AnalyticDB Ray is a fully managed Ray service of AnalyticDB for MySQL. This service optimizes and enhances open source Ray, improving kernel performance and simplifying operations management. AnalyticDB Ray is designed for complex AI scenarios, such as multimodal processing, search recommendations, and financial risk control, enabling enterprises to efficiently build integrated Data + AI architectures and deploy large-scale AI applications.
Prerequisites
An AnalyticDB for MySQL Enterprise Edition, Basic Edition, or Data Lakehouse Edition cluster is created.
What is AnalyticDB Ray?
Open source Ray is a distributed computing framework designed for AI and high-performance computing. It provides a simple API abstraction to efficiently implement distributed scheduling, which allows you to scale single-node tasks to thousand-node clusters with just a few lines of code, scheduling remote resources in the same way that you call local functions. Ray's built-in modules, such as Ray Tune, Ray Train, and Ray Serve, seamlessly integrate with TensorFlow and PyTorch. With active open source community support from companies like Anyscale, Ray has become an important tool for building AI applications.
While open source Ray provides highly flexible distributed computing capabilities, enterprises still face challenges in production environments, such as distributed job optimization, fine-grained resource scheduling, complex cluster operations, system stability, and high availability.
To address these challenges, AnalyticDB for MySQL launches AnalyticDB Ray, a fully managed Ray service. AnalyticDB Ray is built on the rich ecosystem of open source Ray and has been validated for common scenarios such as multimodal processing, embodied intelligence, search recommendations, and financial risk control. It comprehensively enhances Ray's kernel and service capabilities, optimizes kernel performance, simplifies cluster operations, and seamlessly integrates with the AnalyticDB for MySQL data lakehouse platform. This helps enterprises build integrated Data + AI architectures to accelerate the scaled implementation of their AI applications.
Billing rules
When you create a Ray cluster resource group, you are charged for the following resources:
You are charged for the storage size specified by the Worker Disk Storage parameter.
If you set the Worker Resource Type parameter to CPU, you are charged for the used AnalyticDB compute unit (ACU) elastic resources.
If you set the Worker Resource Type parameter to GPU, you are charged for the GPU specifications and quantity.
Usage notes
Deleting or restarting worker nodes may have the following impacts. We recommend that you modify the worker configurations of Ray cluster resource groups during off-peak hours and avoid scheduling jobs on worker nodes that are scheduled for restart to prevent unexpected data loss or job failures.
Drivers, actors, and tasks that are running on the affected worker nodes fail. However, Ray will automatically redeploy the actors and tasks.
Data in Ray's distributed object storage is lost. If other tasks depend on data from the restarted worker node, those tasks also fail.
Resource group changes:
Deleting a resource group: If there are tasks running in a resource group, deleting the resource group will interrupt the tasks.
Deleting a worker group: Deleting a worker group from a Ray cluster resource group will also delete its worker nodes. For more information, see the impact of worker node deletion.
Changing the number of worker nodes: If the maximum number of worker nodes after the change is less than the minimum number of worker nodes before the change, worker nodes will be deleted. For more information, see the impact of worker node deletion.
Changing other configurations: Modifying parameters other than the minimum or maximum number of worker nodes, such as head resource specifications and worker resource types, will restart the head node or worker nodes. For more information, see the impact of worker node restart.
Automatic scaling:
Ray clusters scale based on logical resource requirements, not physical resource utilization. Therefore, automatic scaling may be triggered even when physical resource utilization is low.
Specific third-party applications create as many tasks as possible to maximize resource usage. When automatic scaling is enabled, many tasks are created to quickly scale up Ray clusters to the maximum size. Therefore, it is important to understand the task-creation logic of third-party programs to avoid additional resource consumption.
Disaster recovery mechanism: AnalyticDB Ray provides a Redis-based disaster recovery mechanism to enable the recovery of Ray clusters, actors, and tasks when the head node restarts.
