, history, or runtime of scheduled events.
Difficult O&M: You cannot pause or rerun events. If an event fails, you cannot recover it.
No notifications: The system does not send notifications about the event status (success or failure) by text message or email.
Solution: DMS task orchestration
The task orchestration feature of DMS resolves these issues. It is an external and independent task orchestration and scheduling system that does not rely on the event scheduling capabilities of the database kernel. The task orchestration feature has the following characteristics:
Supports multiple database engines, such as MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server, and various ecosystem tools for data migration, backup, and cross-database analysis. This allows for combined functionality and interaction between different databases and products.
Provides a visual editor. You can create scheduling tasks by dragging and dropping nodes and performing simple configurations.
Supports multiple notification methods, such as DingTalk, text message, and email.
Supports various O&M operations, such as pausing, stopping, and rerunning tasks.
Sample data
This topic uses a database named adb_test. Three tables are created in the database: orders, finish_orders, and large_finish_orders. The following code shows the sample data:
create database adb_test;
create table orders(
order_id bigint not null COMMENT 'Order ID',
order_status varchar not null COMMENT 'Order status',
total_price decimal(15,2) not null COMMENT 'Total price',
order_date date not null COMMENT 'Order date',
PRIMARY KEY (order_id)
);
create table finish_orders(
order_id bigint not null COMMENT 'Order ID',
total_price decimal(15,2) not null COMMENT 'Order status',
order_date date not null COMMENT 'Total price',
PRIMARY KEY (order_id)
);
create table large_finish_orders(
order_id bigint not null COMMENT 'Order ID',
total_price decimal(15,2) not null COMMENT 'Order status',
order_date date not null COMMENT 'Total price',
PRIMARY KEY (order_id)
); Process description
This topic describes the job scheduling process using an AnalyticDB for MySQL Data Warehouse Edition cluster as an example. You can use the task orchestration feature of Data Management Service (DMS) to filter completed orders with an amount greater than 10,000 USD from the orders table in an AnalyticDB for MySQL database.
Step | Description |
Create a task flow. | |
Create the following two task nodes in the task flow:
| |
Enable the task and configure it to run periodically. |
Step 1: Add a new task flow
Log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console. In the upper-left corner of the console, select a region. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters. Find the cluster that you want to manage and click the cluster ID.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Job Scheduling.
NoteIf this is the first time you are using the data asset management feature to log on to an AnalyticDB for MySQL database from the DMS console, you must enter the database logon information. For more information, see Log on to a database.
If you have previously logged on to an AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster database in Flexible Management or Stable Change mode and you did not select Remember Password, a dialog box appears after you log on to the DMS console. You must enter the password for the database account to perform subsequent operations. For more information about control modes, see Control modes.
The end-to-end data management feature is not supported for AnalyticDB for MySQL clusters in the Indonesia (Jakarta) region.
Hover over
 > All Features.
> All Features.Choose .
Add a new task flow. In this example, the task flow is named Order Filtering.
On the Task orchestration page, click Create Task Flow.
In the New Task Flow dialog box, set the Task Flow Name and Description parameters, and then click OK.
Step 2: Create task nodes
On the
Order Filteringtask orchestration page, create and configure two task nodes:Order Cleansing
In the left-side pane, select Single Instance SQL and drag it to the canvas.
Select the new task node, and click the
 icon to rename it to
icon to rename it to Order Cleansing.Double-click the task node or click the
 icon to edit the task node.
icon to edit the task node.From the database drop-down list, select the target database.
In the editor below the database drop-down list, enter the following SQL statement and click Save:
insert into finish_orders select order_id,total_price,order_date from orders where order_status = 'F';NoteIf you selected Automatic Save, the SQL statement is automatically saved.
Large Order Generation
In the left-side pane, select Single Instance SQL and drag it to the canvas.
Select the new task node, and click the
 icon to rename it to
icon to rename it to Large Order Generation.Double-click the task node or click the
 icon to edit the task node.
icon to edit the task node.From the database drop-down list, select the target database.
In the code editor, enter the following SQL statement and click Save:
insert into large_finish_orders select order_id,total_price,order_date from finish_orders where total_price > 10000;NoteIf you selected Automatic Save, the SQL statement is automatically saved.
On the task flow canvas, move the pointer over the
Order Cleansingnode. Click the circle on the right side of the node and drag a line to theLarge Order Generationnode. This connects the two task nodes and creates a dependency in the task flow.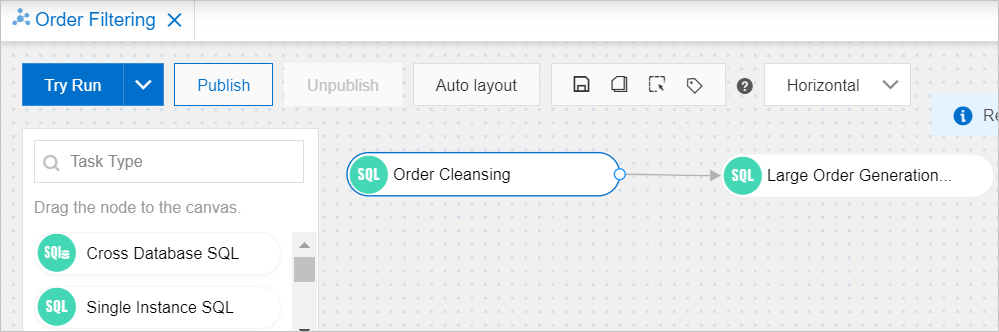
Step 3: Configure task flow scheduling
In the Task Flow Information section below the task flow canvas, turn on the Enable Scheduling switch and configure the parameters.
NoteIn this example, the scheduling task is set to run periodically at 01:00 every day from February 1, 2023 to February 28, 2023. You can also customize the scheduling task as needed. For more information about scheduling parameters, see Configure scheduling.
Publish the task flow.
In the upper-left corner of the canvas, click Publish.
In the Publish dialog box, set the Remarks parameter and click Publish.
View the status of the task flow.
In the upper-right corner of the canvas, click Go to O&M.
On the right side of the page, check the value of the Released parameter.
Published: The task flow is published.
Not published: The task flow is not published.