The Quick UDP Internet Connections (QUIC) protocol provides security comparable to Transport Layer Security (TLS)/SSL but with lower connection and transmission latency. You can enable the QUIC protocol to improve resource access efficiency and ensure data transmission security.
HTTP/3 and QUIC
What is HTTP/3
HTTP/3 is the third major version of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It is built on top of QUIC instead of the traditional TCP and TLS stack. While HTTP/3 retains features from HTTP/2, such as header compression and multiplexing, it uses QUIC to significantly improve congestion control and reduce latency.
What is QUIC
QUIC is a modern transport layer network protocol that provides security comparable to TLS while reducing connection and transmission latency. Because QUIC is built on UDP, it performs well on unreliable networks, maintaining a stable connection even with significant packet loss and high latency. Unlike TCP, QUIC's congestion control is implemented in the application layer, allowing for faster iteration and optimization without requiring OS or kernel updates. This makes it ideal for overcoming the performance limitations of TCP.
Alibaba Cloud Content Delivery Network (CDN) uses QUIC for its Layer 7 services.
Supported QUIC versions
Alibaba Cloud CDN supports IETF QUIC.
Client requirements
To use QUIC, clients must meet the following requirements:
Chrome Browser: Modern versions of Chrome support HTTP/3 and can initiate QUIC requests to Alibaba Cloud CDN.
Custom Applications: Your app must integrate a QUIC-enabled network library, such as lsquic-client, Cronet, ngtcp2, or quiche.
How it works
The following figure shows how QUIC works with Alibaba Cloud CDN.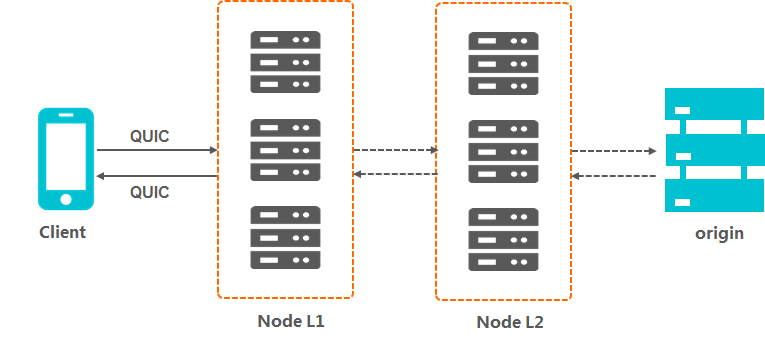
Billing rules
QUIC is a value-added service. You are billed based on the number of QUIC requests. For more information, see the QUIC section of CDN Pricing.
A QUIC protocol request is identified by its use of the UDP protocol.
For requests sent over HTTPS, if a request uses the QUIC protocol, it is billed as a QUIC request. Otherwise, it is billed as an HTTPS request.
Billing method
Billable item | Billing rule | Billing method | Billing cycle |
QUIC requests for static content | Number of requests to the domain name + Number of times static resources associated with the domain name are loaded | Pay-as-you-go | Bills are generated hourly, with a 3-to-4-hour delay. |
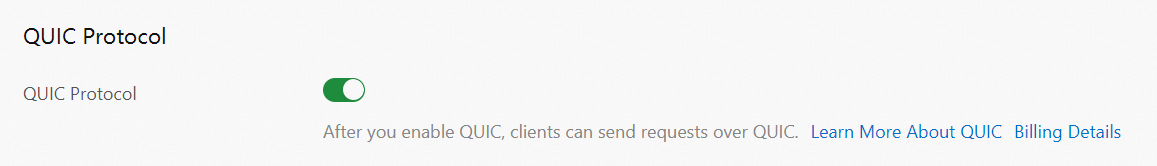
Enable QUIC
Log on to the CDN console.
In the left navigation pane, click Domain Names.
On the Domain Names page, find the target domain name and click Manage in the Actions column.
In the navigation pane on the left for the domain name, click QUIC Protocol and turn on the QUIC Protocol switch.