Create a Ray service
Log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console. In the upper-left corner of the console, select a region. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters. Find the cluster that you want to manage and click the cluster ID.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cluster Management > Resource Management. Click the Resource Groups tab. In the upper-right corner of the resource group list, click Create Resource Group.
In the Create Resource Group panel, specify a resource group name, set the Job Type parameter to AI, and then configure the parameters that are described in the following table.
Parameter
Description
Deployment Mode
The deployment mode of the resource group. Select RayCluster.
Head Resource Specifications
The head node is responsible for managing Ray metadata, running the Global Control Store (GCS) service, and scheduling tasks, but does not execute tasks.
The head resource specifications refer to the number of CPU cores. You can choose specifications such as small, m.xlarge, and m.2xlarge. The number of CPU cores is the same between head resource specifications and Spark resource specifications. For more information, see Spark resource specifications.
ImportantThe head node is responsible for job scheduling. Select the head resource specifications based on the overall scale of the Ray cluster.
Worker Group Name
The name of the worker group. You can configure multiple worker groups with different names in one AI resource group.
Worker Resource Type
The type of the worker group. Valid values: CPU and GPU.
If your business involves daily computing tasks, multitasking, or complex logical operations, we recommend that you select CPU.
If your business involves large-scale data parallel processing, machine learning, or deep learning training, we recommend that you select GPU.
Worker Resource Specifications
If you set the Worker Resource Type parameter to CPU, you can select specifications such as small, m.xlarge, and m.2xlarge. The number of CPU cores is the same between head resource specifications and Spark resource specifications. For more information, see Spark resource specifications.
If you set the Worker Resource Type parameter to GPU, submit a ticket for technical assistance because the specifications are related to GPU models and inventory.
Worker Disk Storage
The disk storage is used to store Ray logs, temporary data, and overflow data from Ray distributed object storage. Unit: GB. Valid values: 30 to 2000. Default value: 100.
ImportantDisks are used for temporary data storage and cannot be used for long-term storage.
Minimum Workers
Maximum Workers
Minimum Workers: the minimum number of worker nodes that are required in a worker group, with a minimum value of 1.
Maximum Workers: the maximum number of worker nodes that are allowed in a worker group, with a maximum value of 8.
Each worker group can be automatically scaled. If the minimum and maximum numbers of worker nodes in a worker group are different, AnalyticDB for MySQL dynamically adjusts the number of worker nodes based on the number of current tasks. If multiple worker groups exist, AnalyticDB for MySQL performs automatic matching to prevent overloading or underutilizing a single worker group.
Distribution Unit
The number of GPUs that are allocated to each worker node. Example: 1/3.
ImportantThis parameter is required only when you set the Worker Resource Type parameter to GPU.
Click OK.
Connect to and use the Ray service
Step 1: Obtain the URL
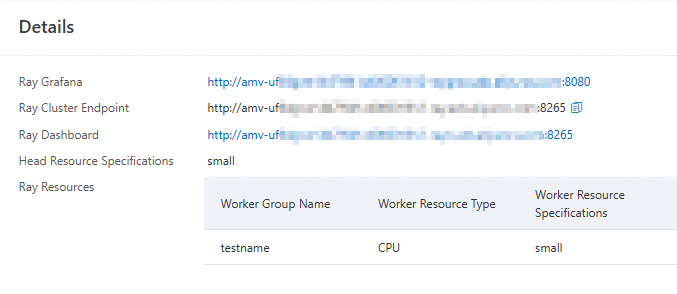
In the left-side navigation pane, choose . Click the Resource Groups tab.
Find the created AI resource group and choose in the Actions column to view the URL.
Ray Grafana: the URL of the Grafana visualization tool. Click the URL to go to the Grafana visualization page.
Ray Cluster Endpoint: the internal URL.
Ray Dashboard: the dashboard URL, which is a public URL. Click the URL to go to the Ray visualization page and view the statuses of the Ray cluster resource group and its jobs.
Step 2: Submit jobs
Prerequisites
Python 3.7 or later is installed.
Procedure
You can use one of the following methods to submit jobs:
(Recommended) Use a cloud task launcher (CTL) to submit jobs: You can use a CTL to package and upload script files to a Ray cluster for execution. The entry program runs in the Ray cluster and consumes resources from the Ray cluster resource group.
Use ray.init to connect to a Ray cluster and execute jobs: You can use ray.init to connect to a Ray cluster. The entry program runs locally and does not consume resources from the Ray cluster resource group. The local Ray and Python versions must match the Ray cluster version. If the Ray cluster version changes, you must update the local environment configuration.
Use a CTL to submit jobs
Run the following command to install Ray:
pip3 install ray[default](Optional) Configure environment variables.
NoteYou can configure the global environment variables to specify the URL. You can also specify the URL when you submit jobs.
export RAY_ADDRESS="RAY_URL"Parameters:
RAY_URL: the Ray URL. Use the URL obtained in Step 1.Submit jobs.
ImportantWhen you submit a job, the system packages and uploads all files in the directory specified by the
working-dirparameter to the Ray head node for execution. Take note of the following items:The directory specified by the
working-dirparameter must be as minimal as possible. Otherwise, large files may cause upload failures.All dependent script files must be stored in the directory specified by the
working-dirparameter. Otherwise, execution may fail due to missing dependencies.
If you have configured environment variables, run the following command to submit a job:
ray job submit --working-dir your_working_directory -- python your_python.pyParameters:
your_working_directory: the path where the script file is located. In this example, the script file path is/root/Ray.your_python.py: the script file. In this example, the script file isscripts.py.
Sample code:
ray job submit --working-dir /root/Ray -- python scripts.pyIf you have not configured environment variables, run the following command to submit a job:
ray job submit --address ray_url --working-dir your_working_directory -- python your_python.pyParameters:
ray_url: the Ray URL. Use the URL obtained in Step 1.your_working_directory: the path where the script file is located.your_python.py: the script file. In this example, the script file isscripts.py.
Sample code:
ray job submit --address http://amv-uf64gwe14****-rayo.ads.aliyuncs.com:8265 --working-dir /root/Ray -- python scripts.py
Query the job status.
You can use one of the following methods to view the job status:
Run the following command:
ray job listUse the visualization page.
On the Resource Groups tab, find the created AI resource group and choose in the Actions column.
Click the URL of the Ray Dashboard parameter to go to the visualization page.
Use ray.init to connect to a Ray cluster and execute jobs
Run the following command to install Ray:
pip3 install ray(Optional) Configure global environment variables.
NoteYou can configure global environment variables to specify the URL. You can also specify the URL in the script file.
export RAY_ADDRESS="RAY_URL"Parameters:
RAY_URL: the Ray URL. The URL obtained in Step 1 is the dashboard URL with port 8265. When you use ray.init() to connect to a Ray cluster, you must replace the port number with 10001 and change the protocol to Ray.For example, if the dashboard URL obtained in Step 1 is
http://amv-uf64gwe14****-rayo.ads.aliyuncs.com:8265, you must replace it withray://amv-uf64gwe14****-rayo.ads.aliyuncs.com:10001.Run the program.
If you have configured the global environment variables, run the following command:
python scripts.pyIf you have not configured the global environment variables, perform the following steps:
Modify the script file to specify the URL.
ray.init(address="RAY_URL")Parameters:
RAY_URL: the Ray URL. The URL obtained in Step 1 is the dashboard URL with port 8265. When you use ray.init() to connect to a Ray cluster, you must replace the port number with 10001 and change the protocol to Ray.For example, if the dashboard URL obtained in Step 1 is
http://amv-uf64gwe14****-rayo.ads.aliyuncs.com:8265, you must replace it withray://amv-uf64gwe14****-rayo.ads.aliyuncs.com:10001.ImportantIf you specify an incorrect Ray URL, ray.init() will start a local Ray cluster to run the program. Check the output logs to ensure that you are connected to the Ray cluster.
Run the following command to run the program:
python scripts.py