Verify QUIC connections
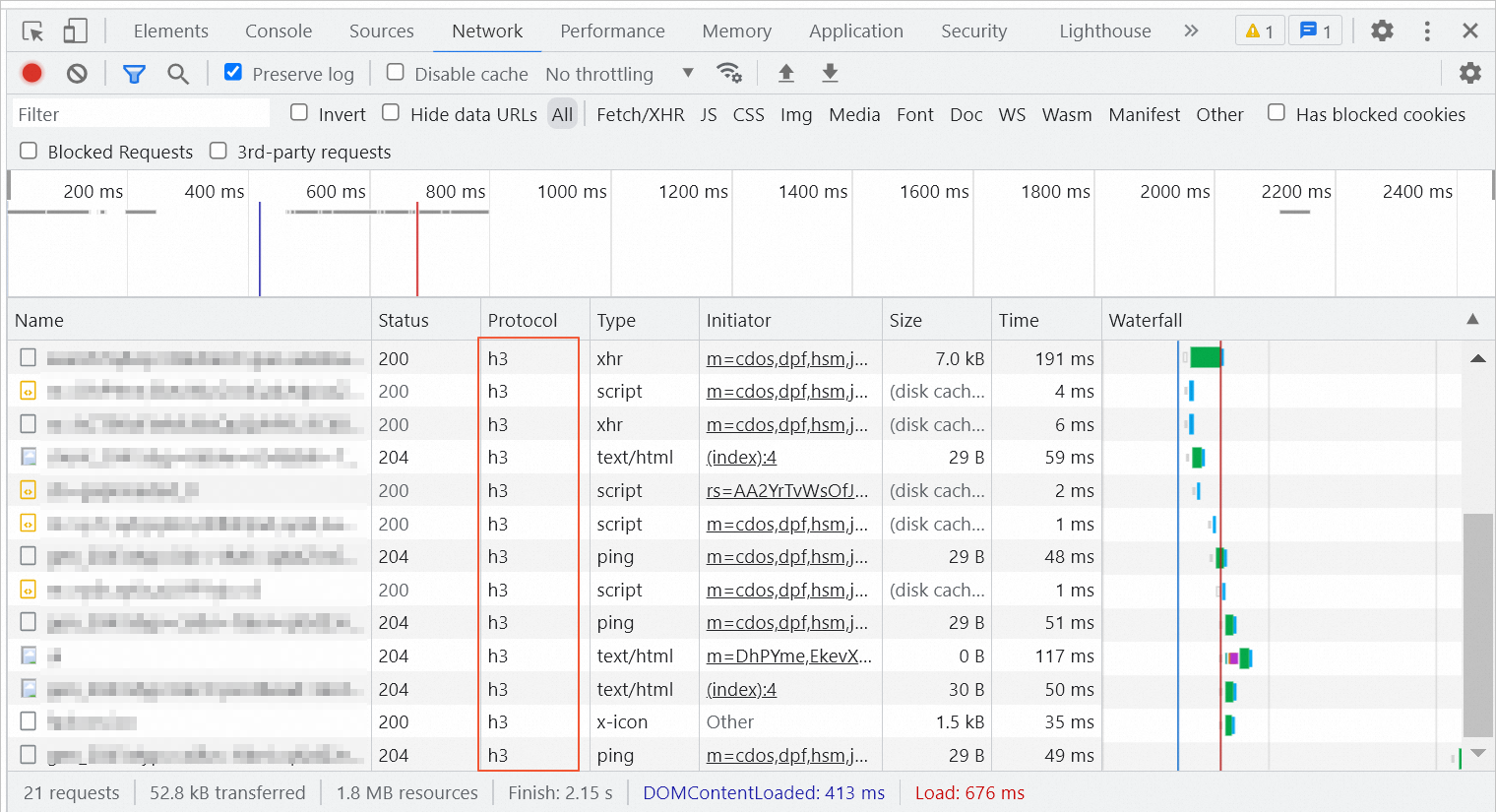
This section explains how to verify that QUIC is working by using Chrome Developer Tools.
1. On your webpage, right-click and select Inspect to open Developer Tools.
2. Go to the Network tab.
3. Check the Protocol column. A value of h3 or a similar identifier (e.g., h3-29) indicates that the request used QUIC.
If the Protocol column is not displayed, refresh the page. Then, right-click the header of the request list and select .
As shown in the following figure, h3 indicates a QUIC request.